Jellagen and NPL’s groundbreaking research unveils jellyfish collagen’s potential for medical applications, from tissue regeneration to lab-grown organs.
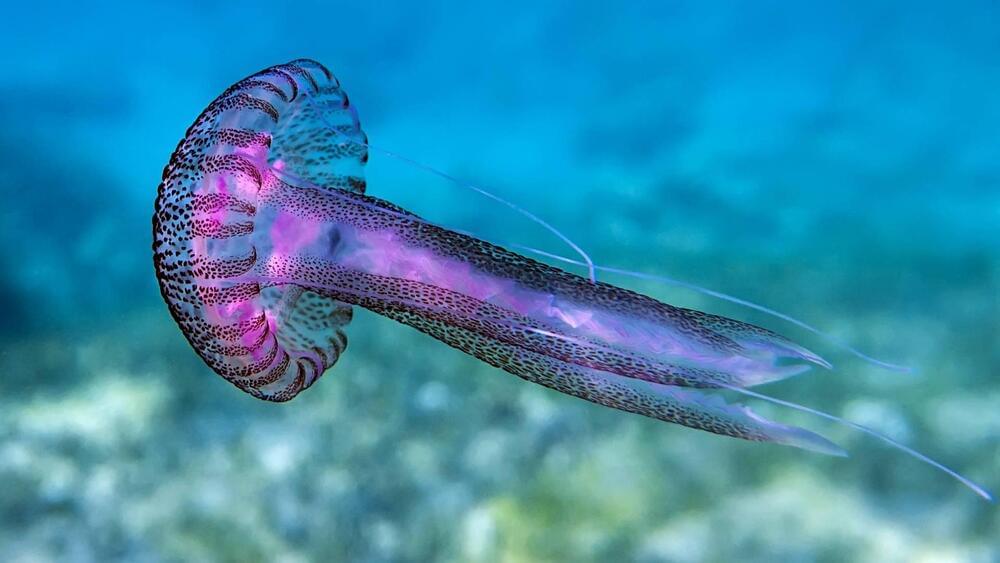



WASHINGTON – Australian in-space servicing startup Space Machines Company announced plans Dec. 5 to work with U.S. on-orbit refueling startup Orbit Fab to validate and demonstrate key technologies.
SMC is the first non-U.S. customer to use Orbit Fab’s fiducial alignment markers. The markers are painted on SMC’s Optimus Orbital Servicing Vehicle, which is set to launch in early 2024 on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rideshare flight.
Orbit Fab’s fiducial markers are designed to act like a QR code, ensuring, for example, that a fuel shuttle replenishes the correct client. The fiducial markers also ensure proper spacecraft alignment for docking.


Thanks for listening! Subscribe to the channel.
Join as a member to gain access to Discord + $TSLA Valuation Model + my screenplay starring Elon: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCe_HuQyI2_vluXeXuUzMfxg/join.
Follow me on X: https://twitter.com/jcubhilton.
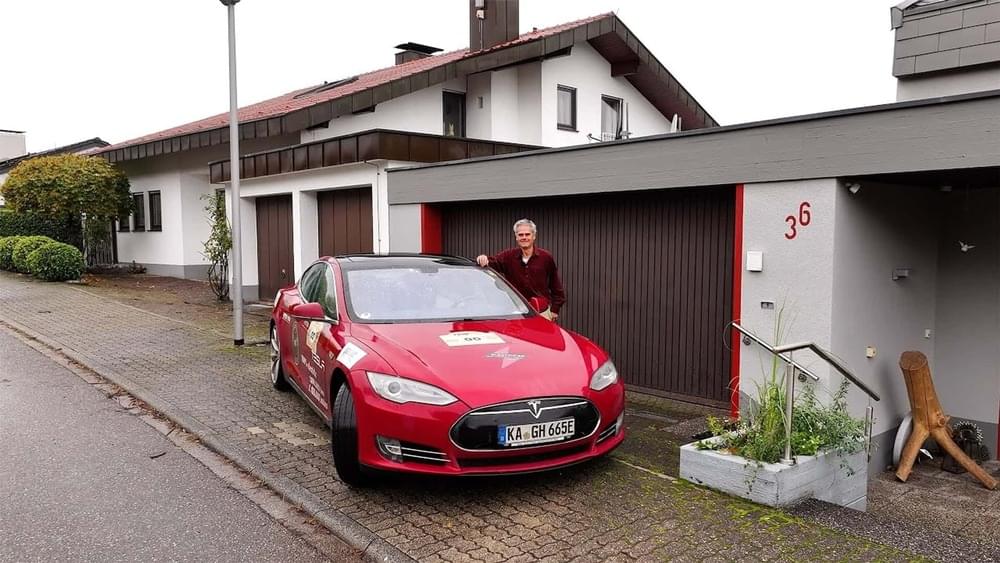

It’s hard to believe that there’s a Tesla Model S out there with nearly 1.2 million miles on its odometer, but indeed there is. And here it is.
The car, a 2014 Model S P85, has racked up 1.18 million miles so far, which works out to approximately 131,000 miles per year. Could you imagine driving that much? And doing so in an electric car, which naysayers often state can’t go the distance. Well, we think this car proves that EVs can be driven a significant amount of miles per year and that the charging infrastructure, at least in some parts of the world, can support high-mileage drives.
Elon Musk hints at a low-cost electric vehicle in the works, made in high volume, with advanced production technology, and the progress in China is a significant factor in Tesla’s success.
Questions to inspire discussion.
What is the status of the next generation Tesla production line?
—Elon Musk reviews the plans for the next generation Tesla production line every week and believes it will be revolutionary. The first production line will be at Giga Texas, with Giga Mexico as the second option.

On their way to building fully autonomous vehicles, self-driving car makers are facing a tall task: training their AIs to be able to respond reliably to any and all scenarios that a car, truck or bus might encounter as well as, or hopefully better, than a human would. Today, a startup with a platform to help with that challenge is announcing a sizeable round of funding to take those strategies up a gear.
Foretellix, which builds verification and validation solutions to test the full range of driver assistance and autonomous systems that are coming out on the market, has closed its Series C at $85 million. The round includes financial investors alongside strategic backers from the automotive and chip industries, a signal of who is already doing business with Foretellix, as well as the longer business trajectory for the startup.
The round is being led by Israeli VC 83North, with Singapore’s Temasek and carmaker Isuzu investing alongside Woven Capital (Toyota’s venture fund), Nvidia, Artofin and previous backers MoreTech, Nationwide, Volvo Group VC, Jump Capital, Next Gear Ventures and OurCrowd. Foretellix may ring a bell for readers: The first close of this round was in May of this year (at $43 million).

As if space travel didn’t present enough challenges — from bone thinning and an elevated risk of cancer to the sheer tedium of spending months confined to a small capsule — scientists have now warned that prolonged exposure to microgravity and cosmic radiation could lead to erectile dysfunction.
For a NASA-funded study, published in The Faseb Journal, researchers exposed rats to doses of radiation equivalent to that found in deep space, and suspended them in harnesses to simulate weightlessness for four weeks. A year later the blood supply to the rats’ erectile tissue was found to be impaired, apparently mainly as a result of the radiation. The scientists described it as “a new health risk to consider with deep space exploration”, but said that there were signs it could be treatable. When astronauts are in orbit, such as on the International Space Station, they are protected from cosmic radiation by Earth’s magnetic field, which deflects the rays. Further out, they’re fully exposed, and transporting the material needed to shield them is difficult and expensive.