Also get 49fps in BG3119fps in CS2, and 41fps in Cyberpunk 2077 using the new AMD Ryzen 8700G, all without the need for an extra CPU cooler.




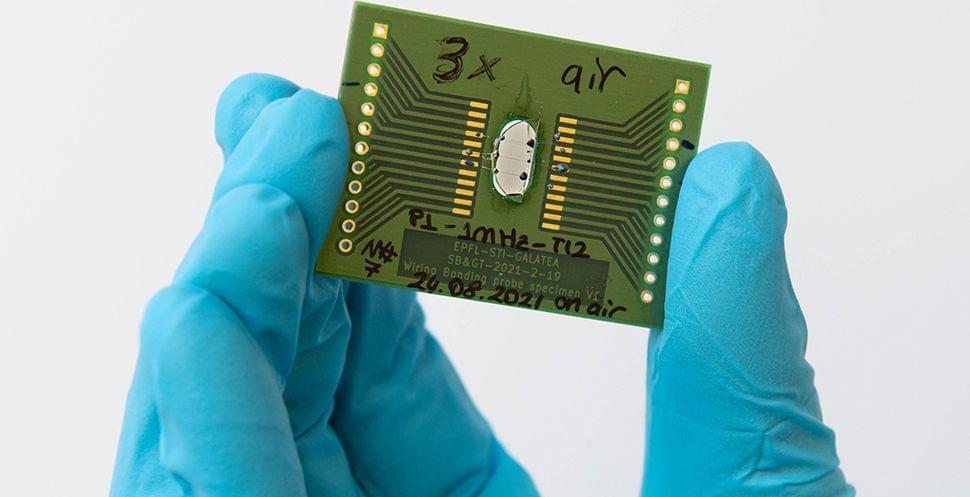
The EPFL team, using tellurite glass produced by their Tokyo Tech colleagues, applied their expertise in femtosecond laser technology to alter the glass and study the laser’s effect. After etching a simple line pattern onto a 1 cm diameter tellurite glass and exposing it to UV light and the visible spectrum, Torun found it could generate a current consistently for months.
Bellouard expressed his excitement at the breakthrough, saying, “We’re locally turning glass into a semiconductor using light. We’re essentially transforming materials into something else, perhaps approaching the dream of the alchemist!”
This development may pave the way for windows to function as single-material light-harvesting and sensing devices in the future.
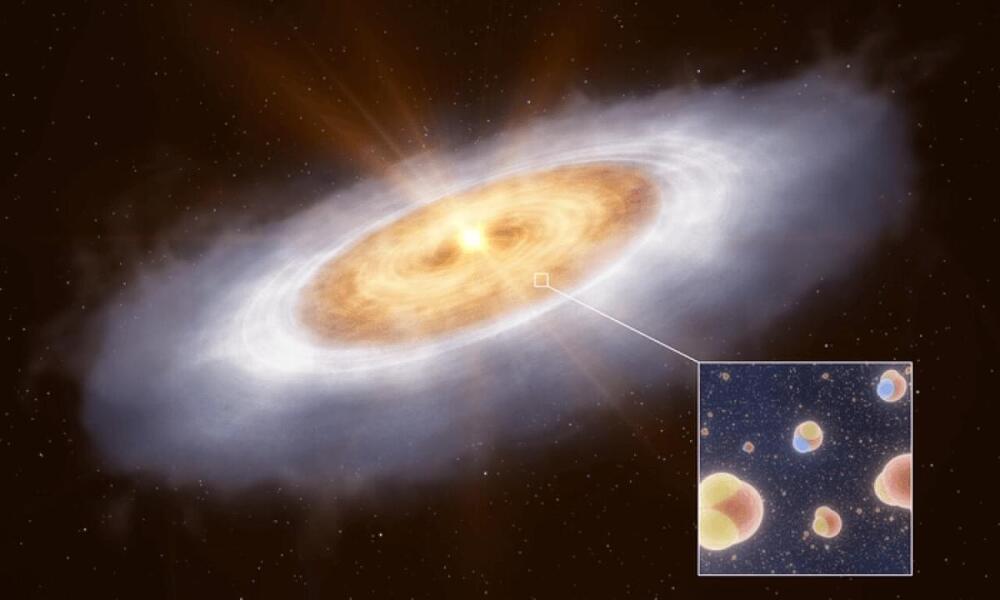

SANTIAGO, Chile — Astronomers have traced the source of Earth’s oceans, rivers, and lakes back to a stellar nursery located 1,300 light years away. They’re describing this finding as the “missing link” in the evolution of life as we know it.
“We can now trace the origins of water in our Solar System to before the formation of the Sun,” says lead author Dr. John Tobin of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.
The international team discovered gaseous water in a substantial planet-forming disc around the star V883 Orionis. This star, located in the Orion constellation in the southwestern sky, was studied using the ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array) telescope in Chile. Upon examination, researchers found that the disc contained at least 1,200 times the quantity of water found in all of Earth’s oceans. This discovery could potentially aid researchers in identifying planets or moons that are most likely to harbor extraterrestrial life.
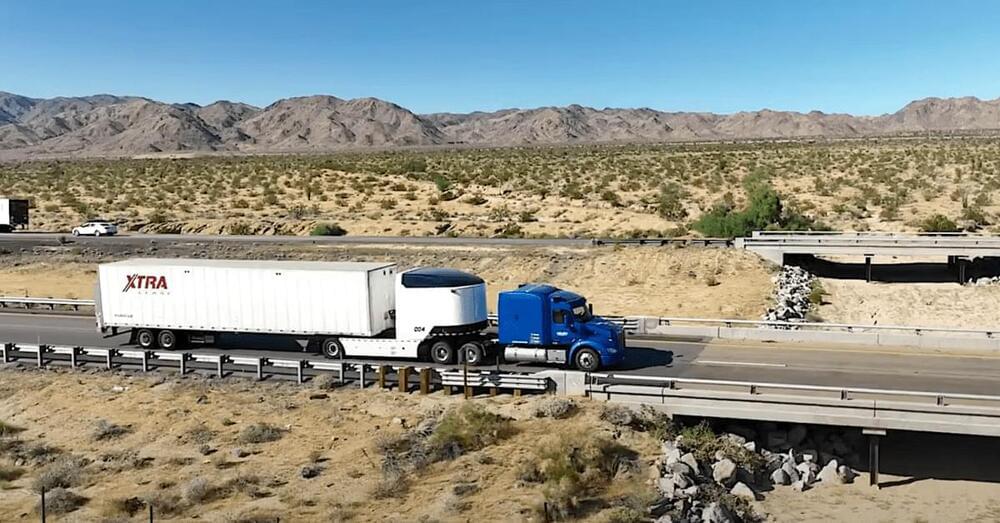

The Revoy EV concept is deceptively simple. A tractor’s 5th wheel pairs up with the Revoy’s hitch. Then the trailer that the semi is set to haul attaches to the Revoy’s 5th wheel. Some AI embedded in the Revoy’s electronic control units does some number-crunching and the three-part truck, trailer, trailer combo then hauls off down the road, with the Revoy’s high-torque e-axle providing most of the power to accelerate the load and diesel power where it’s most efficient: on the highway.
The best part, according to Revoy? Truckers can add the Revoy EV trailer to their rigs with no up-front costs.


A group of astrophysicists led by Mireia Montes, a researcher at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), has discovered the largest and most diffuse galaxy recorded until now. The study has been published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, and has used data taken with the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) and the Green Bank Radiotelescope (GBT).
Nube is an almost invisible dwarf galaxy discovered by an international research team led by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) in collaboration with the University of La Laguna (ULL) and other institutions.
The name was suggested by the 5-year-old daughter of one of the researchers in the group, and is due to the diffuse appearance of the object. Its surface brightness is so faint that it had passed unnoticed in the various previous surveys of this part of the sky, as if it were some kind of ghost. This is because its stars are so spread out in such a large volume that “Nube” (the Spanish for “Cloud”) was almost undetectable.
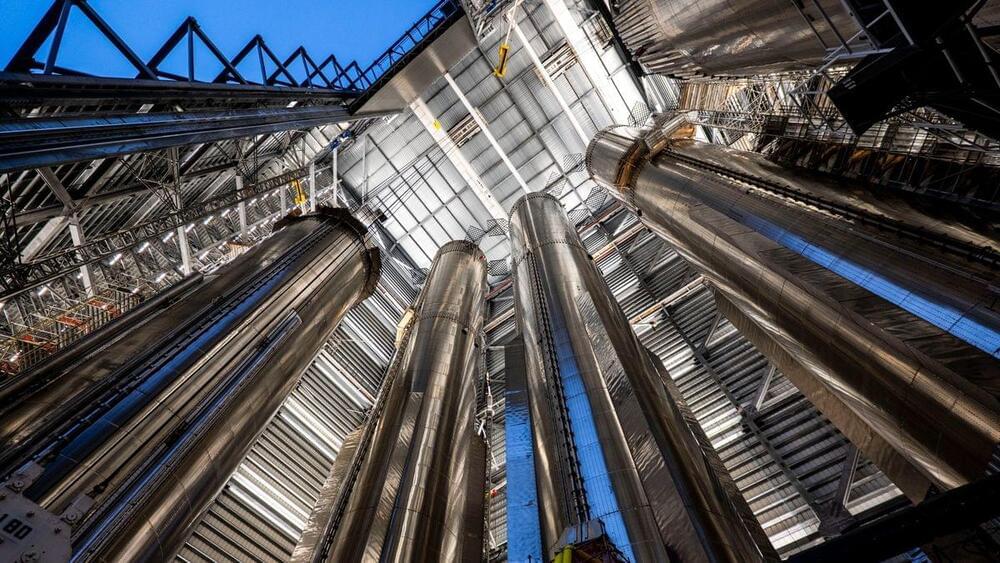

The building is jam-packed with towering stainless-steel cylinders — Super Heavy vehicles, the first stage of SpaceX’s Starship megarocket — which rise nearly to the roof.
“Super Heavy boosters for the next three flights, with a fourth ready to stack, in the Starbase Megabay,” SpaceX wrote in the post.
