Cytonics: Our mission is to rid the world of the pain, suffering, and debilitated quality of life caused by Osteoarthritis (OA).
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Astronomers find a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way that is much older than it should be
Cytonics: Our mission is to rid the world of the pain, suffering, and debilitated quality of life caused by Osteoarthritis (OA).
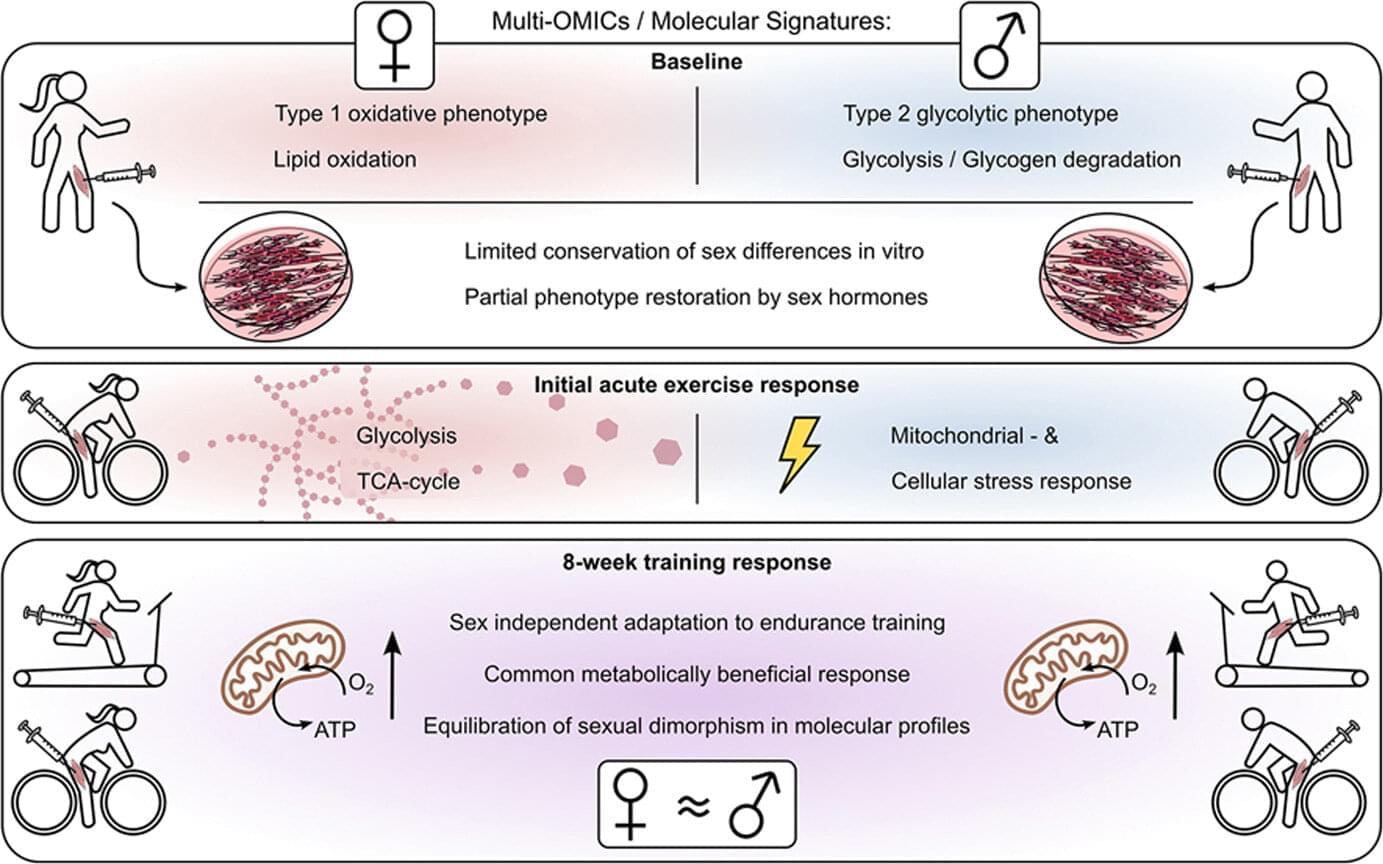
Metabolic differences in male and female muscles may explain diabetes variations
The skeletal muscles of men and women process glucose and fats in different ways. A study conducted by the University Hospital of Tübingen, the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases of Helmholtz Munich and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) e. V. provides the first comprehensive molecular analysis of these differences. The results, published in Molecular Metabolism, possibly give an explanation for why metabolic diseases such as diabetes manifest differently in women and men—and why they respond differently to physical activity.
Skeletal muscles are far more than just “movement driving motors.” They play a central role in glucose metabolism and therefore also in the development of type 2 diabetes. This is due to the fact that around 85% of insulin-dependent glucose uptake takes place in the muscles.
This means that if muscle cells react less sensitively to insulin, for example in the case of insulin resistance, glucose is less easily absorbed from the blood. This process is specifically counteracted by physical activity.

How Data Can Accelerate the Energy Transition
Using data and digitalization technologies could revolutionize industries and contribute to net-zero climate goals.
“Your move, Tesla” — Waymo Swallows Tesla Robotaxi Service Area In One Gulp
Questions to inspire discussion.
🤝 Q: What are the potential issues with the Uber-Lucid-Neuro robotaxi partnership? A: The partnership is a “cluster f waiting to happen” due to independent entities involved, which typically end in a “messy divorce”, making it potentially uncompetitive against fully integrated solutions like Tesla’s.
🗺️ Q: How does Tesla’s robotaxi service area expansion compare to Waymo’s? A: Tesla expanded its service area in 22 days, while Waymo’s first service area expansion in Austin, Texas took 4 months and 13 days, demonstrating Tesla’s faster and more aggressive approach to expansion.
Business Viability.
💼 Q: What concerns exist about the Uber-Lucid-Neuro robotaxi partnership’s business case? A: While considered a “breakout moment” for autonomous vehicles, the business case and return on investment for the service remain unclear, according to former Ford CEO Mark Fields.
🏭 Q: What manufacturing advantage does Tesla have in the robotaxi market? A: Tesla’s fully vertically integrated approach and ability to mass-manufacture Cyber Cabs at a scale of tens of thousands per month gives it a significant cost-per-mile advantage over competitors using more expensive, non-specialized vehicles. ## Key Insights.
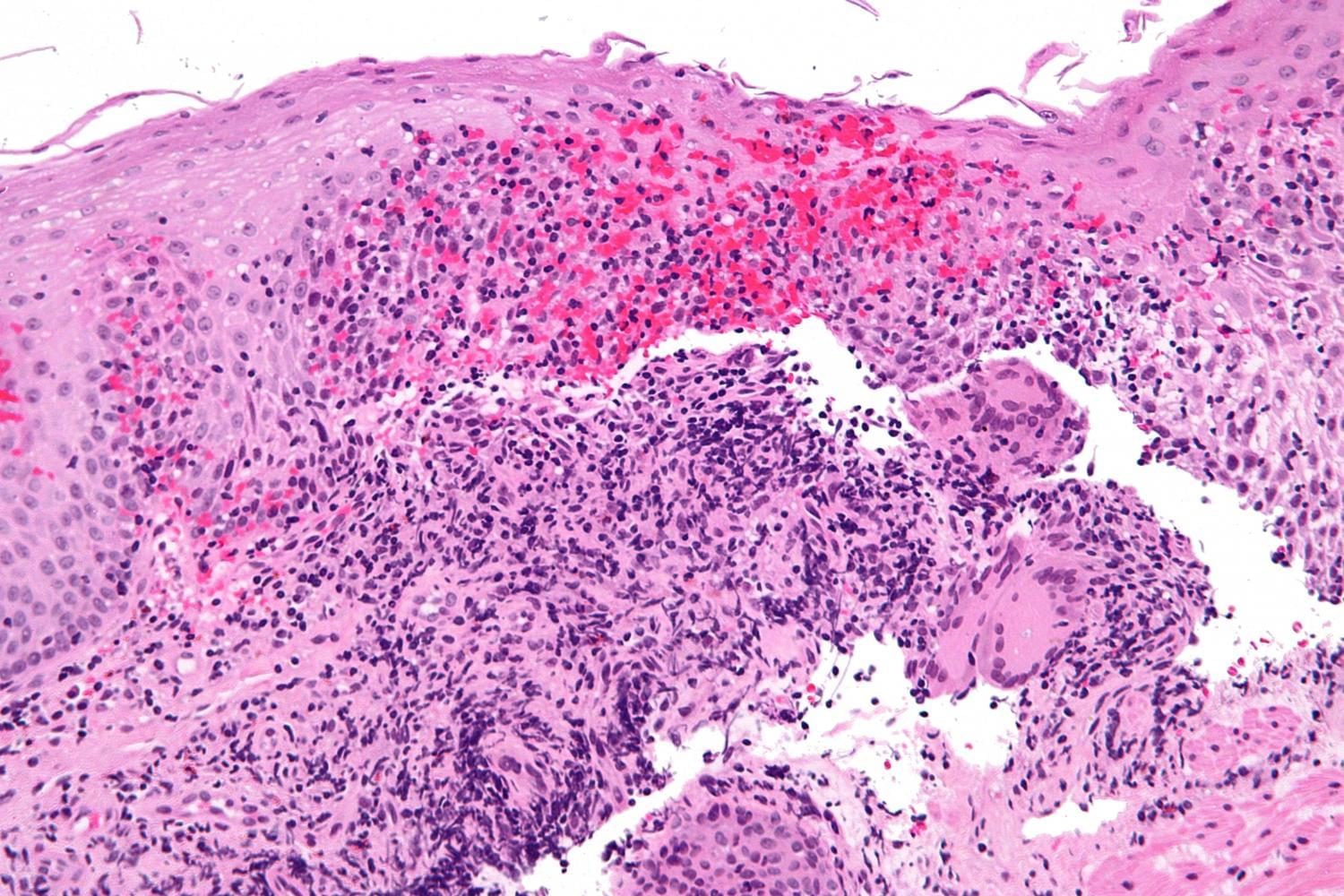
Guselkumab demonstrates superior efficacy in clinical trials, offering new hope to Crohn’s disease patients
In a major advance for patients with Crohn’s disease, a new study led by researchers at Mount Sinai Health System found that guselkumab, a medication with a mechanism of action that is new to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) treatment, outperformed an established standard of care in promoting intestinal healing and symptom relief.
These findings from two pivotal Phase III trials known as GALAXI 2 and 3, published in The Lancet, provided the basis for the recent Food and Drug Administration approval of guselkumab (brand name Tremfya) for the treatment of moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease.
Crohn’s disease affects roughly 780,000 people in the United States and often requires a lifetime of management. Despite numerous available biologic medications, many patients fail to achieve sustained remission. Guselkumab blocks the interleukin-23 (IL-23) pathway, a key driver of chronic intestinal inflammation.


MIT’s new AI can teach itself to control robots by watching the world through their eyes — it only needs a single camera
This framework is made up of two key components. The first is a deep-learning model that essentially allows the robot to determine where it and its appendages are in 3-dimensional space. This allows it to predict how its position will change as specific movement commands are executed. The second is a machine-learning program that translates generic movement commands into code a robot can understand and execute.
The team tested the new training and control paradigm by benchmarking its effectiveness against traditional camera-based control methods. The Jacobian field solution surpassed those existing 2D control systems in accuracy — especially when the team introduced visual occlusion that caused the older methods to enter a fail state. Machines using the team’s method, however, successfully created navigable 3D maps even when scenes were partially occluded with random clutter.
Once the scientists developed the framework, it was then applied to various robots with widely varying architectures. The end result was a control program that requires no further human intervention to train and operate robots using only a single video camera.
Are sand batteries the future of clean energy storage?
Sand batteries are emerging as a viable alternative to lithium-ion for thermal energy storage, capable of holding heat with minimal loss.