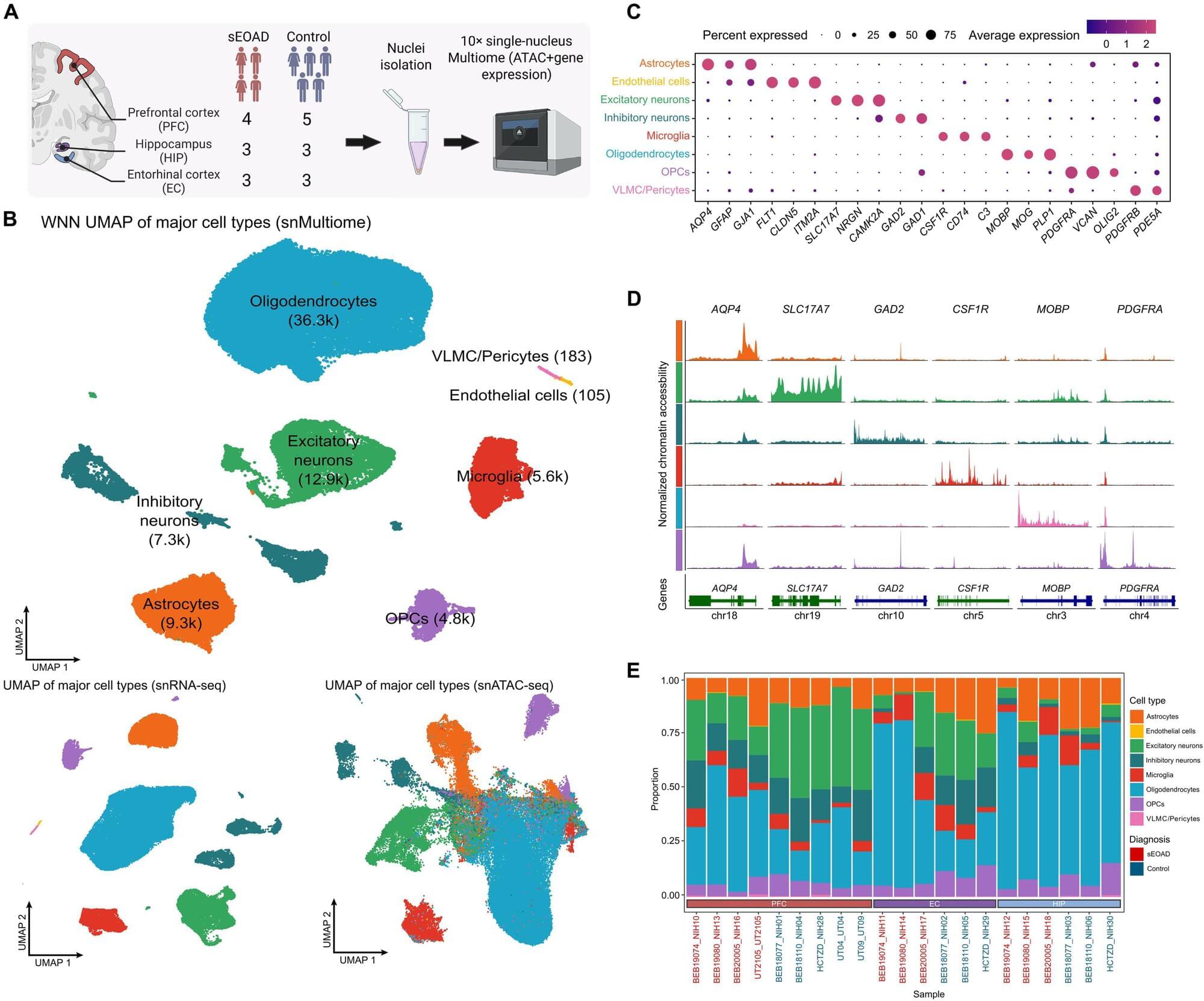
A new study led by researchers at UTHealth Houston investigated both gene expression and regulation at single cell levels to reveal disruptions in gene function in three brain regions of patients with sporadic early onset Alzheimer’s disease.
The findings are published in Science Advances.
Only about 5% to 10% of patients with Alzheimer’s disease are younger than 65. Of those patients, 10% have mutations in the APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 genes, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The other 90% of these cases are classified as sporadic early onset Alzheimer’s, a rare and aggressive form of the disease that begins before age 65. The genetic tie in early onset Alzheimer’s is largely unidentified, representing a significant but understudied population.