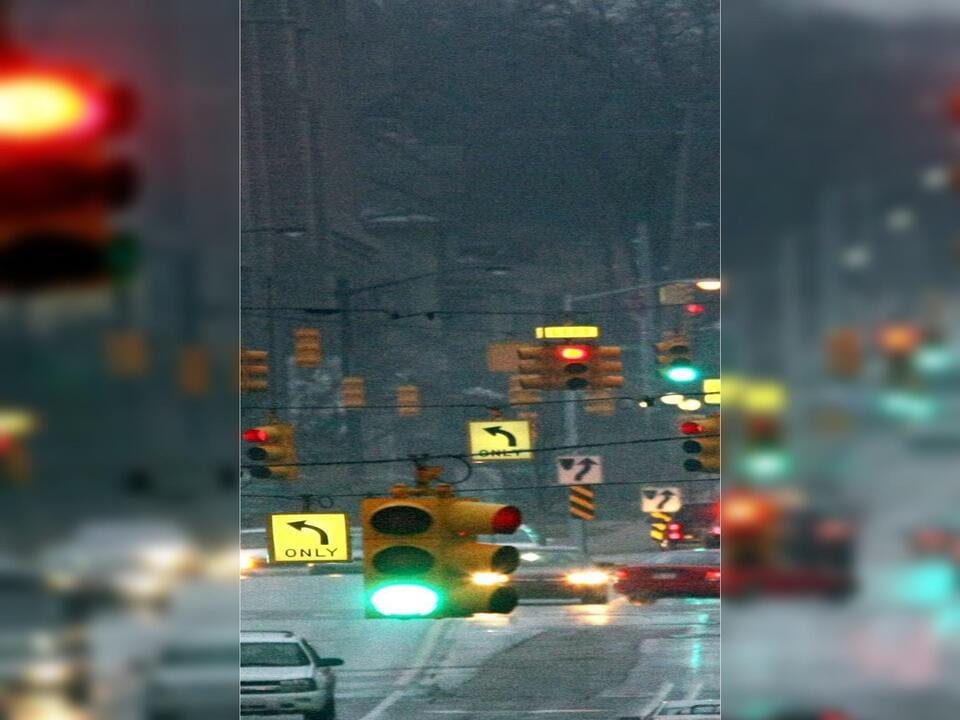
The Paulding Light, a perplexing glow in the Michigan sky, has fueled folklore with its eerie nightly appearances since the 1960s. What was once thought to be a ghostly signal has turned into a case study for scientific inquiry. A team of Michigan Tech students, led by Jeremy Bos, a PhD candidate in electrical engineering, undertook a methodical investigation to expose the truth behind the spectral luminance that intrigued both locals and visitors in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula.
Their rigorous scientific approach involved telescopes, spectrographs, and atmospheric modeling, which demystified the paranormal claims. By observing the phenomenon through a telescope, the researchers identified the lights as nothing more than the headlights and taillights of vehicles on a distant stretch of US Highway 45. This was further supported by spectral analysis, confirming the automotive origin of the lights. The team’s findings pointed to atmospheric conditions and the geography of the Paulding area, which caused the vehicle lights to refract and create the illusion of the unexplained Paulding Light.
Despite the logical explanations provided by these dedicated students, the Paulding Light’s allure remains undiminished. The legend continues to attract those drawn to the supernatural, demonstrating the human fascination with mystery over the mundane. The Paulding Light stands as a symbol of our enduring attraction to the unexplained, a reminder that sometimes, even when the truth is revealed, the legend never dies.