Acoustic tweezers can control target movement through the interaction of momentum between an acoustic wave and an object. Due to their high tissue penetrability and strong acoustic radiation force, such tweezers overcome the limitations of optical and magnetic tweezers, thus making them suitable for in vivo cell manipulation.
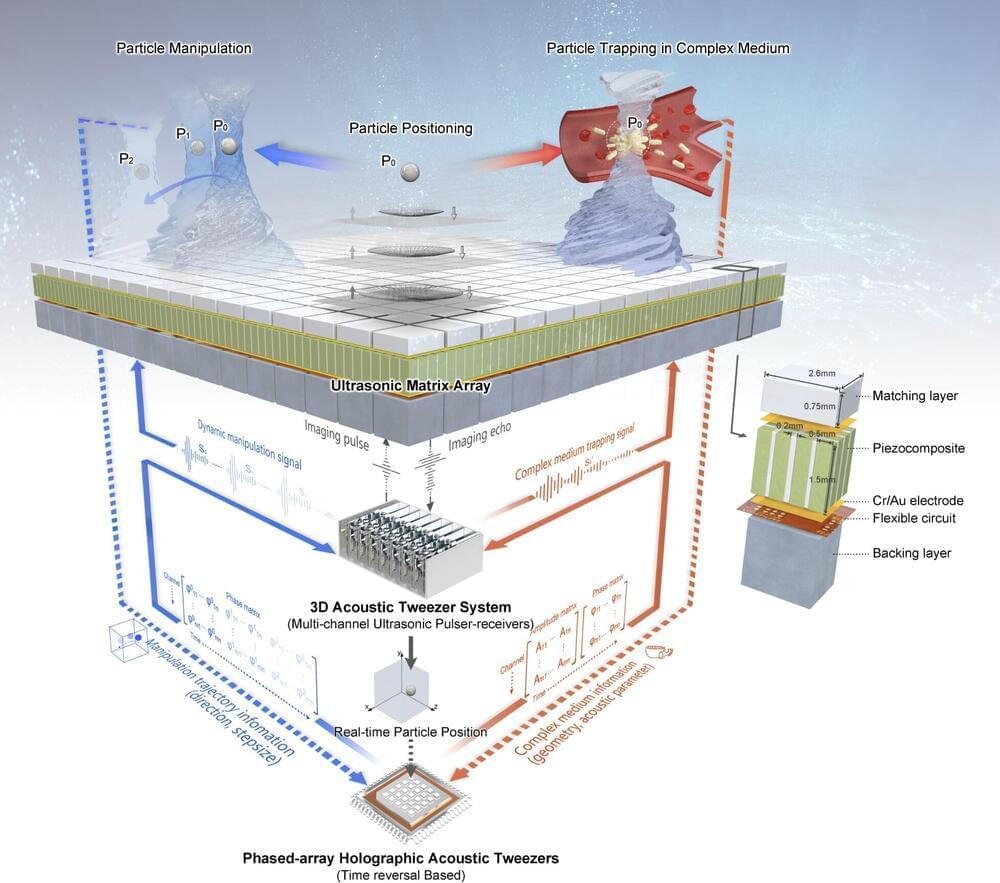
A research team led by Prof. Zheng Hairong from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has recently developed a new type of acoustic tweezers —the phased-array holographic acoustic tweezers (PAHAT) system—which is based on a high-density planar array transducer capable of generating tunable three-dimensional bulk acoustic waves. The researchers hope this system can realize a pharmacological version of “telekinesis.” The study was published in Nature Communications on June 6.
The in vivo environment is extremely complex, due to the different characteristics of various tissues, organs, bones, blood vessels, and blood flow. Such a complex environment creates a huge challenge: How can acoustic methods be used to “trap” bacteria so they can produce therapeutic effects on tumors?