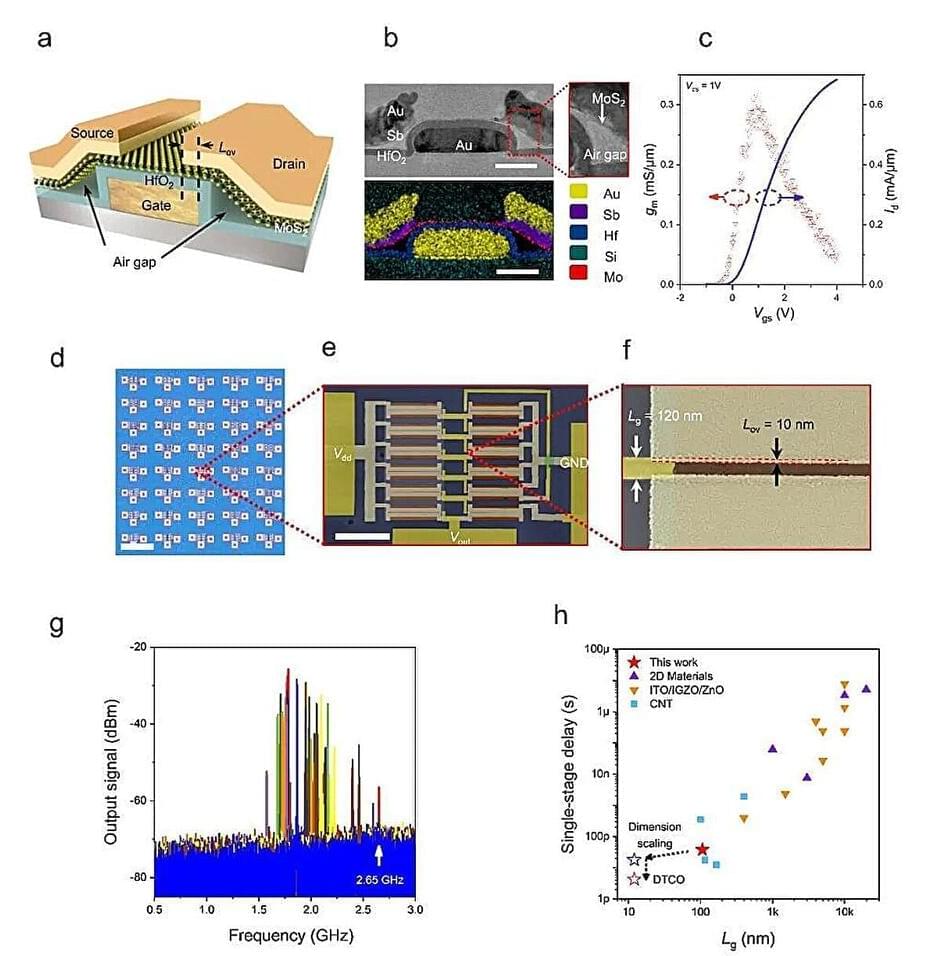
Natural products collection reveals novel enzymes with surprising properties. Scientists have discovered two enzymes that enable bacteria to target and break up DNA. This chemical defense likely evolved to help the organism fight off germs. The chemical riches were found within the institute’s one-of-a-kind Natural Products Discovery Center collection.
Slumbering among thousands of bacterial strains in a collection of natural specimens at The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology, several fragile vials held something unexpected, and possibly very useful.
Writing in the journal Nature Chemical Biology, a team led by chemist Ben Shen, Ph.D., described discovery of two new enzymes, ones with uniquely useful properties that could help in the fight against human diseases including cancer. The discovery, published last week, offers potentially easier ways to study and manufacture complex natural chemicals, including those that could become medicines.