Bought a $100 Android phone? Congrats: you’ve experienced the worst of Android. Please don’t base your opinion of Android on this.


Police in Japan have arrested a Chinese researcher they believe leaked sensitive tech data to a firm in China. We have analysis on efforts to tackle industrial espionage. #japan #china #leaks.
More stories on Japan: https://www3.nhk.or.jp/nhkworld/en/news/tags/2/
Please subscribe HERE: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCSPEjw8F2nQDtmUKPFNF7_A?sub_confirmation=1
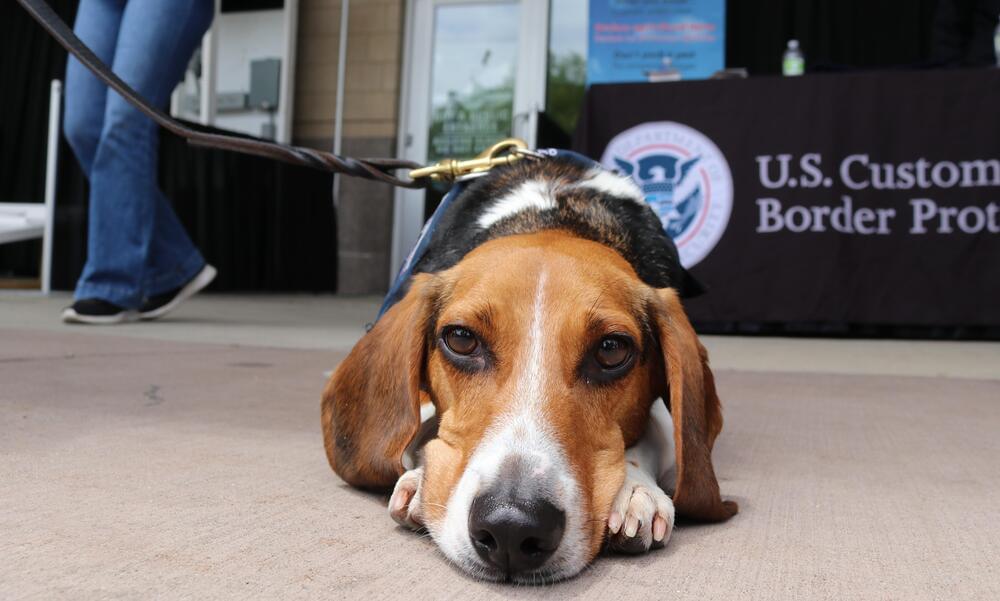


Scheele said that most of the dogs are rescues coming from the Atlanta area, which is near the USDA National Detector Dog Training Center.
Before they can be trained, the dogs are tested for temperament and to make sure they can detect five basic scents. Scheele said the detector dogs have to be food-driven animals, which he said (suprisingly) all dogs are not.
“That’s pork, beef, citrus, mango and apple,” Scheele said. “That’s to prove that the dog has the capability to do it and has the temperament to work in an environment like an airport or at a cargo facility, around the darkness or chaos that goes with imported goods or that sort of thing.”

As AI image generators continue to rock visual industries such as photography and illustration, Nikon is taking a stand against AI and on behalf of humans, cameras, and “natural intelligence.” Little Black Book reports that Nikon Peru recently partnered with the ad agency Circus Grey Peru on a new “Natural Intelligence” ad campaign.
Even though AI can now generate photorealistic images with just a simple text prompt, Nikon wants to remind everyone that the real world is full of incredible scenes that are best captured with a camera rather than imagined with AI.

Certain plant species.
A species is a group of living organisms that share a set of common characteristics and are able to breed and produce fertile offspring. The concept of a species is important in biology as it is used to classify and organize the diversity of life. There are different ways to define a species, but the most widely accepted one is the biological species concept, which defines a species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable offspring in nature. This definition is widely used in evolutionary biology and ecology to identify and classify living organisms.
The new 12-qubit “Tunnel Falls” chip announced by Intel packs important features into its tiny form factor that could help accelerate research in quantum computing.
Intel has announced a new 12-qubit “silicon spin” chip, Tunnel Falls, and is making it available to the research community. In addition, Intel is collaborating with the Laboratory for Physical Sciences (LPS) at the University of Maryland’s Qubit Collaboratory (LQC), to advance quantum computing research.

The process that powers much of life on Earth, photosynthesis, is so finely tuned that just one photon is enough to kick it off.
Scientists have long suspected that photosynthesis must be sensitive to individual photons, or particles of light, because despite the way it dominates our days, the sun’s light is surprisingly sparse at the level of individual plant cells. But only now, with the help of quantum physics, have researchers been able to watch a single packet of light begin the process in an experiment described on June 14 in the journal Nature.
“It makes sense that photosynthesis only requires a single photon, but to actually be able to measure that … is really groundbreaking,” says Sara Massey, a physical chemist at Southwestern University in Texas, who was not involved with the new research. “Being able to actually see that hands-on with the data from these experiments is very valuable.”
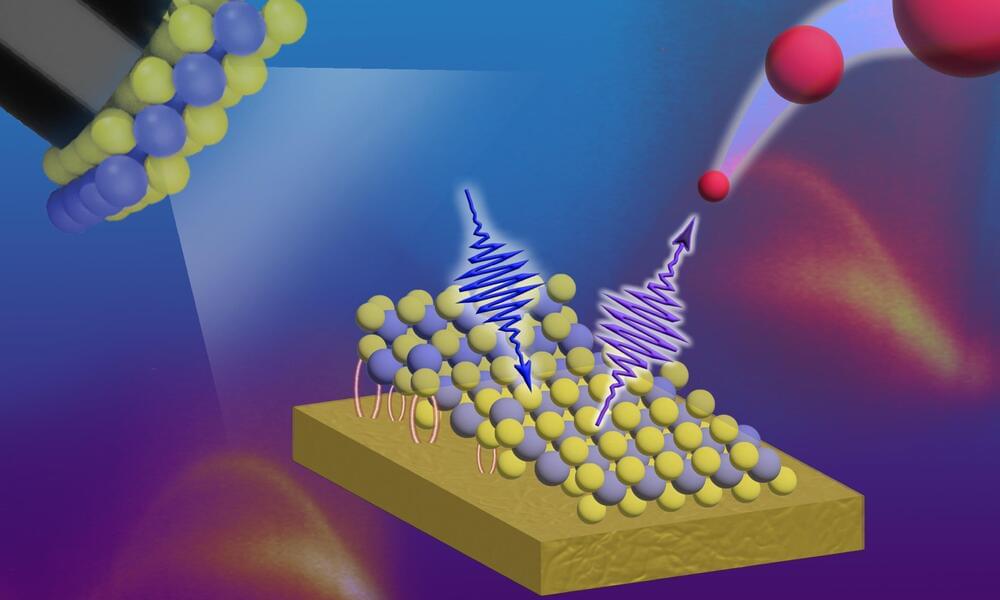
It has almost been 20 years since the establishment of the field of two-dimensional (2D) materials with the discovery of unique properties of graphene, a single, atomically thin layer of graphite. The significance of graphene and its one-of-a-kind properties was recognized as early as 2010 when the Nobel prize in physics was awarded to A. Geim and K. Novoselov for their work on graphene. However, graphene has been around for a while, though researchers simply did not realize what it was, or how special it is (often, it was considered annoying dirt on nice, clean surfaces of metals REF). Some scientists even dismissed the idea that 2D materials could exist in our three-dimensional world.
Today, things are different. 2D materials are one of the most exciting and fascinating subjects of study for researchers from many disciplines, including physics, chemistry and engineering. 2D materials are not only interesting from a scientific point of view, they are also extremely interesting for industrial and technological applications, such as touchscreens and batteries.
We are also getting very good at discovering and preparing new 2D materials, and the list of known and available 2D materials is rapidly expanding. The 2D materials family is getting very large and graphene is not alone anymore. Instead, it now has a lot of 2D relatives with different properties and vastly diverse applications, predicted or already achieved.
