Join the discussion on this paper page.


After taking the so-called longevity supplement NMN for 11 months, alongside my 80-year-old parents, in this video I reveal our surprising test results! Plus I discuss the effects of NMN that we experienced, whether we intend to keep taking it long term and why. #longevity #nmn #healthyaging
Sunlight provides so much more than just Vitamin D: learn from Dr. Seheult of https://bit.ly/44MTKR2 about the myriad of benefits from optimizing our exposure to light.
Roger Seheult, MD is the co-founder and lead professor at https://bit.ly/44MTKR2
He is board certified in internal medicine, pulmonary disease, critical care, and sleep medicine and an associate professor at the university of california, riverside school of medicine.
I believe nanomachines or new advanced rna antivirals that can target one’s own variants of viruses will be game changers to prevent future global pandemics. Also eventually new genetic engineering could allow for the end to all viruses with some sorta Omni vaccine.
Measurement(s) Pandemic-and epidemic-prone disease outbreaks Technology Type(s) Text mining using R Sample Characteristic — Organism Disease outbreaks Sample Characteristic — Environment spatiotemporal region Sample Characteristic — Location Global.
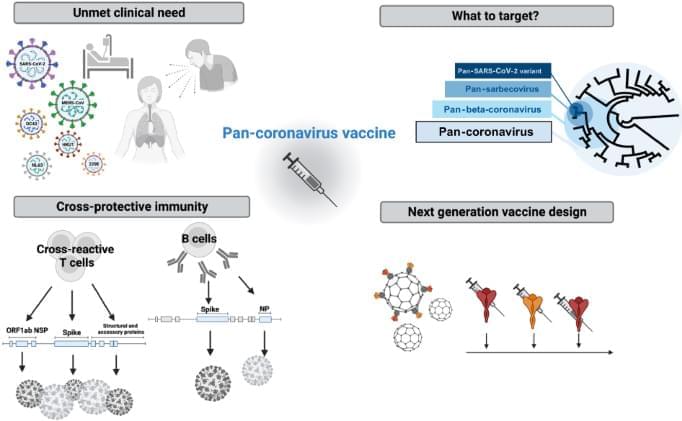
Cankat, S., Demael, M.U. & Swadling, L. In search of a pan-coronavirus vaccine: next-generation vaccine design and immune mechanisms. Cell Mol Immunol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-023-01116-8
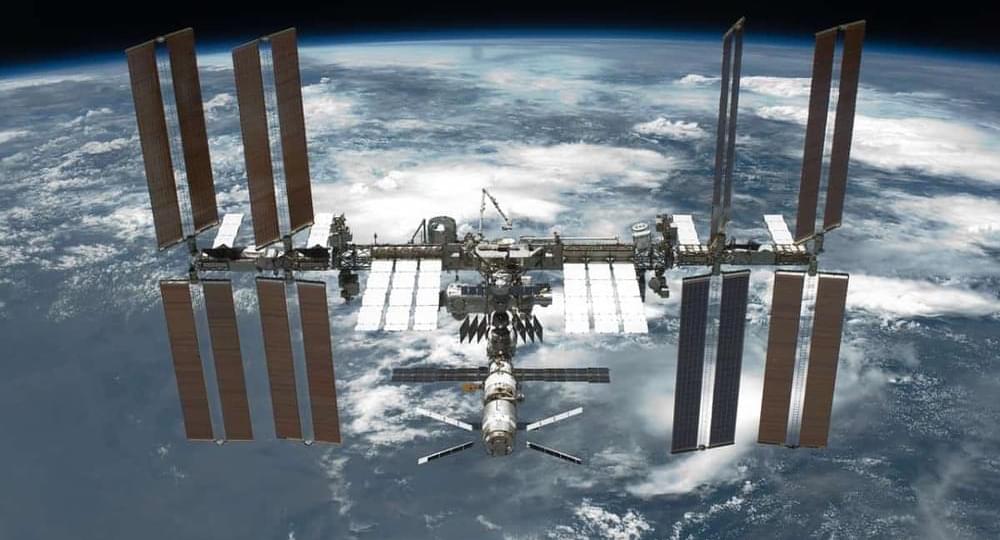

Well, many of those who partied hard on New Year’s may be regretting their decision because of the hangover. But once the clutches of alcoholic after-effects decide to free you, you are ready to party again. But even the most hardcore partygoers would not dare to face this challenge. How about having 16 New Years’ Party in a single day? Tough right? But if partying would be high on the list of astronauts at the International Space Station (ISS), they would really have been able to do it.
The reason?
They witness 16 sunrises and sunsets in a ‘single day’ aboard the ISS.

Artificial intelligence (AI) has been advancing rapidly, but its inner workings often remain obscure, characterized by a “black box” nature where the process of reaching conclusions is not visible. However, a significant breakthrough has been made by Prof. Dr. Jürgen Bajorath and his team, cheminformatics experts at the University of Bonn. They have devised a technique that uncovers the operational mechanisms of certain AI systems used in pharmaceutical research.
Surprisingly, their findings indicate that these AI models primarily rely on recalling existing data rather than learning specific chemical interactions for predicting the effectiveness of drugs. Their results have recently been published in Nature Machine Intelligence.
Which drug molecule is most effective? Researchers are feverishly searching for efficient active substances to combat diseases. These compounds often dock onto protein, which usually are enzymes or receptors that trigger a specific chain of physiological actions.

