ShadowSilk hit 36 victims across Central Asia and APAC in July, using Telegram bots to exfiltrate government data.



Microsoft warns that a threat actor tracked as Storm-0501 has evolved its operations, shifting away from encrypting devices with ransomware to focusing on cloud-based encryption, data theft, and extortion.
The hackers now abuse native cloud features to exfiltrate data, wipe backups, and destroy storage accounts, thereby applying pressure and extorting victims without deploying traditional ransomware encryption tools.
Storm-0501 is a threat actor who has been active since at least 2021, deploying the Sabbath ransomware in attacks against organizations worldwide. Over time, the threat actor joined various ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) platforms, where they used encryptors from Hive, BlackCat (ALPHV), Hunters International, LockBit, and, more recently, Embargo ransomware.

Threat researchers discovered the first AI-powered ransomware, called PromptLock, that uses Lua scripts to steal and encrypt data on Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.
The malware uses OpenAI’s gpt-oss:20b model through the Ollama API to dynamically generate the malicious Lua scripts from hard-coded prompts.

The U.S. National Security Agency (NSA), the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), and partners from over a dozen countries have linked the Salt Typhoon global hacking campaigns to three China-based technology firms.
According to the joint advisories [NSA, NCSC], Sichuan Juxinhe Network Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing Huanyu Tianqiong Information Technology Co., and Sichuan Zhixin Ruijie Network Technology Co. Ltd. have provided cyber products and services to China’s Ministry of State Security and the People’s Liberation Army, enabling cyber espionage operations tracked as Salt Typhoon.
Since at least 2021, the Chinese threat actors have breached government, telecommunications, transportation, lodging, and military networks worldwide, stealing data that can be used to track targets’ communications and movements worldwide.
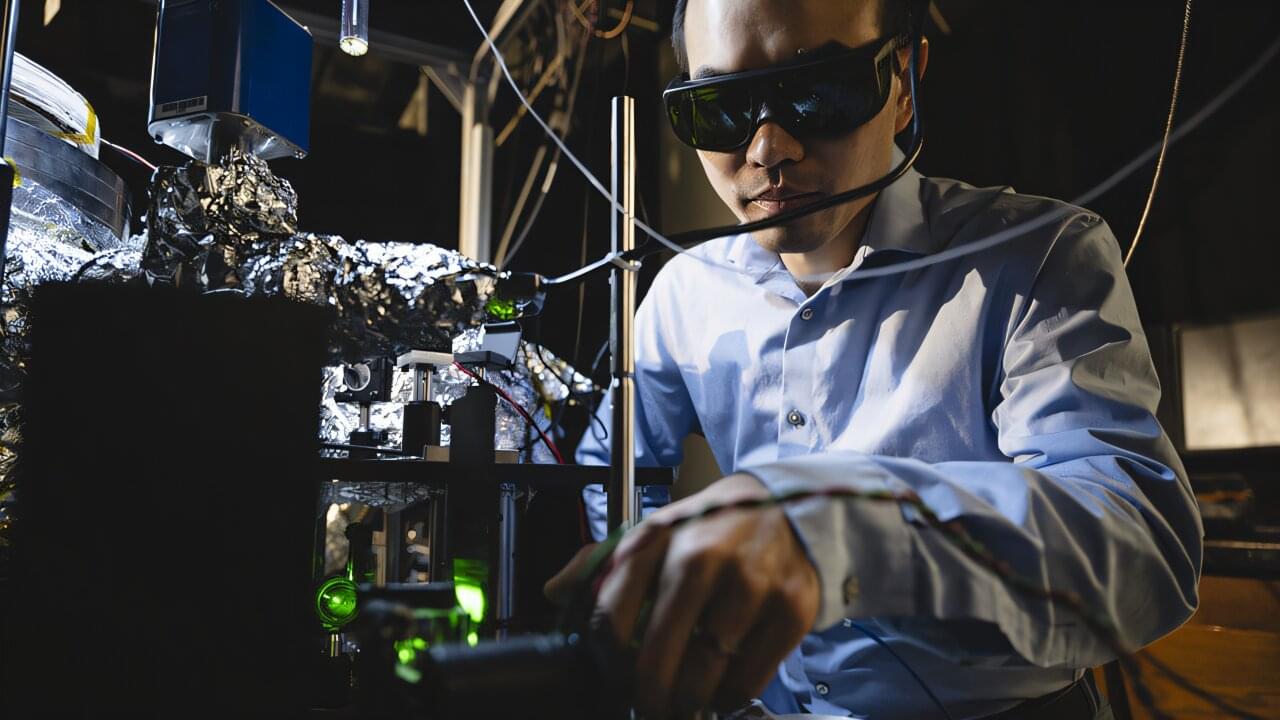
The same technology behind MRI images of injury or disease also powers nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, which is used to analyze biological molecules for research on diseases and therapeutics. While NMR spectroscopy produces valuable data about the structure of molecules, the resolution is too low to sense individual atoms.
Now, quantum researchers at Purdue University are advancing an approach that could improve the resolution of NMR spectroscopy to the atomic scale and may also have applications in developing quantum computing and quantum communications.
“Conventional NMR spectroscopy is limited to measuring large samples of molecules. We’re interested in developing technologies that can detect and analyze a single molecule,” said Tongcang Li, professor of physics and astronomy in the College of Science and of electrical and computer engineering in the College of Engineering.


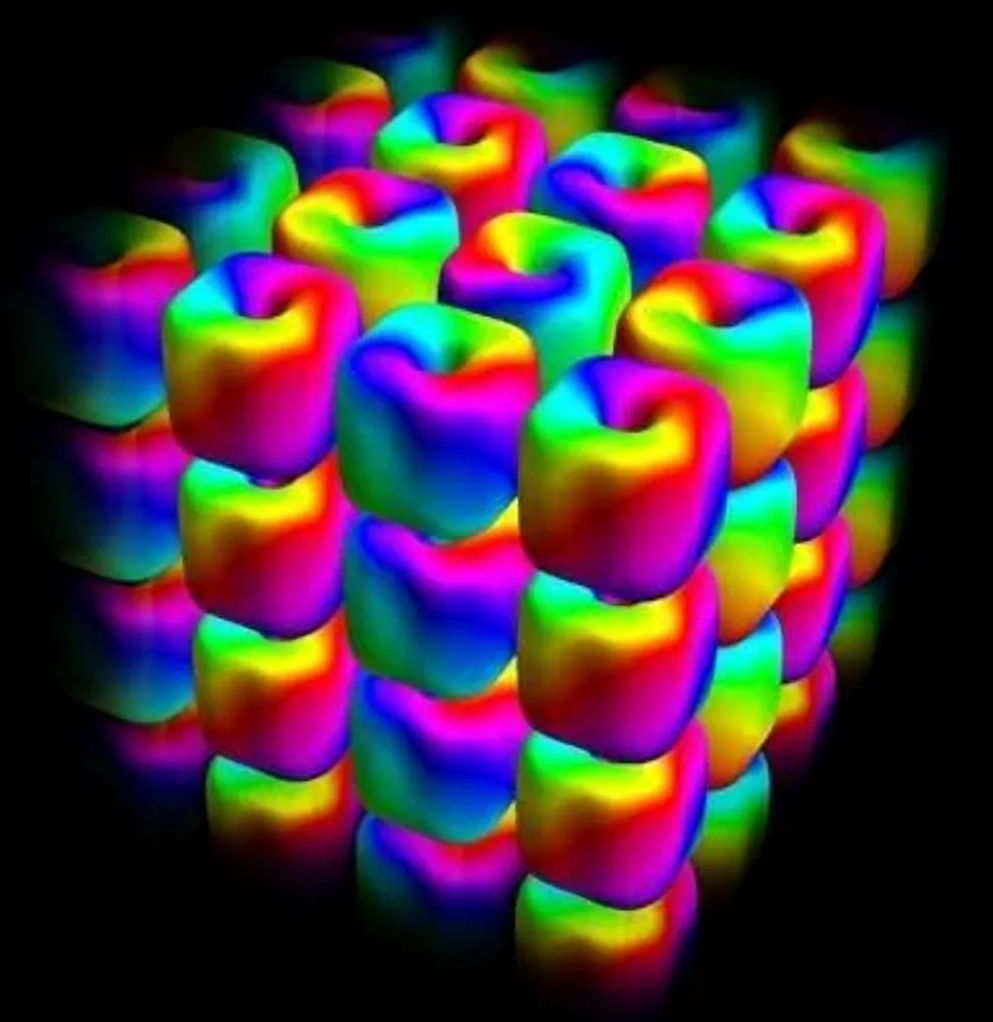
Researchers have developed a blueprint for weaving hopfions—complex, knot-like light structures—into repeating spacetime crystals. By exploiting two-color beams, they can generate ordered chains and lattices with tunable topology, potentially revolutionizing data storage, communications, and photonic processing.

One of Earth’s most unique geological formations is volcanoes, as they can be located either on land or underwater. They are even found on other planets. These formations come in all shapes and sizes, varying from shields to composites and cinder cones. When they erupt, they spew lava. As more and more of the world’s volcanoes are waking, they are also erupting pure technology. That’s right, within these unique geological formations, there are valuable elements that could revolutionize the renewable industry.
The world is gradually transitioning to renewable energy sources as alternatives to burning fossil fuels. This transition forms part of a greater goal to reduce the total greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. Unfortunately, the renewable technologies that we rely on to harness energy from renewable sources are not as environmentally friendly as we want to believe.
According to the SPIE Digital Library, renewable energy technology needs particular elements for production, and obtaining these elements has proven to be challenging. Without these elements, we cannot address other challenges that these technologies face, which are intermittency and storage. For example, solar panels and wind turbines are both dependent on specific weather conditions, which result in intermittency in power supply.
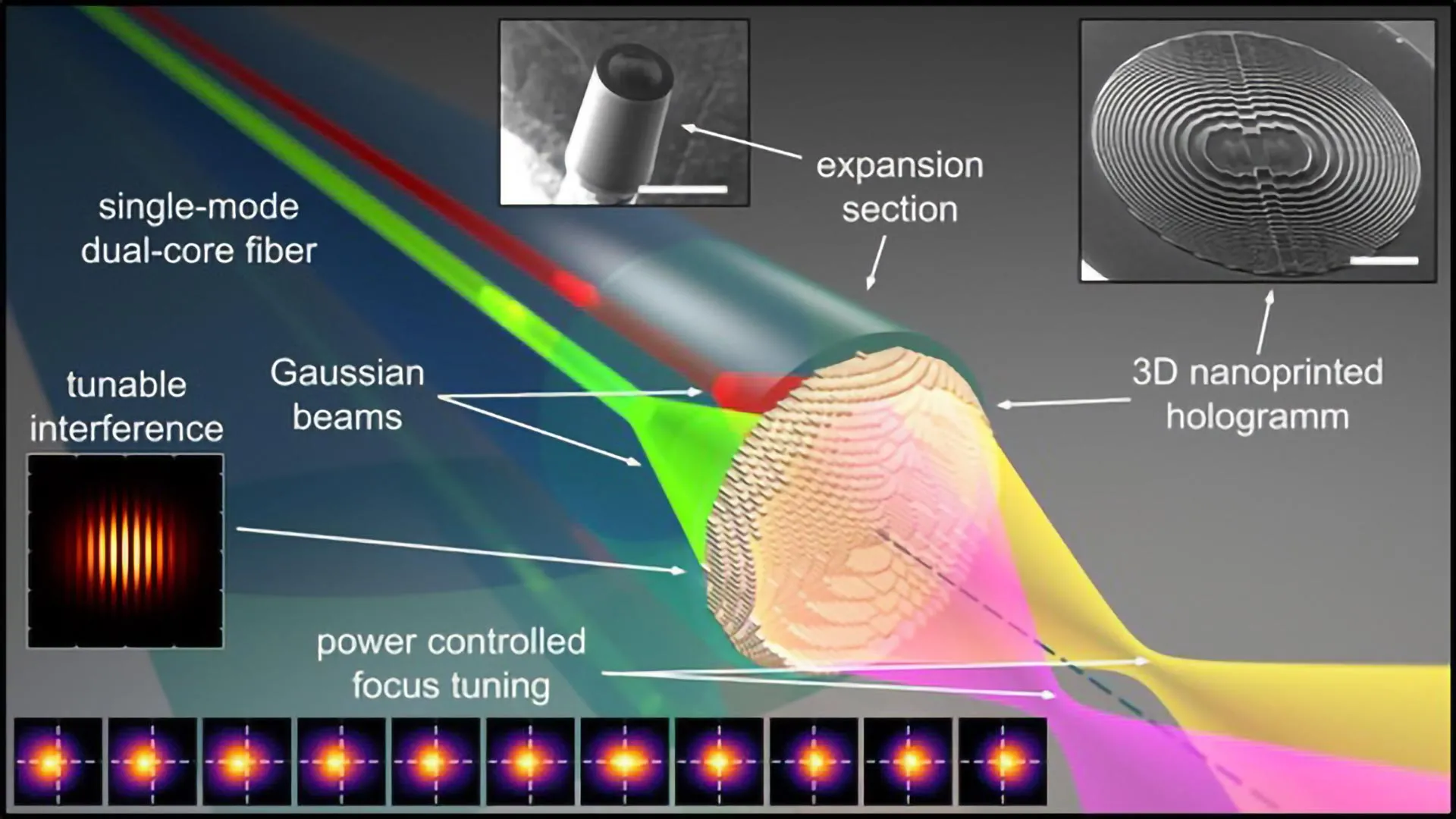
Researchers in Germany have unveiled the Metafiber, a breakthrough device that allows ultra-precise, rapid, and compact control of light focus directly within an optical fiber. Unlike traditional systems that rely on bulky moving parts, the Metafiber uses a tiny 3D nanoprinted hologram on a dual-core fiber to steer light by adjusting power between its cores. This enables seamless, continuous focus shifts over microns with excellent beam quality.