The laws of thermodynamics don’t accurately account for the complex processes in living cells – do we need a new one to accurately measure the ways living systems are out of equilibrium?
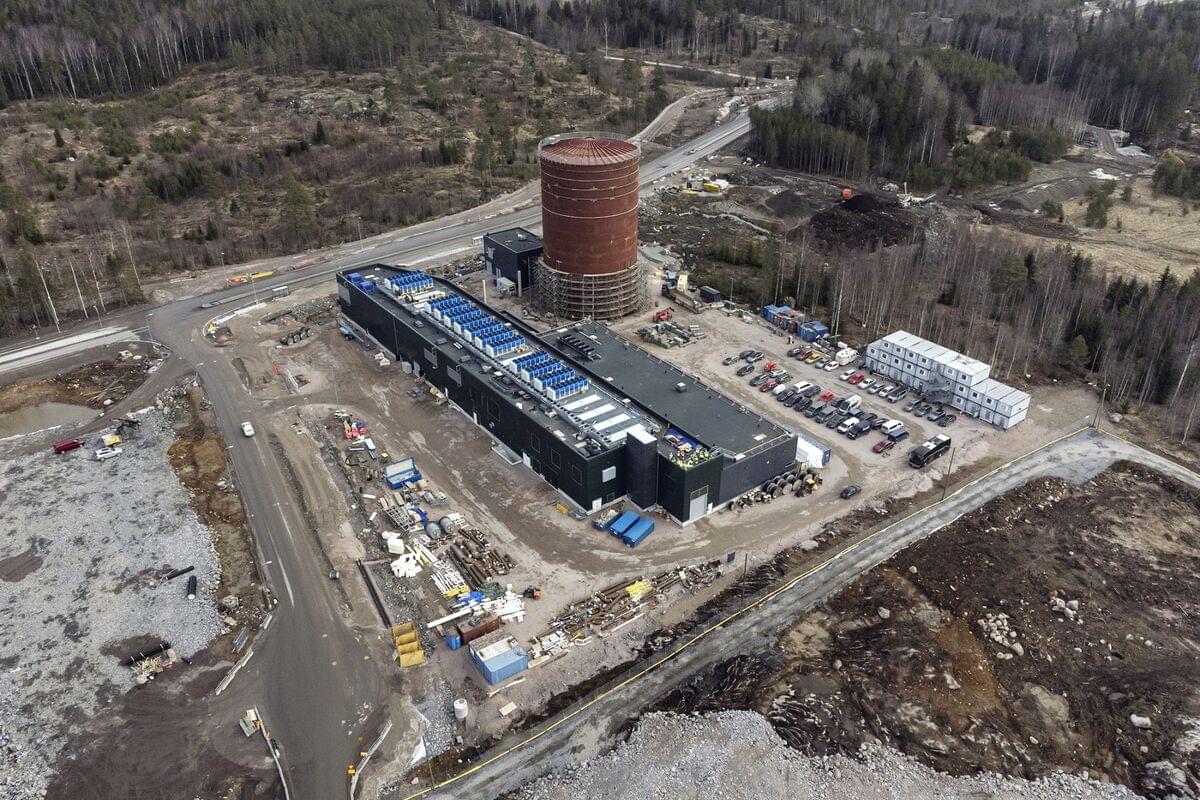


When Finnish engineer Ari Kurvi takes a hot shower or turns up the thermostat in his apartment, he’s tapping into waste heat generated by a 75-megawatt data center 5 kilometers away. As its computer servers churn through terabytes of digital information to support video calls, car navigation systems and web searches, an elaborate system of pipes and pumps harvests the cast-off energy and feeds it to homes in the town of Mantsala in southern Finland.
Since it began operation about a decade ago, the data center has provided heat for the town. Last year, it heated the equivalent of 2,500 homes, about two-thirds of Mantsala’s needs, cutting energy costs for residents and helping to blunt the environmental downsides associated with power-hungry computing infrastructure. Some of the world’s biggest tech companies are now embracing heat recovery from data centers in an effort to become more sustainable.
Kurvi is one of the pioneers of this emerging technology: As an engineer and project manager for Hewlett Packard starting in the 1980s, he spent years working with humming stacks of hardware in hot server rooms during the freezing Finnish winters. That made him think that there must be a good way to put that wasted heat to use.
By pairing computer processing facilities with district heating systems, countries like Finland and Sweden are trying to limit their environmental downsides.

Lymphopenia represents a critical, widely unaddressed problem. Modern oncology regularly intervenes to reverse anemia or neutropenia, because decades of investment created drugs capable of restoring those cell populations. But when the lymphocyte compartment collapses, physicians have had no approved way to rebuild it. As a result, the most important immunologic marker in cancer care has remained largely unacted upon. The decline of the body’s cancer-killing lymphocytes has been observed, documented, and then largely ignored. Oncology is entering a new phase. The field is beginning to recognize that defeating cancer is not merely about targeting malignant cells; it is about ensuring that the immune system remains intact enough to participate in that fight…
…Once the lymphocyte compartment collapses, no drug can compensate.
The warning has been visible for decades, printed in plain text on every CBC panel run for every cancer patient in the country. If clinicians measure it, if regulators recognize it, and if the system supports restoring it, patient survival can change at scale.
Patrick Soon-Shiong, Chairman of Chan Soon-Shiong Family Foundation, Executive Chairman at ImmunityBio, and Executive Chairman of the Los Angeles Times, shared a post on X:
Every cancer patient undergoes a complete blood count. Within that routine report is a measurement that almost never makes its way into clinical conversations, yet it carries independent prognostic weight that often exceeds imaging, molecular markers, or tumor stage. That measurement is the absolute lymphocyte count, the readout of the circulating natural killer cells and T cells responsible for controlling malignant growth. When that number drops below 1,000 cells per microliter, the body enters a state of immune failure known as lymphopenia. In that state, the cellular machinery required to restrain cancer is no longer available.

This accomplishment breaks the previous record of 48 qubits set by Jülich scientists in 2019 on Japan’s K computer. The new result highlights the extraordinary capabilities of JUPITER and provides a powerful testbed for exploring and validating quantum algorithms.
Simulating quantum computers is essential for advancing future quantum technologies. These simulations let researchers check experimental findings and experiment with new algorithmic approaches long before quantum hardware becomes advanced enough to run them directly. Key examples include the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE), which can analyze molecules and materials, and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), used to improve decision-making in fields such as logistics, finance, and artificial intelligence.
Recreating a quantum computer on conventional systems is extremely demanding. As the number of qubits grows, the number of possible quantum states rises at an exponential rate. Each added qubit doubles the amount of computing power and memory required.
Although a typical laptop can still simulate around 30 qubits, reaching 50 qubits requires about 2 petabytes of memory, which is roughly two million gigabytes. ‘Only the world’s largest supercomputers currently offer that much,’ says Prof. Kristel Michielsen, Director at the Jülich Supercomputing Centre. ‘This use case illustrates how closely progress in high-performance computing and quantum research are intertwined today.’
The simulation replicates the intricate quantum physics of a real processor in full detail. Every operation – such as applying a quantum gate – affects more than 2 quadrillion complex numerical values, a ‘2’ with 15 zeros. These values must be synchronized across thousands of computing nodes in order to precisely replicate the functioning of a real quantum processor.
The JUPITER supercomputer set a new milestone by simulating 50 qubits. New memory and compression innovations made this breakthrough possible. A team from the Jülich Supercomputing Centre, working with NVIDIA specialists, has achieved a major milestone in quantum research. For the first time, they successfully simulated a universal quantum computer with 50 qubits, using JUPITER, Europe’s first exascale supercomputer, which began operation at Forschungszentrum Jülich in September.
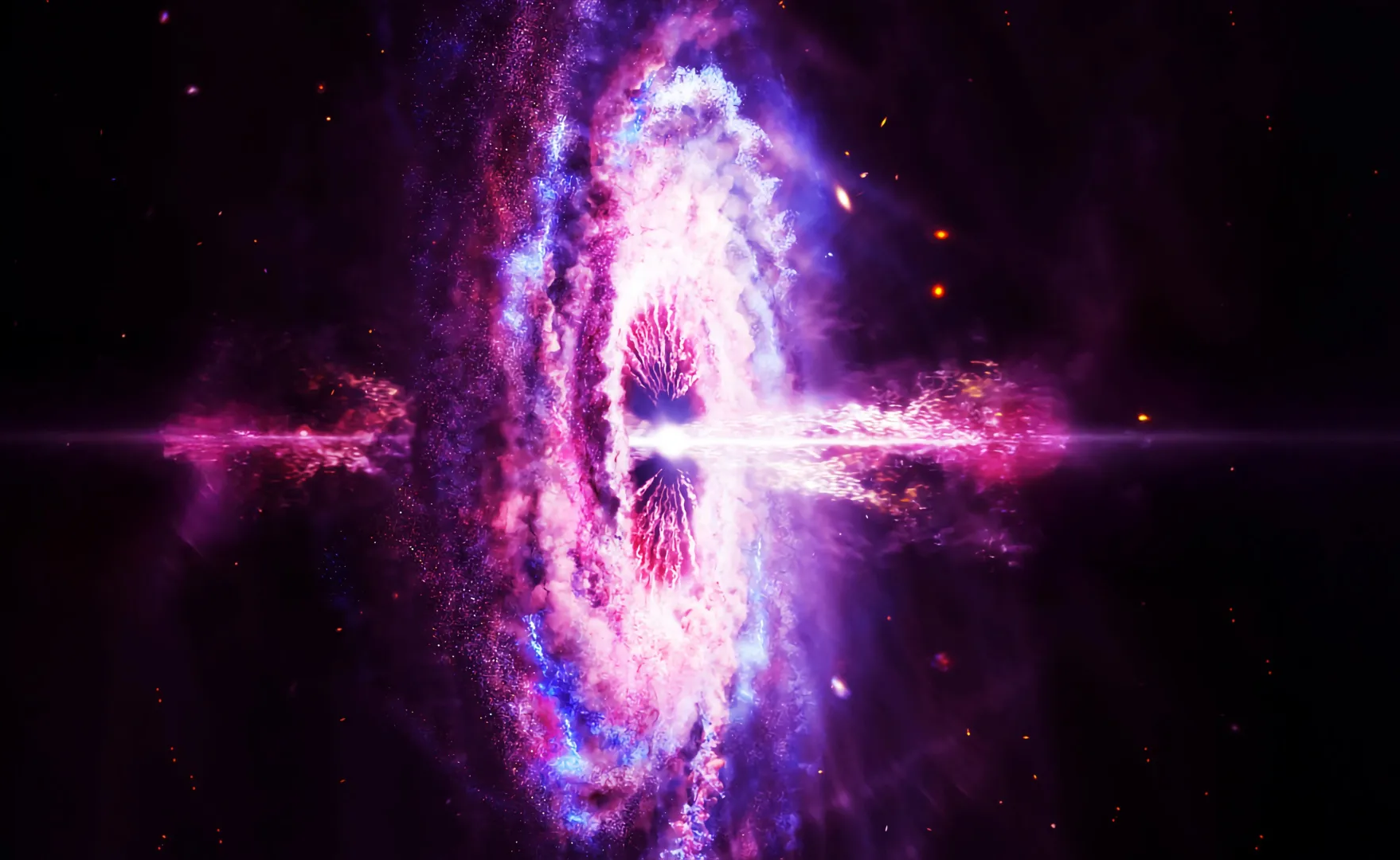



LHAASO has traced the mysterious cosmic ray “knee” to powerful micro-quasars firing ultra-energetic particles across the galaxy. LHAASO has uncovered that micro-quasars, black holes feeding on companion stars, are powerful PeV particle accelerators. Their jets produce ultra-high-energy gamma rays and protons that exceed long-held expectations. Precise cosmic-ray measurements reveal a new high-energy component, suggesting multiple sources within the Milky Way. These findings finally tie the “knee” structure to black hole jet systems.
Milestone results released by the Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) on November 16 have finally clarified a decades-old puzzle in astrophysics: the unusual drop in cosmic ray counts above 3 PeV that produces what scientists call the “knee” in the cosmic ray energy spectrum.
The cause of this steep decline has remained mysterious since it was first identified nearly 70 years ago. Researchers long suspected that the feature reflects the highest energies that cosmic ray sources can reach, marking a shift in the spectrum from one power-law behavior to another.
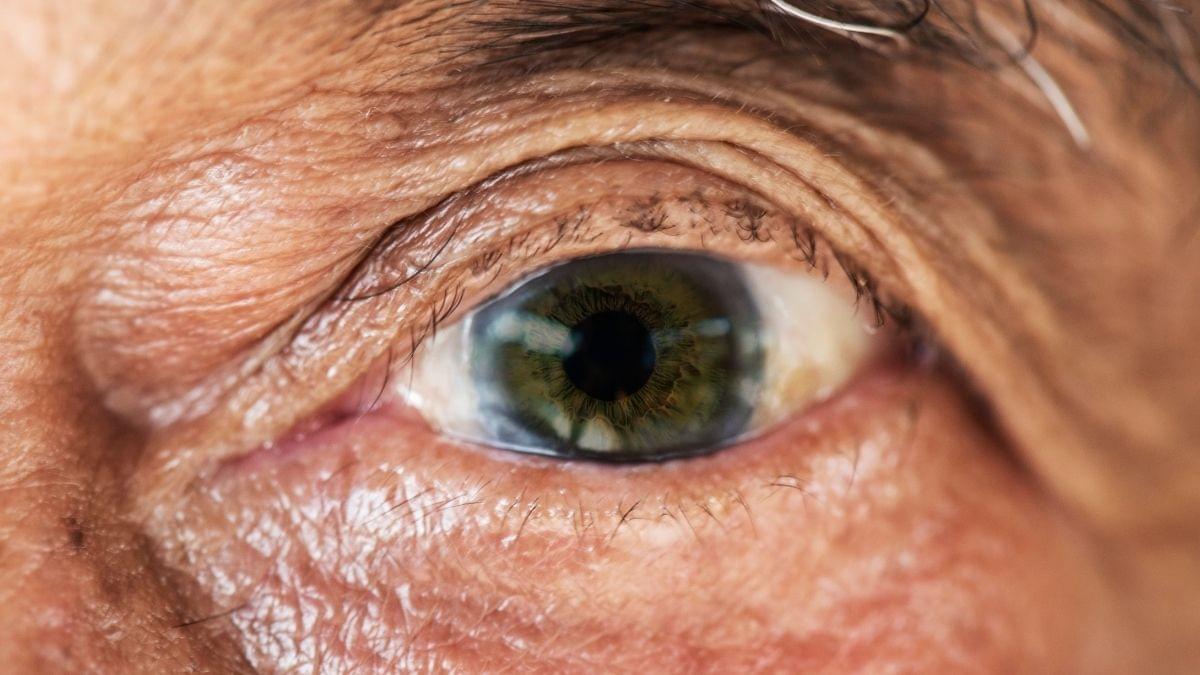
Taking a photo of a friend? You’ve probably got their face centered and focused. Driving down a highway? Eyes on the road.
But for millions of adults with age-related macular degeneration, that crucial, central field of sight is blurred beyond recognition. Current treatments can only slow its progression or augment vision, but the blur will usually continue to worsen.
A recent clinical trial of a treatment based on stem cell transplants has found the procedure may be able to safely reverse the cumulative damage to the hard-working macula – that part of the retina responsible for all you see directly in front of you.
