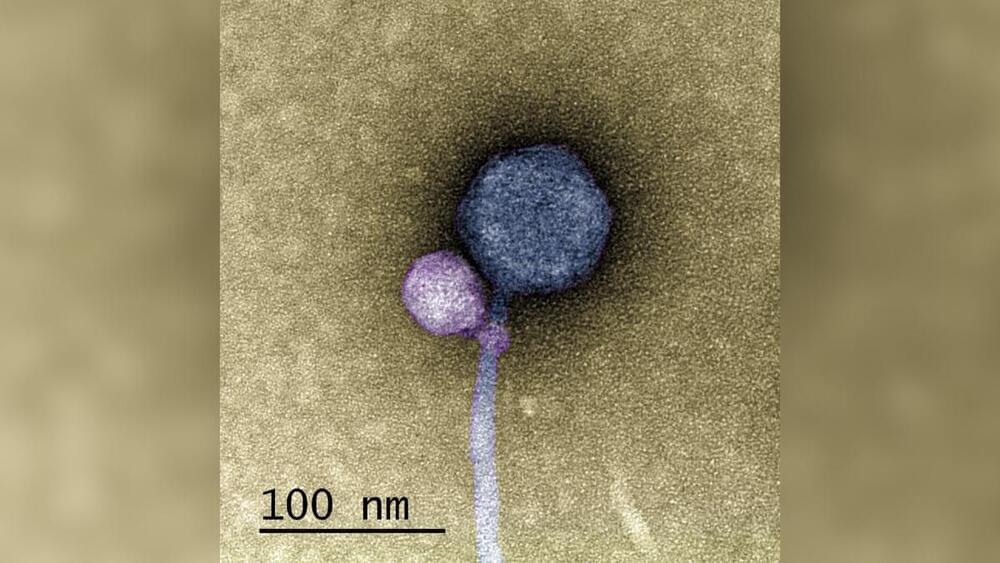
The interaction was captured using a specialized piece of kit called a transmission electron microscope.
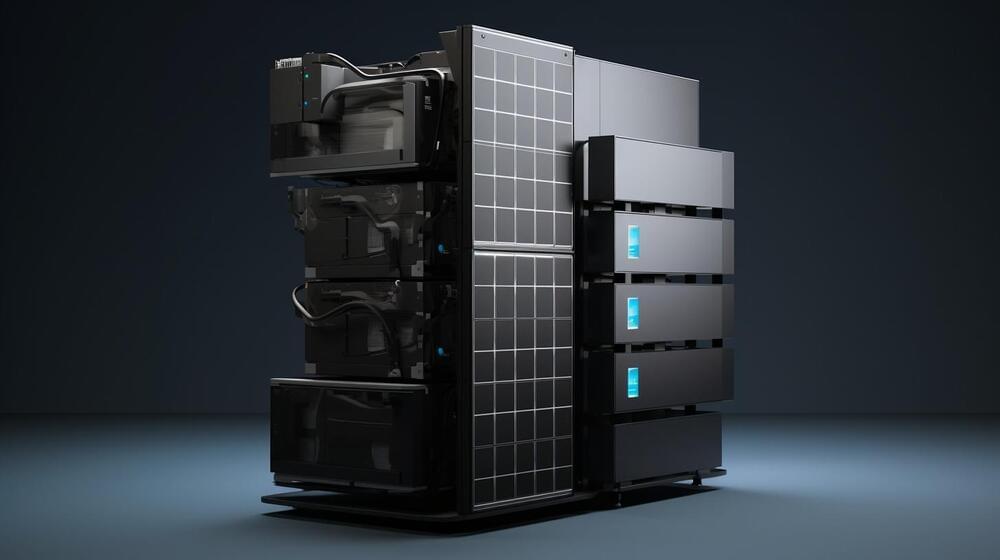


Bluetti, a leading US solar and storage specialist, has announced the launch of its groundbreaking EP760 battery system, offering a highly customizable energy storage solution for residential settings. This innovative system introduces a modular design that allows users to stack up to four lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery modules, providing a flexible energy storage capacity of 9.9 kWh to 19.8 kWh.
Unlike traditional fixed-capacity battery systems, the EP760 offers adaptability and scalability, enabling homeowners to tailor their energy storage setup to meet their specific needs. By combining the EP760 with two to four B500 battery packs, users can create an energy storage system ranging from 9,920 Wh to a maximum of 19,840 Wh. With the ability to deliver up to 7,600 W of single-phase power in grid or off-grid mode, the EP760 ensures reliable and efficient operation.
Bluetti’s EP760 comes equipped with several advanced features that make it an ideal choice for residential applications. The system’s intelligent peak load shifting feature allows homeowners to take advantage of off-peak electricity pricing by charging the battery system when grid electricity is cheap and discharging it during peak hours, reducing overall energy costs. Additionally, the EP760 can be seamlessly integrated with existing or future solar systems, supporting up to 9,000 W of solar charging.

HUMANS could get the power to see in the dark after mice were injected with nanoparticles which gave them the ability to see infrared light.
The rodents were given infrared night vision for 10 weeks after the injection, with only minor side effects, in an experiment conducted by Chinese and US scientists.
The team at the University of Science and Technology of China said they could modify a human’s vision to detect a wider spectrum of colours.

Ilya Sutskever, one of the leading AI scientists behind ChatGPT, reflects on his founding vision and values. In conversations with the film-maker Tonje Hessen Schei as he was developing the chat language model between 2016 and 2019, he describes his personal philosophy and makes startling predictions for a technology already shaping our world. Reflecting on his ideas today, amid a global debate over safety and regulation, we consider the opportunities as well as the consequences of AI technology. Ilya discusses his ultimate goal of artificial general intelligence (AGI), ‘a computer system that can do any job or task that a human does, but better’, and questions whether the AGI arms race will be good or bad for humanity.
These filmed interviews with Ilya Sutskever are part of a feature-length documentary on artificial intelligence, called iHuman.
The Guardian publishes independent journalism, made possible by supporters. Contribute to The Guardian today ► https://bit.ly/3uhA7zg.
Sign up to the Guardian’s free new daily newsletter, First Edition ► http://theguardian.com/first-edition.
Website ► https://www.theguardian.com.
Facebook ► https://www.facebook.com/theguardian.
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/guardian.
Instagram ► https://instagram.com/guardian.
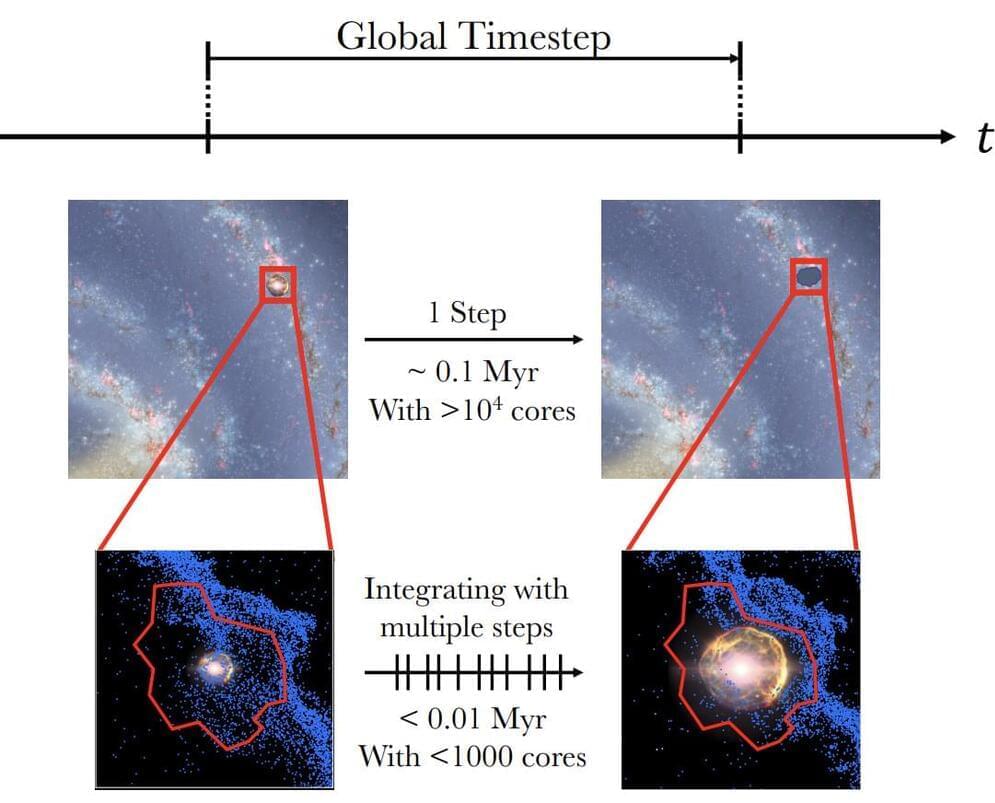
A new way to simulate supernovae may help shed light on our cosmic origins. Supernovae, exploding stars, play a critical role in the formation and evolution of galaxies. However, key aspects of them are notoriously difficult to simulate accurately in reasonably short amounts of time. For the first time, a team of researchers, including those from The University of Tokyo, apply deep learning to the problem of supernova simulation. Their approach can speed up the simulation of supernovae, and therefore of galaxy formation and evolution as well. These simulations include the evolution of the chemistry which led to life.
When you hear about deep learning, you might think of the latest app that sprung up this week to do something clever with images or generate humanlike text. Deep learning might be responsible for some behind-the-scenes aspects of such things, but it’s also used extensively in different fields of research. Recently, a team at a tech event called a hackathon applied deep learning to weather forecasting. It proved quite effective, and this got doctoral student Keiya Hirashima from the University of Tokyo’s Department of Astronomy thinking.
“Weather is a very complex phenomenon but ultimately it boils down to fluid dynamics calculations,” said Hirashima. “So, I wondered if we could modify deep learning models used for weather forecasting and apply them to another fluid system, but one that exists on a vastly larger scale and which we lack direct access to: my field of research, supernova explosions.”
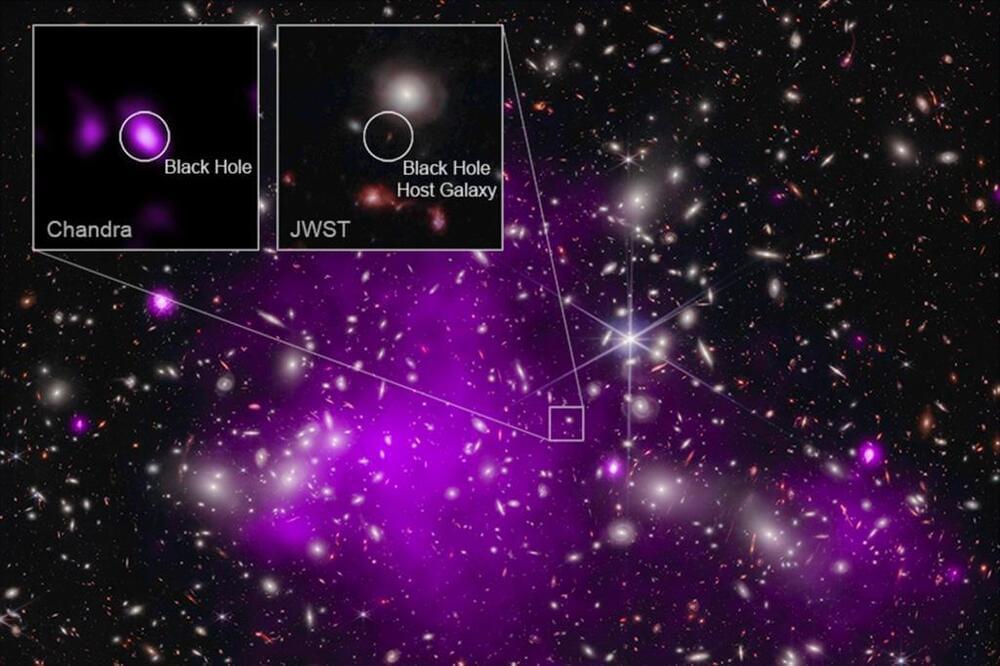
The oldest known black hole — a 13.2 billion-year-old ‘behemoth’ — has been discovered by scientists.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and Chandra X-Ray Observatory spent the past year working together to find and confirm the black hole and on Monday, researchers published their findings which confirmed beliefs that supermassive black holes existed at the start of the universe.
They believe the newly-located black hole was formed just 470 million years after the Big Bang and is 10 times larger than the black hole in the Milky Way.
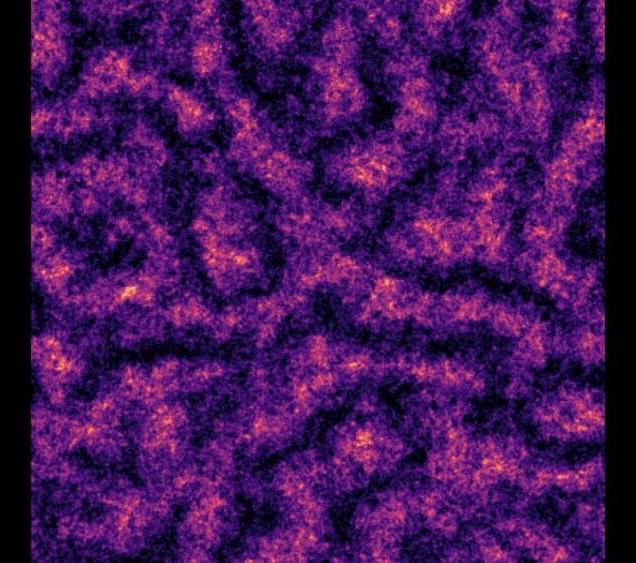
In a new study, researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara, (UCSB) have reported the discovery of a spin microemulsion in two-dimensional systems of spinor Bose-Einstein condensates, shedding light on a novel phase transition marked by the loss of superfluidity, complex pseudospin textures, and the emergence of topological defects.
A Bose-Einstein (B-E) condensate is a state of matter that occurs at extremely low temperatures, where bosons, such as photons, become indistinguishable and behave as a single quantum entity, forming a superfluid or superconducting state.
B-E condensates can exhibit unique quantum properties, such as a spin microemulsion. When the internal spin states of atoms in a B-E condensate are coupled to their motion, a unique phase called a spin microemulsion can emerge.
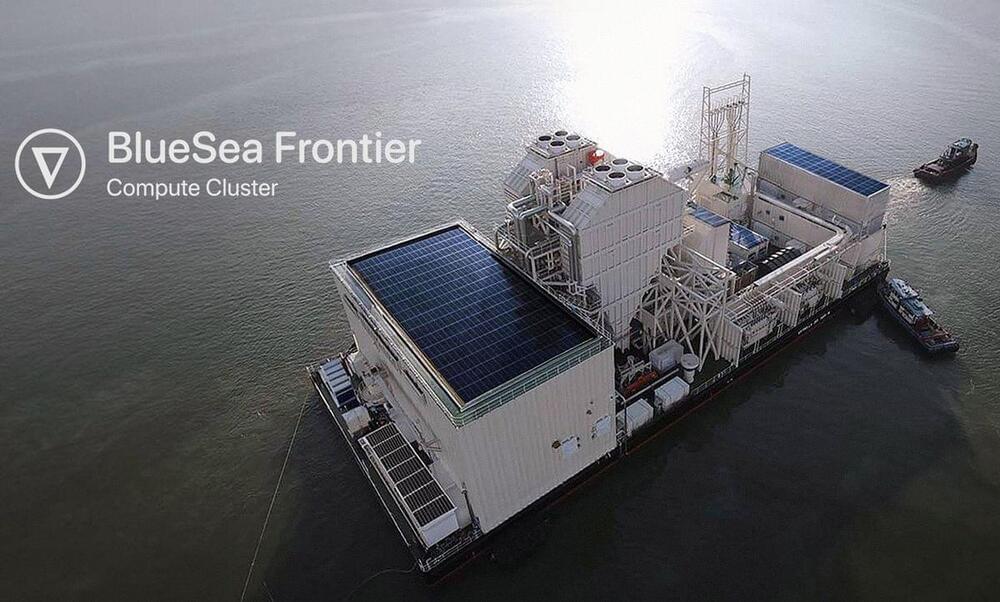

Almost like a tax shelter in a sense but to avoid AI regulations.
A floating data center containing thousands of Nvidia GPUs has raised questions over whether the practice could result in the creation of sovereign AI states in the future.