How artificial intelligence will transform fame.



This is why i laughed at all that un canny valley crap talk in early 2010s. notice term is almost never used anymore. And, as for makin robots more attractive than most people. done in mid 2030s.
Does ChatGPT ever give you the eerie sense you’re interacting with another human being?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has reached an astounding level of realism, to the point that some tools can even fool people into thinking they are interacting with another human.
The eeriness doesn’t stop there. In a study published today in Psychological Science, we’ve discovered images of white faces generated by the popular StyleGAN2 algorithm look more “human” than actual people’s faces.


NEW YORK, Nov 13 (Reuters) — Electric air taxis could be transporting passengers from JFK Airport to downtown Manhattan by 2025 — on quiet, emissions-free journeys that take around seven minutes.
Manufacturer Joby Aviation (JOBY.N) carried out an exhibition flight at the Downtown Manhattan Heliport in New York on Sunday, the city’s first-ever electric air taxi flight and the first time Joby has flown in an urban setting.
The craft can recharge in about five minutes, while passengers are unloading and boarding, said CEO JoeBen Bevirt. The idea is that travelers will book their trip, similar to a rideshare app.
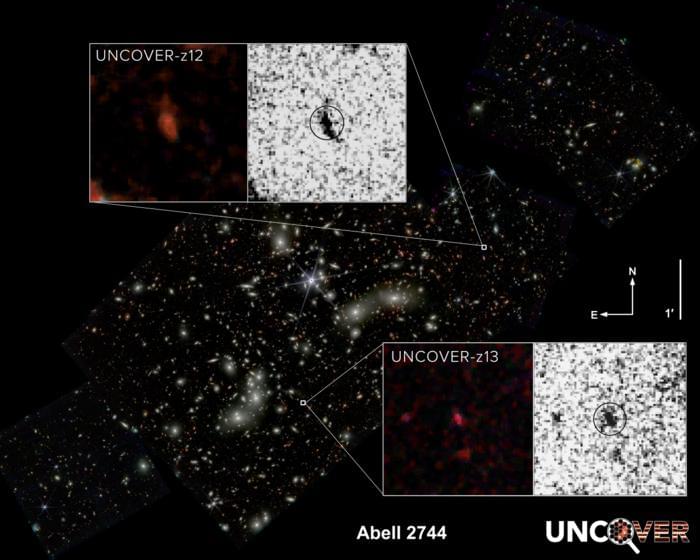
A recent study published in Astrophysical Journal Letters discusses how new data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has identified the second-and fourth-farthest and oldest galaxies in the universe, which are located approximately 33 billion light years from Earth and part of Abell 2744, also known as Pandora’s Cluster. The reason the galaxies are estimated to be 33 billion light years from Earth is due to the expansion of the universe, but astronomers hypothesize the two were first formed approximately 330 million years after the Big Bang, which is incredibly young in cosmic terms.
The two galaxies are named UNCOVER z-12 and UNCOVER z-13 since they were discovered by the JWST UNCOVER (Ultradeep NIRSpec and NIRCam ObserVations before the Epoch of Reionization) team. This study was conducted by an international team of more than two dozen researchers, who refer to the two galaxies as appearing like a peanut and fluffy ball, and this study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of the first galaxies after the Big Bang.
“Very little is known about the early universe, and the only way to learn about that time and to test our theories of early galaxy formation and growth is with these very distant galaxies,” said Dr. Bingjie Wang, who is a postdoctoral scholar in the Penn State Eberly College of Science and lead author of the study. “Prior to our analysis, we knew of only three galaxies confirmed at around this extreme distance. Studying these new galaxies and their properties has revealed the diversity of galaxies in the early universe and how much there is to be learned from them.”
Spacedock delves into animalistic bioship designs from across science fiction.
THE SOJOURN — AN ORIGINAL SCI-FI AUDIO DRAMA:
https://www.thesojournaudiodrama.com/
BECOME A CHANNEL MEMBER:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCfjaAUlTZRHJapJmCT6eyIg/join.
SUPPORT SPACEDOCK:
https://www.patreon.com/officialspacedock?ty=h.
MERCHANDISE:
https://teespring.com/en-GB/stores/spacedock-2
Do not contact regarding network proposals.

The world’s most valuable chip maker has announced a next-generation processor for AI and high-performance computing workloads, due for launch in mid-2024. A new exascale supercomputer, designed specifically for large AI models, is also planned.
H200 Tensor Core GPU. Credit: NVIDIA
In recent years, California-based NVIDIA Corporation has played a major role in the progress of artificial intelligence (AI), as well as high-performance computing (HPC) more generally, with its hardware being central to astonishing leaps in algorithmic capability.

In the evolving landscape of space warfare, conflict is shifting into what experts commonly call the “gray zone.”
Unlike traditional conflicts defined by clear boundaries, rules of engagement and identifiable actors, space battles in the gray zone are ambiguous, with military and civilian activities that can be difficult to discern.
“It’s crucial for U.S. policymakers and military leaders to understand the nuances of future competition in space, and how it will likely play out,” said John Klein, military strategist and adjunct professor at George Washington University’s Space Policy Institute.