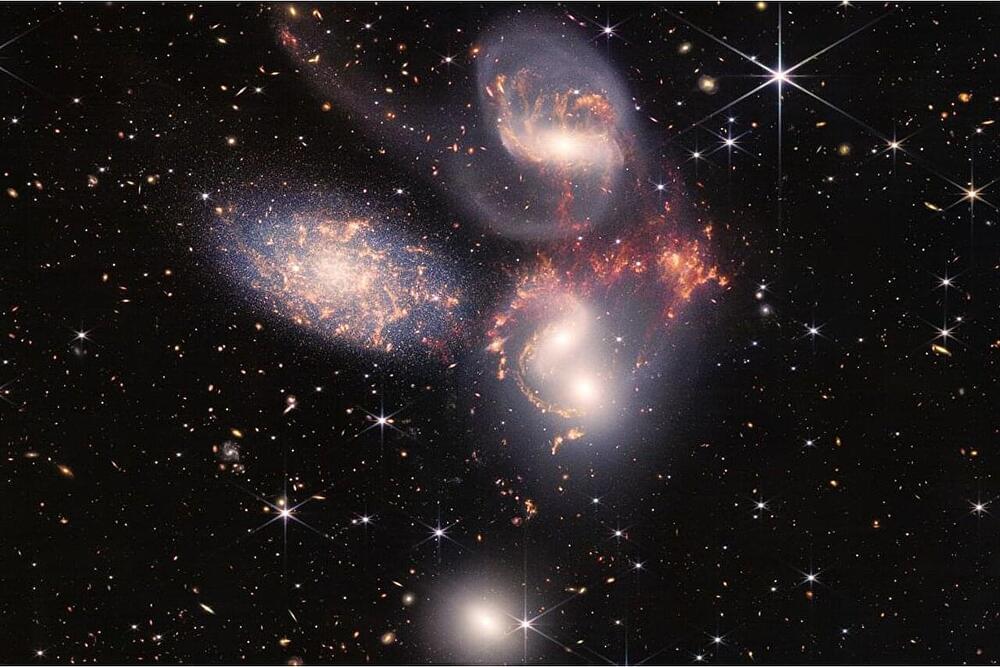
For the past year and a half, the James Webb Space Telescope has delivered astonishing images of distant galaxies formed not long after the Big Bang, giving scientists their first glimpses of the infant universe. Now, a group of astrophysicists has upped the ante: Find the tiniest, brightest galaxies near the beginning of time itself, or scientists will have to totally rethink their theories about dark matter.
The team, led by UCLA astrophysicists, ran simulations that track the formation of small galaxies after the Big Bang and included, for the first time, previously neglected interactions between gas and dark matter. They found that the galaxies created are very tiny, much brighter, and form more quickly than they do in typical simulations that don’‘t take these interactions into account, instead revealing much fainter galaxies.
Small galaxies, also called dwarf galaxies, are present throughout the universe, and are often thought to represent the earliest type of galaxy. Small galaxies are thus especially interesting to scientists studying the origins of the universe. But the small galaxies they find don’t always match what they think they should find. Those closest to the Milky Way spin quicker or are not as dense as in simulations, indicating that the models might have omitted something, such as these gas-dark matter interactions.