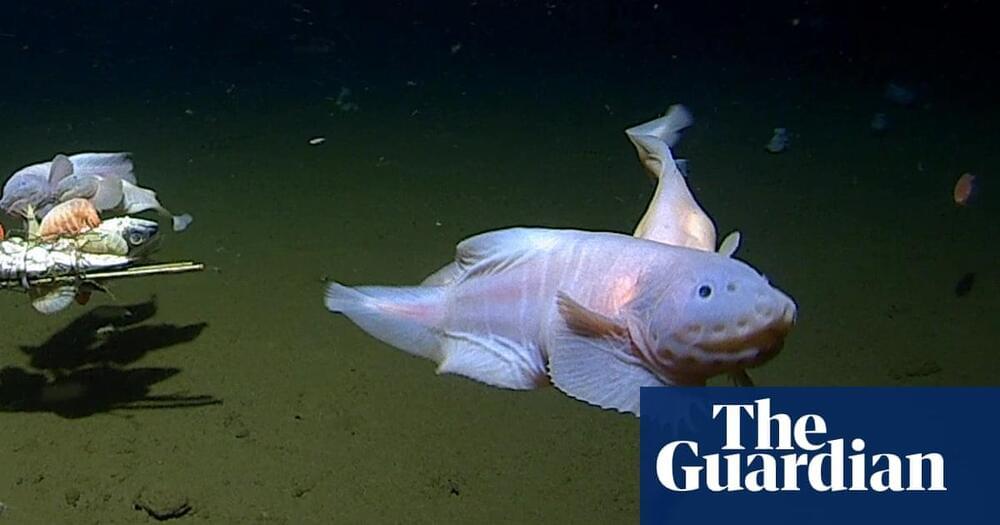
Footage of unknown snailfish captured by researchers from Western Australia and Tokyo in Izu-Ogasawara trench.
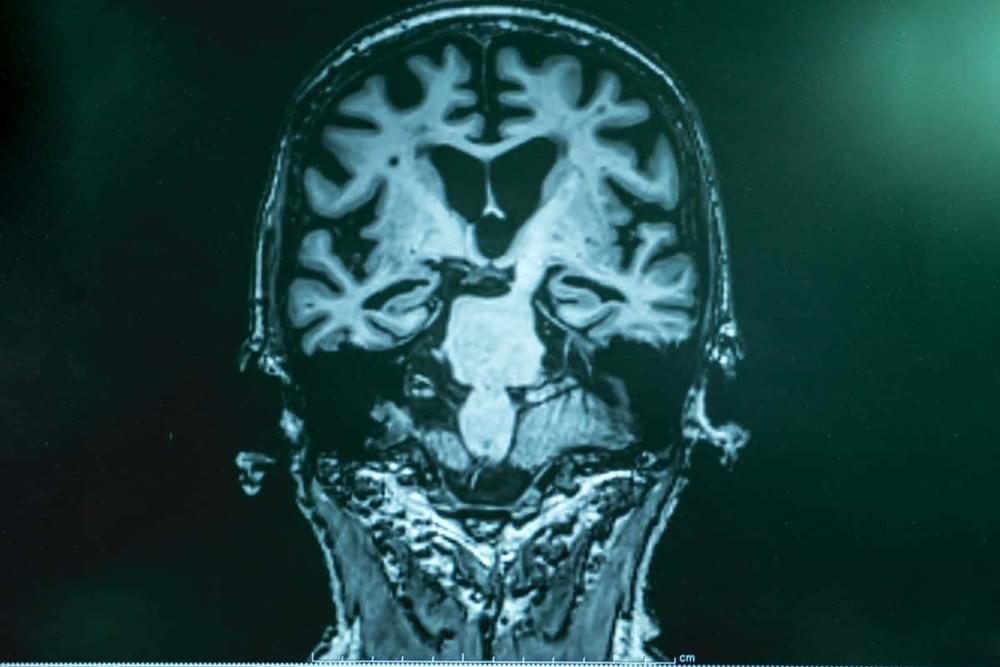
A “grand unifying theory” of brain ageing suggests malfunctioning mitochondria might be to blame for Alzheimer’s and other brain conditions. And this new avenue of exploration already has some potential therapies at the ready.
A paper in Nature reports the discovery of a superconductor that operates at room temperatures and near-room pressures. The claim has divided the research community.
An open letter signed by more than 1,100 technology and business industry leaders calls for a six-month moratorium on the race to develop artificial intelligence (AI), and in particular large language models like ChatGPT-4.
ChatGPT-4 is an example of AI exhibiting human-competitive intelligence and poses a risk to humanity without managed care.
Putting two forms of semiconductor material called gallium oxide together seems to make it completely resistant to radiation.
By Alex Wilkins
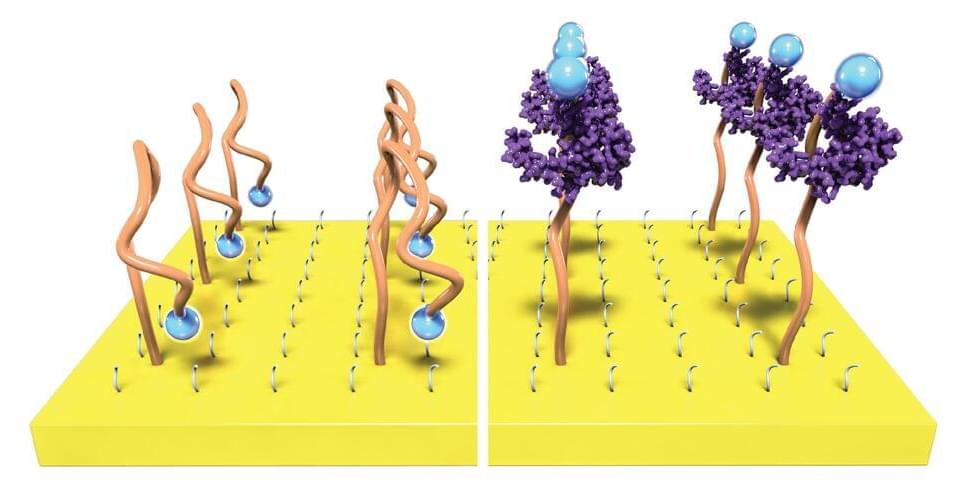
The molecules in our bodies are in constant communication. Some of these molecules provide a biochemical fingerprint that could indicate how a wound is healing, whether or not a cancer treatment is working or that a virus has invaded the body. If we could sense these signals in real time with high sensitivity, then we might be able to recognize health problems faster and even monitor disease as it progresses.
Now Northwestern University researchers have developed a new technology that makes it easier to eavesdrop on our body’s inner conversations.
While the body’s chemical signals are incredibly faint—making them difficult to detect and analyze—the researchers have developed a new method that boosts signals by more than 1,000 times. Transistors, the building block of electronics, can boost weak signals to provide an amplified output. The new approach makes signals easier to detect without complex and bulky electronics.
Presented by Madhumita Murgia and John Thornhill, produced by Josh Gabert-Doyon and Edwin Lane. Executive producer is Manuela Saragosa. Sound design by Breen Turner and Samantha Giovinco. Original music by Metaphor Music. The FT’s head of audio is Cheryl Brumley. Special thanks to The Hospital for Sick Children.
We’re keen to hear more from our listeners about this show and want to know what you’d like to hear more of, so we’re running a survey which you can find at ft.com/techtonicsurvey. It takes about 10 minutes to complete and you will be in with a chance to win a pair of Bose QuietComfort earbuds.
Classic Drama Movie: A Boy and His Dog — A young man and his telepathic dog wander through a post-apocalyptic wasteland.
A Boy and His Dog (1975)
Director: L.Q. Jones.
Writers: L.Q. Jones(screenplay), Harlan Ellison(novella), Wayne Cruseturner(uncredited)
Stars: Don Johnson, Jason Robards, Susanne Benton.
Genre: Comedy, Drama, Sci-Fi, Thriller.
Country: United States.
Language: English.
Release Date: March 1975 (USA)
Duration: 86 min.
Filming locations: Coyote Dry Lake, California, USA
Storyline:
A post-apocalyptic tale based on a novella by Harlan Ellison. A boy communicates telepathically with his dog as they scavenge for food and sex, and they stumble into an underground society where the old society is preserved. The daughter of one of the leaders of the community seduces and lures him below, where the citizens have become unable to reproduce because of being underground so long. They use him for impregnation purposes, and then plan to be rid of him.
Reviews:
“A frank tale about a recklessly horny boy and his calculative dog sums up this strange, very strange Sci-fi post-apocalyptic wasteland adventure yarn. It’s a unique product of the 70s, as it’s ambitious, daring and warped in its mind-set that makes this considerably low-budget effort a hypnotic cult item that nothing else would even come close to it. Based upon a novel by Harlan Ellison, the premise follows that of a young loner Vic (splendidly performed by Don Johnson) and his telepathic pooch Blood (exceptionally voiced by Tim McIntire) travelling the desert landscapes caused by the after-effects of WWIV in the search of food, shelter and women.
What goes on to make this film is the biting conversations and budding rapport and dependable friendship between Vic and Blood. It ranged from hysterical to moving, and surprisingly done in a believable manner. The satirical edge to the script is innovatively penned and to the point with its drama, frictions and kinky fixations. Sometimes quite unpleasant in the details where a quirky side is etched and the humour is engraved with a morbid sense of curiosity. While slow-grinding, the pace breezes by and the impulsively random nature helps a lot with a shock ending (twisted but still quite touching though) that comes from nowhere. Director LQ Jones’ economical touch makes the most of it limited resources and manages to get plenty out of it despite the minor feel. His use of the camera provocatively achieved and the humming electronic score and playful acoustic cues cement an atmosphere and grow upon the imagination. Mainly consisting in the underground scenes, than on the openly isolated and dusty desert backdrop.
The support cast are picture-perfect in their roles. Susanne Benton shines and likes of Jason Robards, Charles McGraw and Alvy Moore were good fun.
These hominids — a now-extinct race of humans found in South Africa — had big eyes, child-like faces and an average intelligence of around 150, making them geniuses among Homo sapiens.