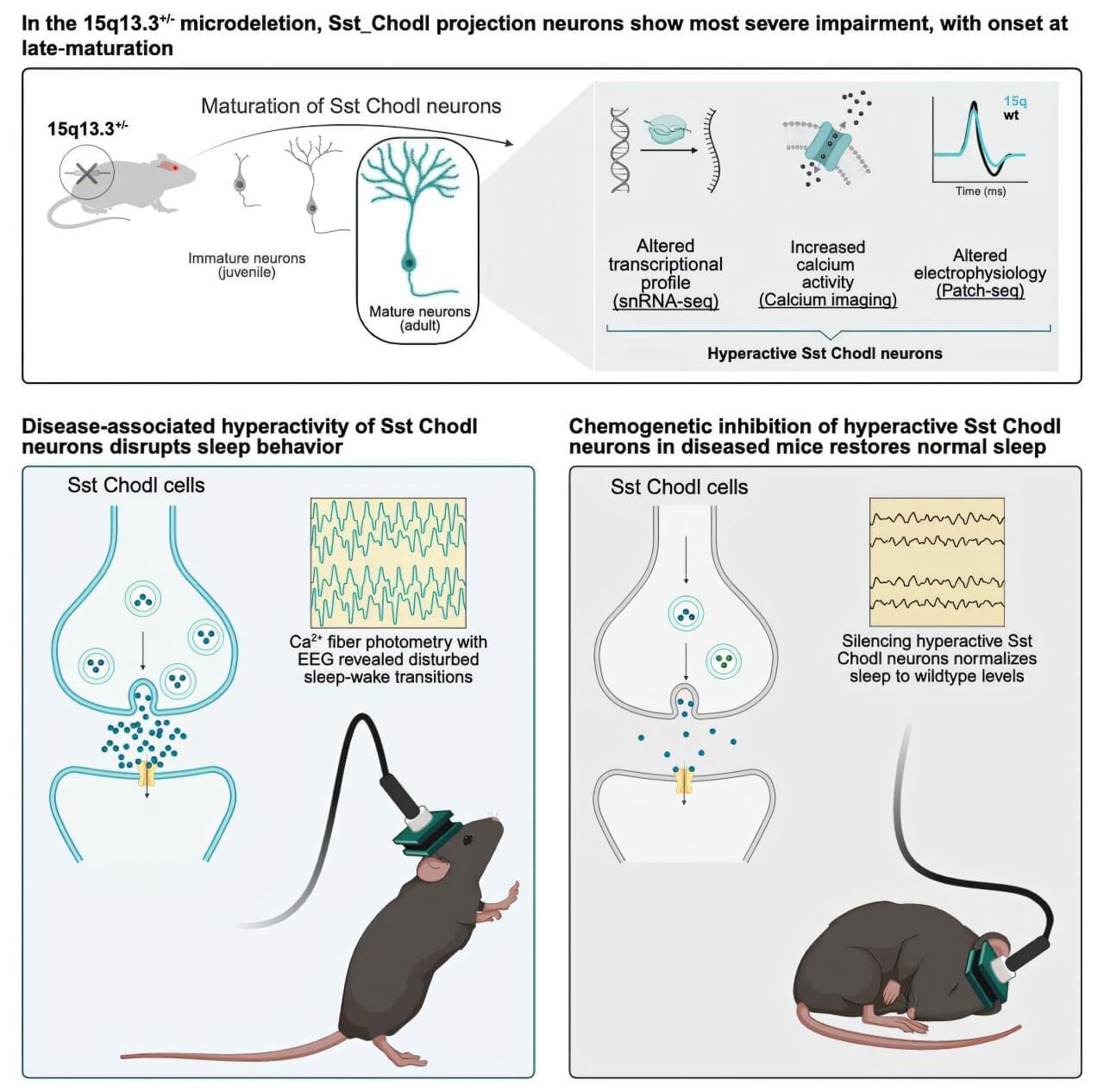
Difficulty completing everyday tasks. Failing memory. Unusually poor concentration. For many people living with schizophrenia, cognitive challenges are part of daily life. Alongside well-known symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions, these difficulties can make it hard to live the life they want. That is why researchers at the University of Copenhagen are working to find ways to prevent such symptoms—and they may now be one step closer.
In a new study, researchers discovered that a specific type of brain cell is abnormally active in mice displaying schizophrenia-like behavior. When the researchers reduced the activity of these cells, the mice’s behavior changed. The findings are published in the journal Neuron.
“Current treatments for cognitive symptoms in patients with diagnoses such as schizophrenia are inadequate. We need to understand more about what causes these cognitive symptoms that are derived from impairments during brain development. Our study may be the first step toward a new, targeted treatment that can prevent cognitive symptoms,” says Professor Konstantin Khodosevich from the Biotech Research and Innovation Center at the University of Copenhagen, and one of the researchers behind the study.