Researchers detail NANOREMOTE, a Windows backdoor using Google Drive API for covert control and data theft.





Researchers at UCLA have developed an artificial intelligence tool that can use electronic health records to identify patients with undiagnosed Alzheimer’s disease, addressing a critical gap in Alzheimer’s care: significant underdiagnosis, particularly among underrepresented communities.
The study appears in the journal npj Digital Medicine.
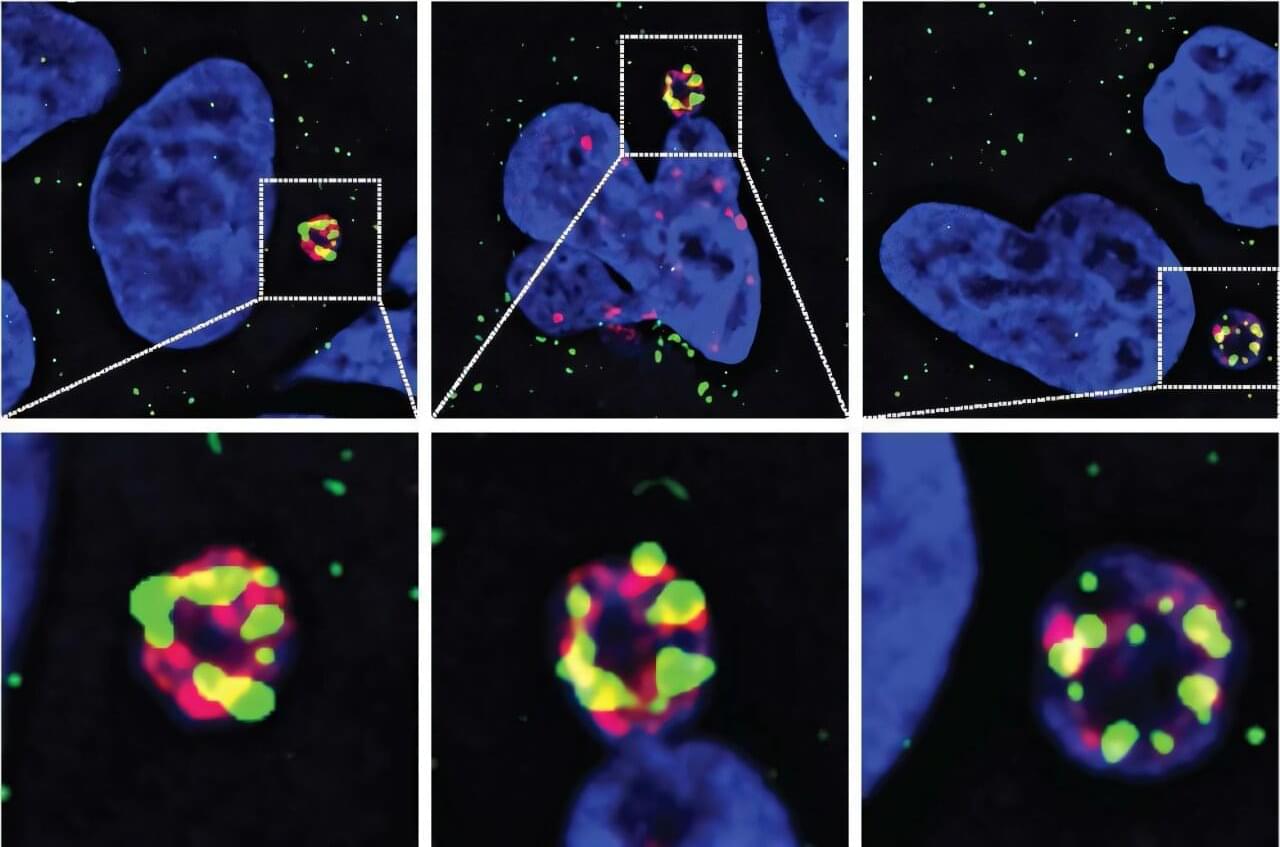
University of California San Diego researchers have discovered the enzyme responsible for chromothripsis, a process in which a single chromosome is shattered into pieces and rearranged in a scrambled order, allowing cancer cells to rapidly evolve and become resistant to treatment.
Since its discovery more than a decade ago, chromothripsis has emerged as a major driver of cancer progression and treatment resistance, but scientists haven’t learned what causes it. Now, UC San Diego scientists have solved this longstanding mystery in cancer biology, opening up new possibilities for treating the most aggressive cancers. The results are published in Science.

Researchers have made a major advance in quantum computing with a new device that is nearly 100 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair.
Published in the journal Nature Communications, the breakthrough optical phase modulators could help unlock much larger quantum computers by enabling efficient control of lasers required to operate thousands or even millions of qubits—the basic units of quantum information.
Critically, the team of scientists have developed these devices using scalable manufacturing, avoiding complex, custom builds in favor of those used to make the same technology behind processors already found in computers, phones, vehicles, home appliances—virtually everything powered by electricity (even toasters).
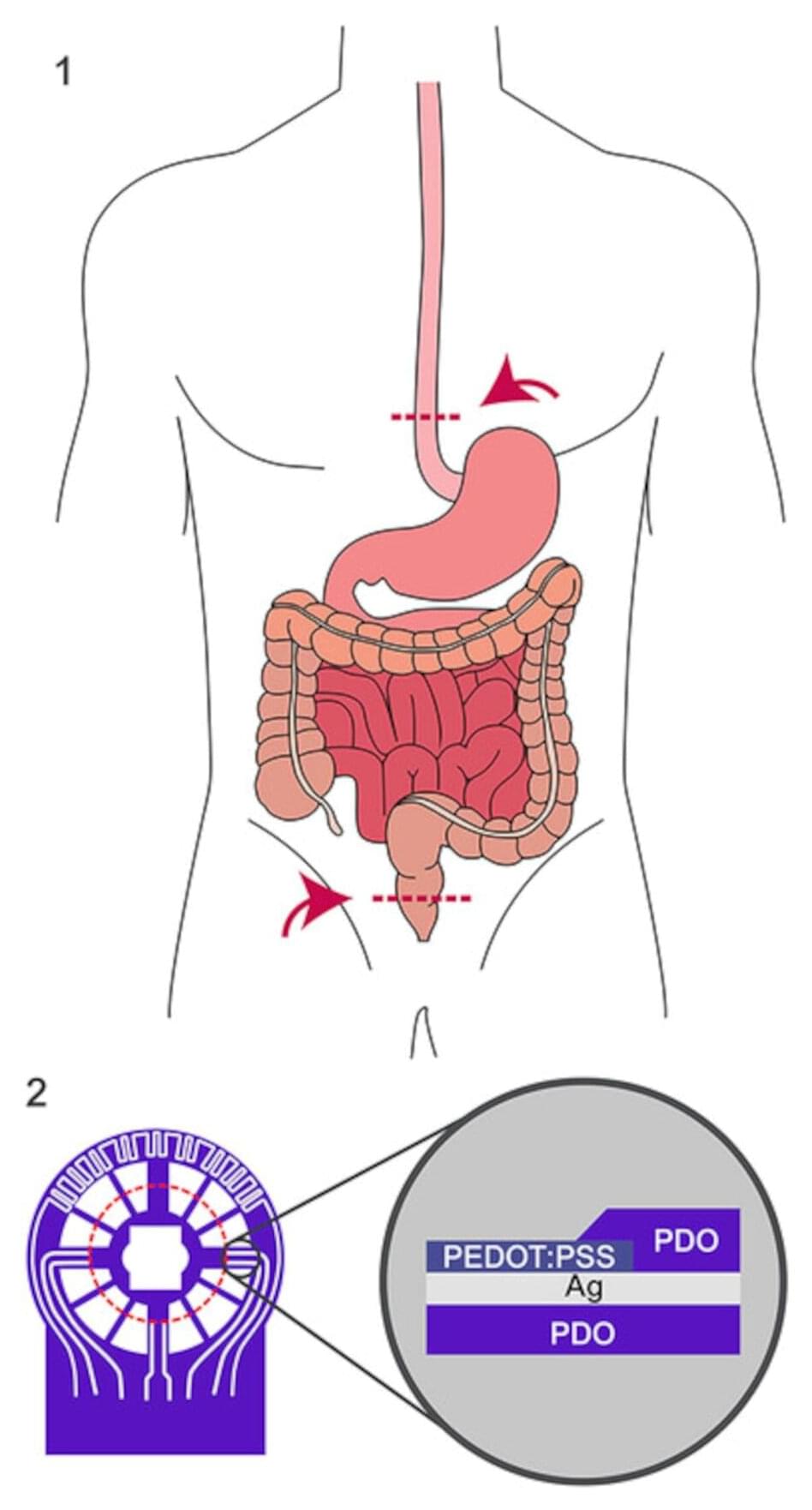
An interdisciplinary research team from Dresden University of Technology (TUD), Rostock University Medical Center (UMR) and Dresden University Hospital has developed an innovative, implantable and fully absorbable sensor film. For the first time, it enables reliable early detection of circulatory disorders in intestinal anastomoses—one of the riskiest surgical procedures in the abdominal cavity. The results have now been presented in the journal Advanced Science.
Intestinal anastomoses, which is the surgical connection of two sections of the intestine after the removal of diseased tissue, carry a considerable risk of post-operative complications. In particular, circulatory disorders or immunological reactions can lead to serious consequential damage or even death within a short period of time. However, direct monitoring of the suture site has not been possible until now, which often entails corresponding risks for patients as well as considerable costs due to follow-up operations and long hospital stays.
Based on this specific medical need, the interdisciplinary network of the Else Kröner Fresenius Center (EKFZ) for Digital Health at TUD and Dresden University Hospital brought together key experts from Dresden and Rostock.

After reviewing thousands of benchmarks used in AI development, a Stanford team found that 5% could have serious flaws with far-reaching ramifications.
Each time an AI researcher trains a new model to understand language, recognize images, or solve a medical riddle, one big question remains: Is this model better than what went before? To answer that question, AI researchers rely on batteries of benchmarks, or tests to measure and assess a new model’s capabilities. Benchmark scores can make or break a model.
But there are tens of thousands of benchmarks spread across several datasets. Which one should developers use, and are all of equal worth?

Compelling evidence that the structure of matter surrounding supermassive black holes has changed over cosmic time has been uncovered by an international team of astronomers.
If true, the research led by the National Observatory of Athens and published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society would challenge a fundamental law which has existed for almost five decades.