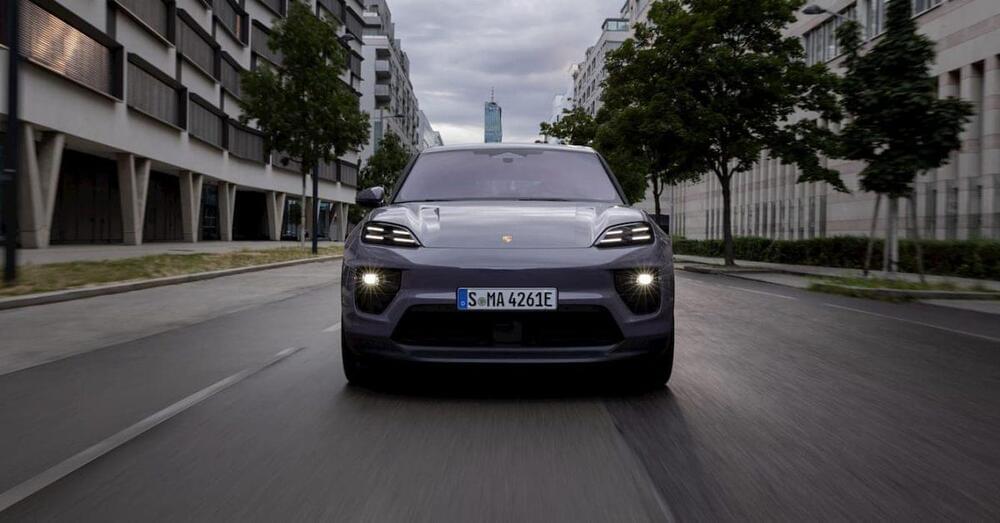
We finally got our first look at the new all-electric Porsche Macan EV this week. Porsche’s electric Macan features a 100 kWh battery pack that will reportedly be supplied by China’s CATL.
Ten years after debuting the SUV, Porsche revealed the all-electric Macan Thursday. The electric Macan is Porsche’s second EV, after the Taycan and the first fully electric SUV to wear the iconic badge.
The Macan EV is also the first existing Porsche model to receive an electric upgrade. With 87,355 Macan models handed over last year, the SUV plays a critical role in Porsche’s lineup.