Over the past few years, engineers have been trying to devise alternative hardware designs that would allow a single device to both perform computations and store data. These emerging electronics, known as computing-in-memory devices, could have numerous advantages, including faster speeds and enhanced data analysis capabilities.
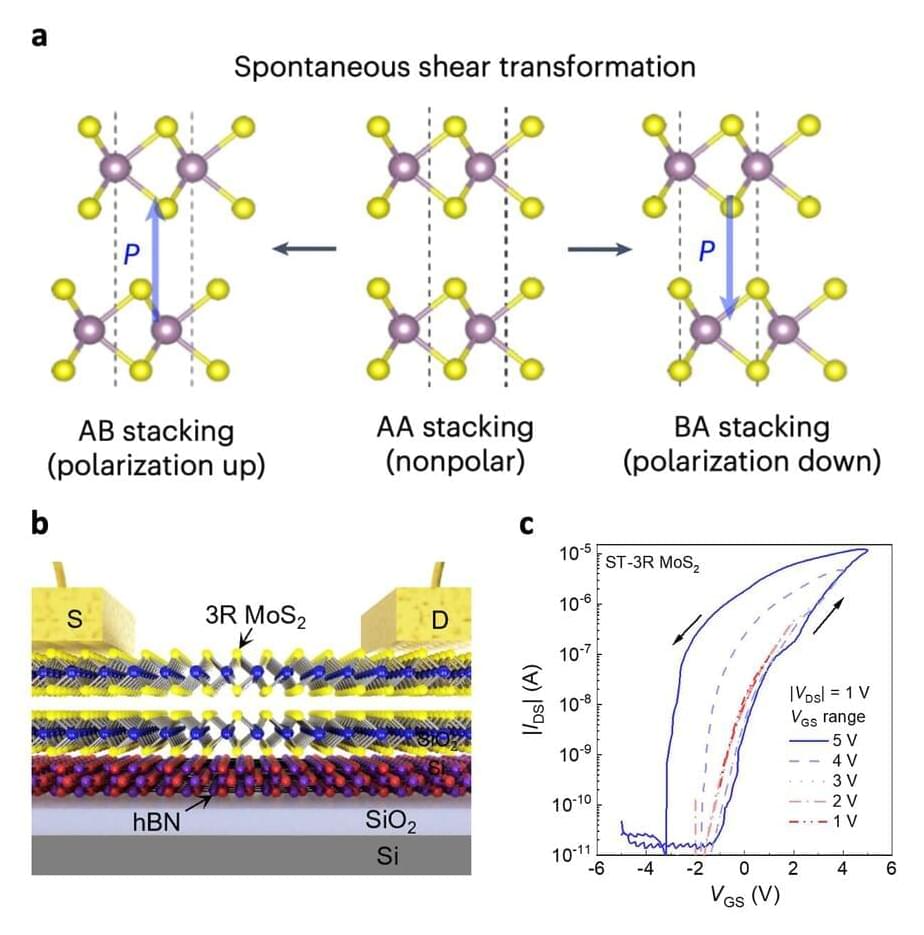
To store data safely and retain a low power consumption, these devices should be based on ferroelectric materials with advantageous properties and that can be scaled down in terms of thickness. Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors that exhibit a property known as sliding ferroelectricity have been found to be promising candidates for realizing computing-in-memory, yet attaining the necessary switchable electric polarization in these materials can prove difficult.
Researchers at National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan Semiconductor Research Institute, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University and National Cheng Kung University recently devised an effective strategy to achieve a switchable electric polarization in molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). Using this method, outlined in a Nature Electronics paper, they ultimately developed new promising ferroelectric transistors for computing-in-memory applications.