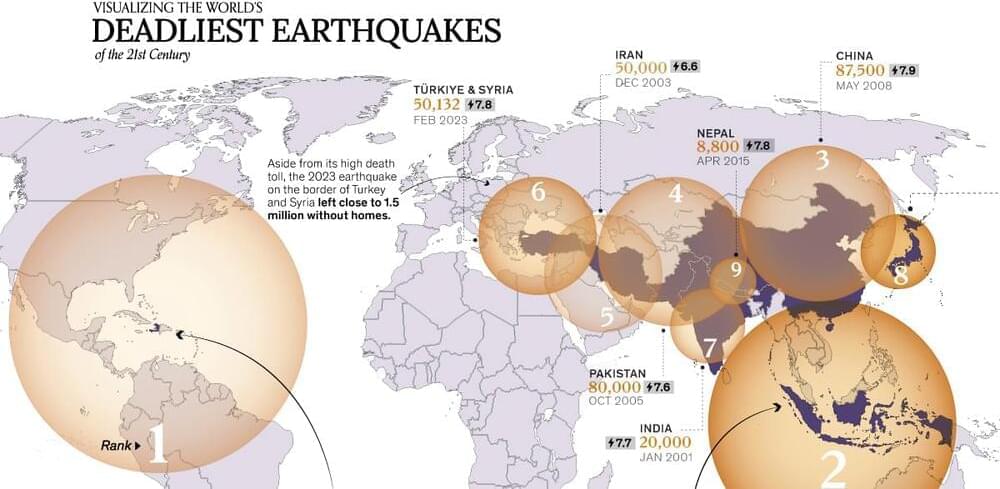
A powerful earthquake rocked Morocco on September 8, 2023, potentially killing thousands. Here are the deadliest earthquakes this century so far.


By Deborah Pirchner, Frontiers science writer.
Malaria is an infectious disease claiming more than half a million lives each year. Because traditional diagnosis takes expertise and the workload is high, an international team of researchers investigated if diagnosis using a new system combining an automatic scanning microscope and AI is feasible in clinical settings. They found that the system identified malaria parasites almost as accurately as experts staffing microscopes used in standard diagnostic procedures. This may help reduce the burden on microscopists and increase the feasible patient load.
Each year, more than 200 million people fall sick with malaria and more than half a million of these infections lead to death. The World Health Organization recommends parasite-based diagnosis before starting treatment for the disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. There are various diagnostic methods, including conventional light microscopy, rapid diagnostic tests and PCR.

From VC Elements—bridging the gap between global trends shaping our future, and the raw materials powering them ⚡️.
Coal is Still King
Coal still leads the charge when it comes to electricity, representing 35.4% of global power generation in 2022, followed by natural gas at 22.7%, and hydroelectric at 14.9%.


The threat group behind the fast-growing Rhysida ransomware-as-a-service operation has claimed credit for an Aug. 19 attack that crippled systems at Singing River Health System, one of Mississippi’s largest healthcare entities.
The attack follows one against California’s Prospect Medical Holdings in August that affected 16 hospitals and more than 160 clinics around the country. The wide scope of that incident prompted an alert from the Health Sector Cybersecurity Coordination Center to other organizations in the industry.
The attack on Singing River impacted three hospitals and some 10 clinics belonging to the system and is likely to reinforce Rhysida’s credentials as a growing threat to healthcare organizations in the US. It’s also a reminder of the surging interest in the sector from ransomware actors who, early in the COVID-19 pandemic, had piously vowed to stay away from attacking hospitals and other healthcare entities.

Scientists have shown that the biomass of 12 previously unstudied strains of cyanobacteria from around the globe is efficient at the biosorption of the rare earth elements lanthanum, cerium, neodymium, and terbium from aqueous solutions. This allows these rare elements, for which demand is steadily growing, to be collected from wastewater from mining, metallurgy, and the recycling of e-waste, and reused.
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar metals, which got their name because they typically occur at low concentrations (between 0.5 and 67 parts per million) within the Earth’s crust. Because they are indispensable in modern technology such as light emitting diodes, mobile phones, electromotors, wind turbines, hard disks, cameras, magnets, and low-energy lightbulbs, the demand for them has increased steadily over the past few decades, and is predicted to rise further by 2030.
A hairless, pale-skinned lamb lies on its side in what appears to be an oversized sandwich bag filled with hazy fluid. Its eyes are closed, and its snout and limbs jerk as if the animal — which is only about three-quarters of the way through its gestation period — is dreaming.
The lamb was one of eight in a 2017 artificial-womb experiment carried out by researchers at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) in Pennsylvania. When the team published its research1 in April of that year, it released a video of the experiments that spread widely and captured imaginations — for some, evoking science-fiction fantasies of humans being conceived and grown entirely in a laboratory.
Now, the… More.
US regulators will consider clinical trials of a system that mimics the womb, which could reduce deaths and disability for babies born extremely preterm.
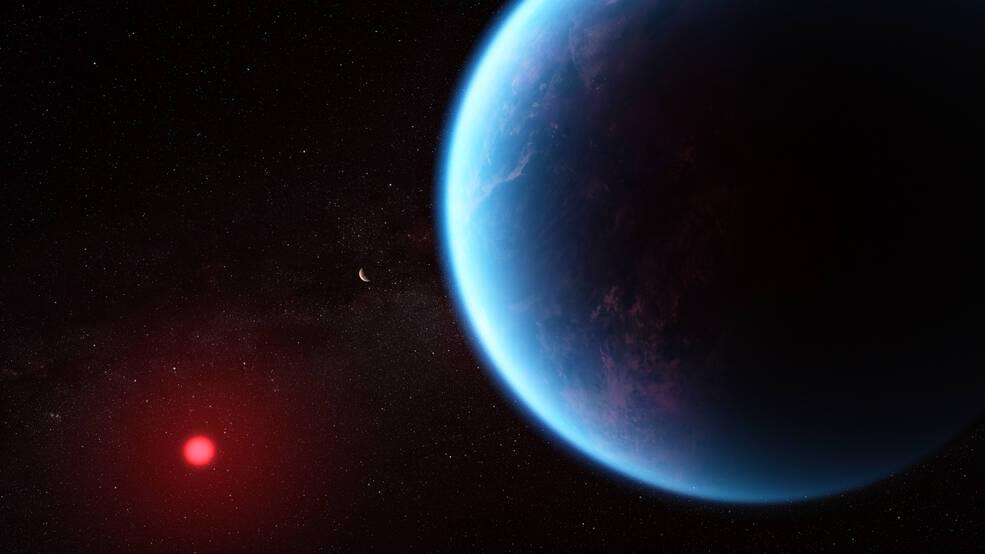

(WTAJ) — Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope say they have stumbled onto possible signs of life coming from a massive Earth-like exoplanet, NASA confirmed in a release.
K2-18 b is an exoplanet — a planet outside our solar system — that’s 8.6 times as massive as Earth. A new investigation with the JWST revealed the presence of “carbon-bearing molecules” that include methane and carbon dioxide. The findings add to recent studies that suggest that K2-18 b could be a Hycean exoplanet, meaning it has the potential to hold a hydrogen-rich atmosphere and a water-covered surface, NASA reported.
Astronomers first studied K2-18 b’s atmosphere with NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope in 2019. The results prompted further studies of the massive exoplanet that have changed experts understanding of the system.

In a recent attack against a construction company, hackers who failed to execute LockBit in a target network were observed deploying a second, never-before-seen ransomware, which managed to break through.
The new tool is rather standard fare, blocking various cybersecurity and backup-related software before locking up files on its host computer. But it distinguishes itself with an adorable little theme: 3 a.m., a time when perhaps only insomniacs, hardcore night owls, and black hat hackers are still up and working away.
In a report this week, researchers from Symantec described the first observed use of 3AM — a double-whammy attack in which the LockBit ransomware was blocked but then 3AM squeaked through in one compromised machine.
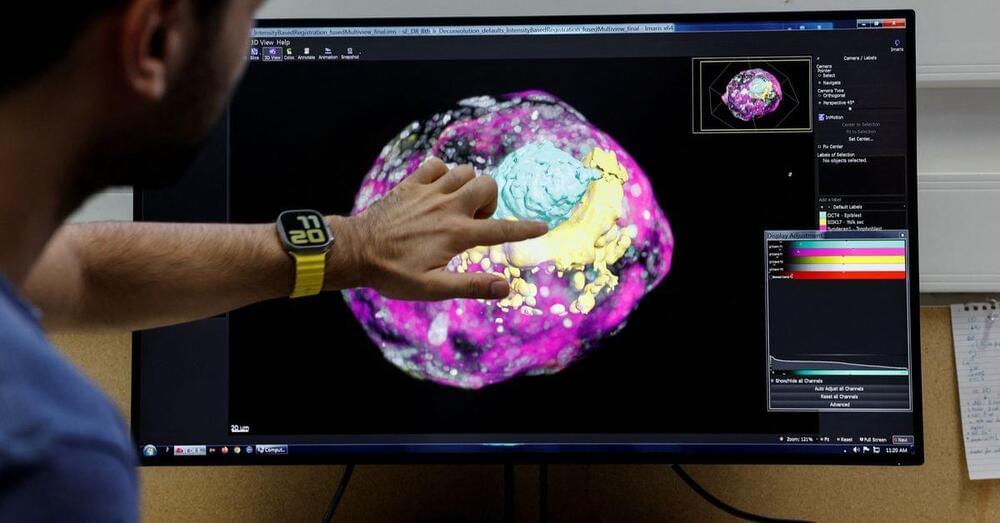
Scientists in Israel have created a model of a human embryo from stem cells in the laboratory, without using sperm, eggs or a womb, offering a unique glimpse into the early stages of embryonic development.
The model resembles an embryo at day 14, when it acquires internal structures but before it lays down the foundations for body organs, according to the team at Israel’s Weizmann Institute of Science.
The Israeli team emphasised that they were a long way from being able to create an embryo from scratch.
“The question is, when does an embryo model become considered an embryo? When that happens, we know the regulations. At the moment we are really, really far off from that point,” said team leader Jacob Hanna.