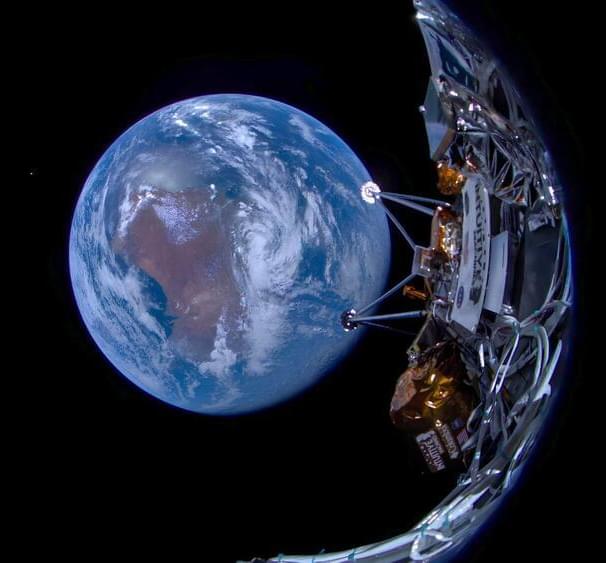
The ADRAS-J satellite, which weighs 150 kilograms (330 pounds), lifted off on top of an Electron rocket from Rocket Lab’s launch site in New Zealand at 9:52 am EST (1452 GMT; 3:52 am local New Zealand time on February 19).
Lift-off for #OnCloserInspection! ADRAS-J is on its way to orbit. pic.twitter.com/1cu9BI7BBp — Rocket Lab (@RocketLab) February 18, 2024
Astroscale Japan was tasked by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency to lead Phase I of its Commercial Removal of Debris Demonstration program, which involved designing, manufacturing, testing, launching, and operating the ADRAS-J spacecraft.