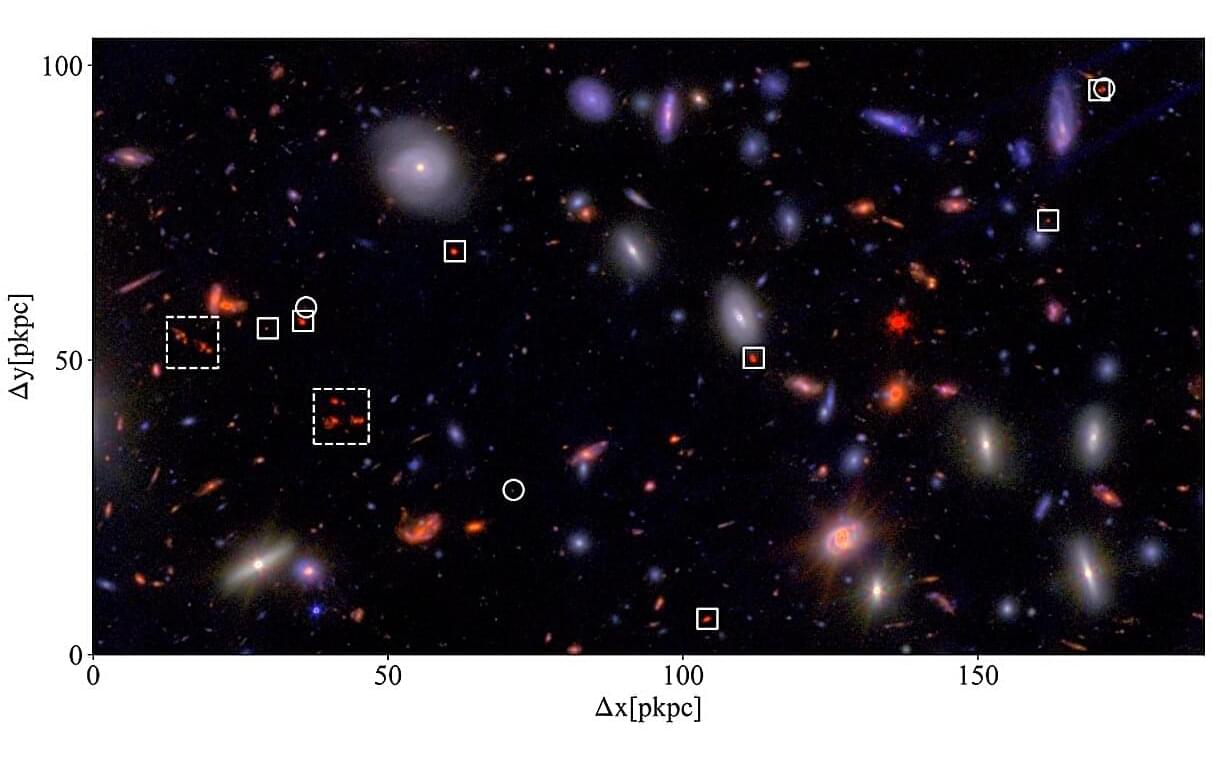
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of astronomers has performed deep and high spectral resolution imaging of a distant protocluster of galaxies, designated A2744-z7p9OD. Results of the new observations, published July 8 on the arXiv preprint server, shed more light on the properties of this protocluster, revealing that it hosts a remarkably evolved core.
Galaxy clusters are collections of hundreds to thousands of galaxies bound together by gravity. Such clusters are the most immense gravitationally bound structures in the universe, and therefore they could serve as excellent laboratories for studying galaxy evolution and cosmology.
Of special interest for astronomers are studies of protoclusters of galaxies—the progenitors of clusters. These objects, found at high redshifts (over 2.0), could provide essential information about the early phases of the universe.