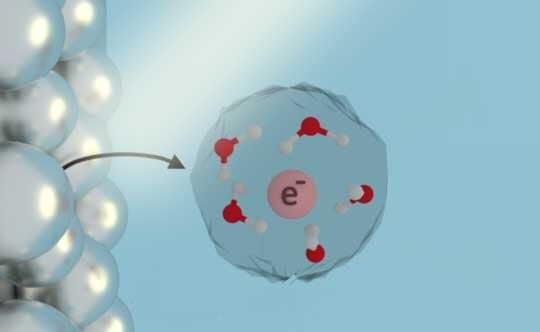
There are many ways to initiate chemical reactions in liquids, but placing free electrons directly into water, ammonia and other liquid solutions is especially attractive for green chemistry because solvated electrons are inherently clean, leaving behind no side products after they react.
In theory, solvated electrons could be used to safely and sustainably break down carbon dioxide or chemical pollutants in contaminated water, but it has been impractical to find out because they’ve been difficult and expensive to make in pure form.
That could change thanks to new research from chemists at Rice University, Stanford University and the University of Texas at Austin. In a published study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from the Center for Adapting Flaws into Features (CAFF) uncovered the long-sought mechanism of a well-known but poorly understood process that produces solvated electrons via interactions between light and metal.