Raspberry Pi smart home technology brings AI image generation into your living room.
Speak your thoughts to life, from the comfort of your couch.


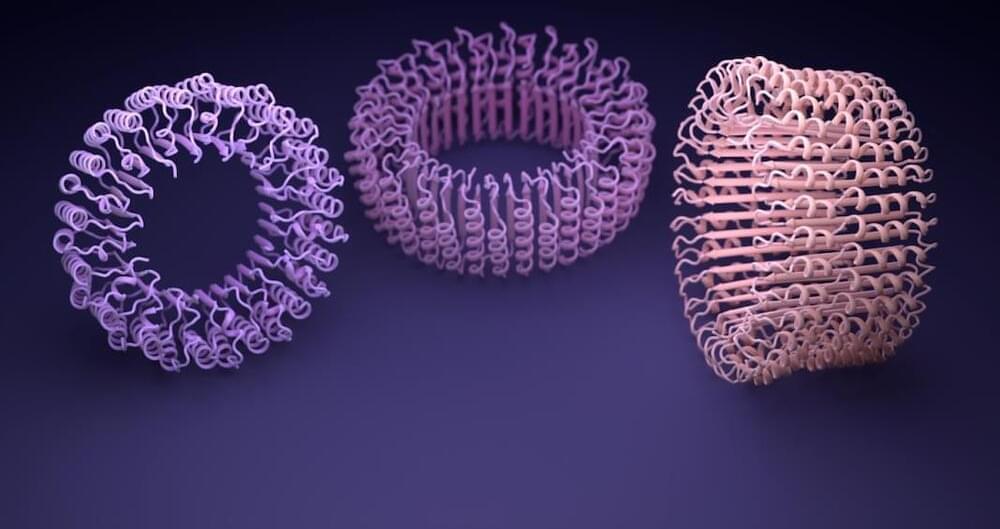
Two decades ago, engineering designer proteins was a dream.
Now, thanks to AI, custom proteins are a dime a dozen. Made-to-order proteins often have specific shapes or components that give them abilities new to nature. From longer-lasting drugs and protein-based vaccines, to greener biofuels and plastic-eating proteins, the field is rapidly becoming a transformative technology.
Custom protein design depends on deep learning techniques. With large language models—the AI behind OpenAI’s blockbuster ChatGPT—dreaming up millions of structures beyond human imagination, the library of bioactive designer proteins is set to rapidly expand.
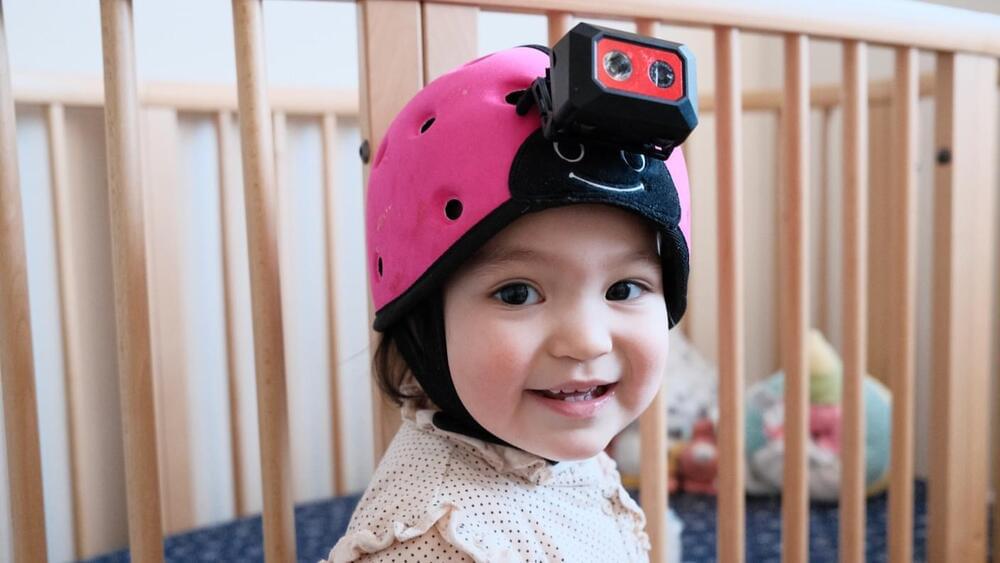

For the next year and a half, the camera captured snippets of his life. He crawled around the family’s pets, watched his parents cook, and cried on the front porch with grandma. All the while, the camera recorded everything he heard.
What sounds like a cute toddler home video is actually a daring concept: Can AI learn language like a child? The results could also reveal how children rapidly acquire language and concepts at an early age.
A new study in Science describes how researchers used Sam’s recordings to train an AI to understand language. With just a tiny portion of one child’s life experience over a year, the AI was able to grasp basic concepts—for example, a ball, a butterfly, or a bucket.

Google has launched Gemini, a new artificial intelligence system that can seemingly understand and speak intelligently about almost any kind of prompt—pictures, text, speech, music, computer code, and much more.
This type of AI system is known as a multimodal model. It’s a step beyond just being able to handle text or images like previous algorithms. And it provides a strong hint of where AI may be going next: being able to analyze and respond to real-time information from the outside world.
Although Gemini’s capabilities might not be quite as advanced as they seemed in a viral video, which was edited from carefully curated text and still-image prompts, it is clear that AI systems are rapidly advancing. They are heading towards the ability to handle more and more complex inputs and outputs.


Does perception exist outside of our own nervous system? Philosopher Alva Noë thinks so. We can visualize the back of a tomato, even if our eyes cannot see it. We aren’t offended by profane statements written in a language we aren’t fluent in. This is because our perception is based on more than our five senses; it relies on experience and context as well.
Alva Noë unpacks this puzzle with a few examples, from being able to visualize things we are not looking at, to a phenomenon called “change blindness.”
Ultimately, this information can be used to challenge our original understanding of perception, and can expand on the idea that the way one person assesses an object may not precisely match the assessment of another.
In Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking-Glass, the Red Queen tells Alice, “It takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place.” The race between innovation and obsolescence is like this.
Recent evidence about the slowing of technological and scientific progress in contrast to the accelerating epidemiological risks in a globalized world—in the opposite direction—indicates the importance of the relative rates of innovation and obsolescence.
When does innovation outpace, or fail to outpace, obsolescence? Understanding this dynamic is nascent, and the way that innovation is discussed is largely fragmented across fields. Despite some qualitative efforts to bridge this gap, insights are rarely transferred.