Time to move philosophers into the lab. AI is making theories of consciousness testable.


Consciousness is one of the most mysterious and fascinating aspects of human existence. It is also one of the most challenging to study scientifically, as it involves subjective experiences that are not directly observable or measurable. David Chalmers, a professor of philosophy and neural science at NYU mentions in his book The Conscious Mind.
“It may be the largest outstanding obstacle in our quest for a scientific understanding of the universe.”
The real questions are: how can we approach the problem of consciousness from a rigorous and objective perspective? Is there a way to quantify and model the phenomena of awareness, feelings, thoughts, and selfhood? There is no definitive answer to this question, but some researchers have attempted to use mathematical tools and methods to study these phenomena. Self-awareness, for instance, is the ability to perceive and understand the things that make you who you are as an individual, such as your personality, actions, values, beliefs, and even thoughts. Some studies have used the mirror test to assess the development of self-awareness in infants and animals.

The enduring mystery of dark matter has led some physicists to propose that it was forged in a distinct moment of cosmic creation, potentially transforming our view of the early universe.
By Stuart Clark
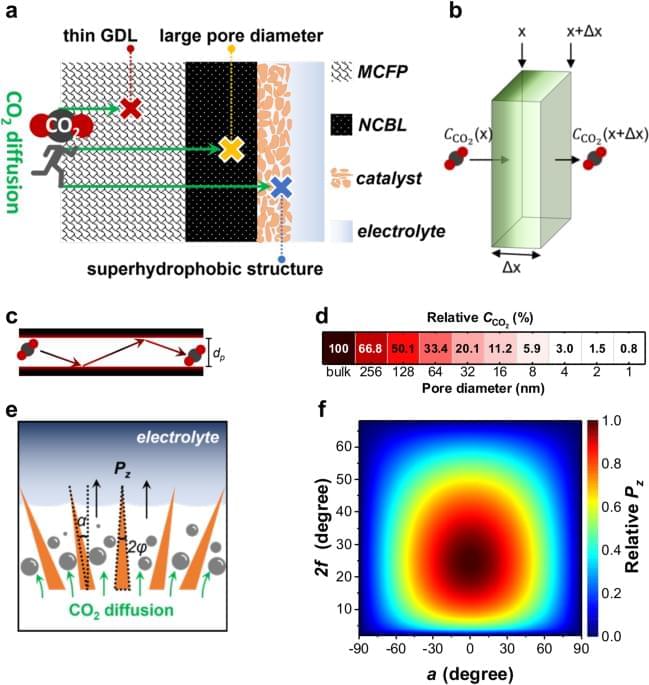
Carbon dioxide electroreduction in acidic environments has been suboptimal. Here, the authors addressed this issue by designing a gas diffusion electrode with a special metal structure, which achieves efficient electroreduction while conducting a systematic investigation of the underlying mechanism.
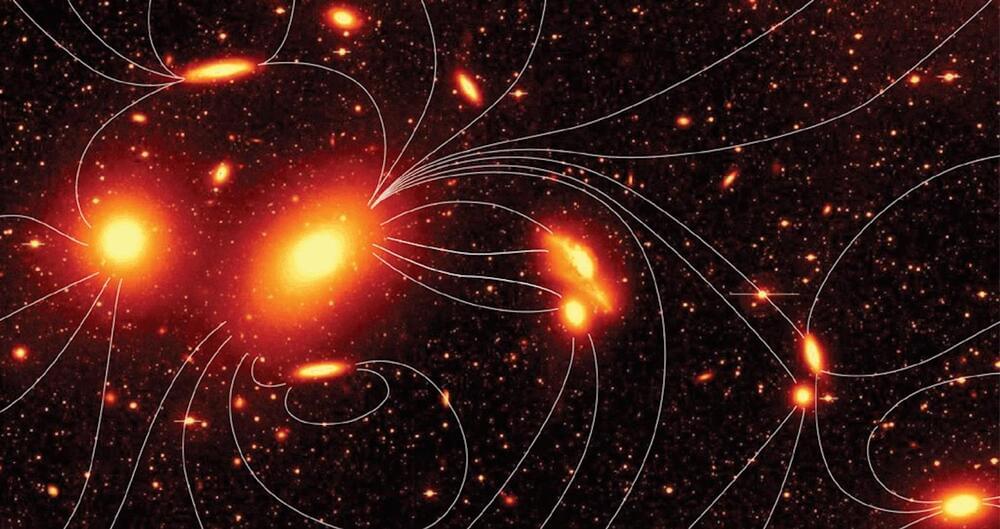
So the idea is that intergalactic magnetic fields would tend to cluster electrons and ionized intergalactic hydrogen along their field lines, making those regions of the intergalactic voids just slightly denser than the rest of the void. This would cause dark matter to cluster a bit along the field lines as well. The gravitational effect would be extremely tiny, but over the entire history of the Universe, it would add up. So if primordial magnetic fields did form in the early Universe, tendrils of dark matter should be present along the same lines.
In a recent work in Physical Review Letters the authors argue that this effect would produce minihalos of dark matter. Just as galaxies are surrounded by a halo of dark matter due to gravitational clustering, faint halos of dark matter should exist around primordial magnetic field lines to do the gravitational tug of ionized matter along the field lines.
What’s interesting about this idea is that over time the charged ions and electrons would interact with the primordial magnetic fields and tend to cancel them out. The ions and electrons could even merge to create neutral hydrogen, so in the modern Universe, there would be no trace of these early magnetic fields in regular matter. But the microhalos of dark matter would still exist, and they could be seen through the gravitational lensing of distant light sources. These tendrils of dark matter could be the only evidence remaining of the earliest magnetic fields in the cosmos.


The Dark Energy Survey took an entire decade to produce a value for the cosmological constant—and it’s smaller than you might think! There were other stories as well, including one about primeval black holes, and because I am inescapably drawn by the relentless gravity of black hole news, it’s included below, along with two other stories related in one way or another to heads.
Dogs’ primary sense is olfactory, and if their visual perception flags something interesting in the environment, the first thing they do is stick their cute little noses in it. But the opposite is true for humans; we are able to perceive millions of colors, but only a fraction of the olfactory stimuli dogs are usually way too engaged with.
If you smell natural gas in your house, you go looking for the source with your cute little retinas and their super-dense constellation of photoreceptive cells to determine that one of the gas knobs on the stove is open. Researchers at Johns Hopkins University grew retinal organoids in a lab to determine how human visual perception develops.
We are already living in the era of the fourth industrial revolution, but in the near future we will be facing another one that could really change everything. We are talking about the revolution of humanoid robots — versatile, intelligent and dexterous machines that can not only help, but also replace humans in tight places. In this video, we’ll tell you about the top 10 newest and most advanced humanoid robots in the world, and what technologies will make them truly versatile! Onward to a brighter future)
👉For business inquiries: [email protected].
✅ Instagram: / pro_robots.
✅ Telegram: https://t.me/PRO_robots.
✅ Facebook https://www.facebook.com/PRO.Robots.I…
0:00 A breakthrough in humanoid robots.
1:17 What technologies could make robots as dexterous as humans?
3:46 Digit, the first commercial humanoid robot from Agility Robotics.
5:18 New humanoid robot from Singapore.
6:45 What kind of humanoid robot has OpenAI invested in?
7:34 New Apollo robot from Apptronik.
9:00 CyberOne humanoid robot project from Xiaomi.
10:20 Unitree’s H1 robot.
11:07 XPENG’s agile and stable robot PX5
12:05 Sanctuary AI’s most agile robot Phoenix.
13:13 The world’s most advanced humanoid robot by Figure AI
15:18 Tesla Bot: Ilon Musk’s Humanoid Robot.
16:15 The world’s most advanced humanoid robot from Boston Dynamics.
Boston Dynamics Atlas. If you’ve been following robotics, you’ve likely seen this humanoid robot in action. Atlas is a pinnacle of robotic achievement, showcasing impressive mobility and coordination. Its advanced control system allows it to perform backflips, handstands, and navigate complex environments with ease. Atlas is not just a demonstration of technological prowess; it’s a glimpse into the future of robotics assisting in real-world scenarios.
Moving on to the Valkyrie robot from NASA. Initially designed for space exploration, Valkyrie boasts a humanoid form with an emphasis on strength and adaptability. Its design includes 44 degrees of freedom, making it highly flexible and capable of mimicking human movements. While initially intended for space missions, Valkyrie’s applications extend to disaster response and exploration of challenging terrains.
Now, let’s talk about the Tesla Bot. Yes, you heard it right, Tesla is venturing into humanoid robotics. Elon Musk unveiled the Tesla Bot with a vision to eliminate dangerous, repetitive, and boring tasks performed by humans. While specific details are still emerging, the idea is to create a humanoid robot using Tesla’s expertise in electric vehicles and AI. The Tesla Bot aims to be a general-purpose, capable machine for a variety of everyday tasks.

Historically, JILA (a joint institute established by the National Institute of Standards and Technology [NIST] and the University of Colorado Boulder) has been a world leader in precision timekeeping using optical atomic clocks. These clocks harness the intrinsic properties of atoms to measure time with unparalleled precision and accuracy, representing a significant leap in our quest to quantify the most elusive of dimensions: time.