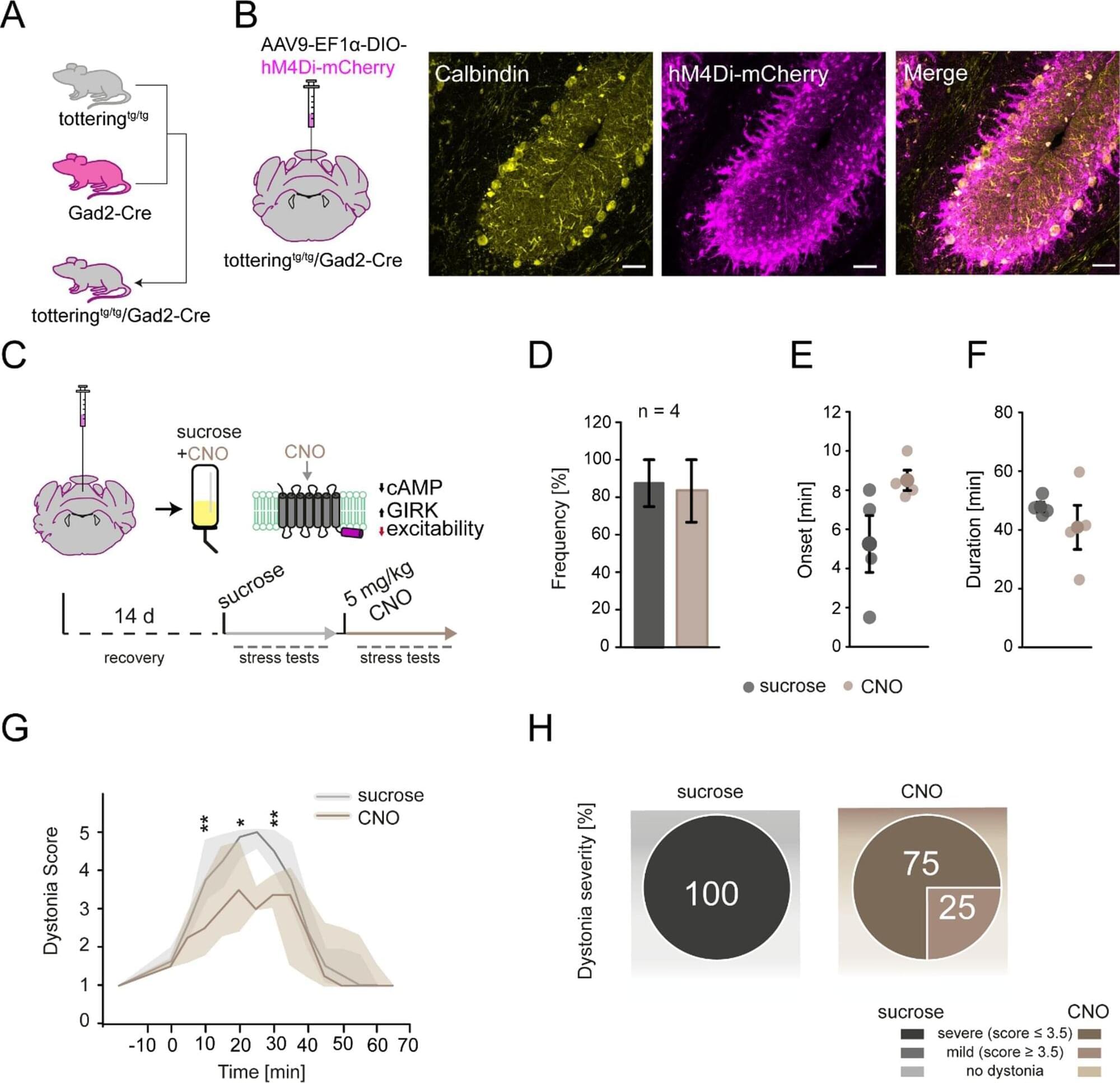
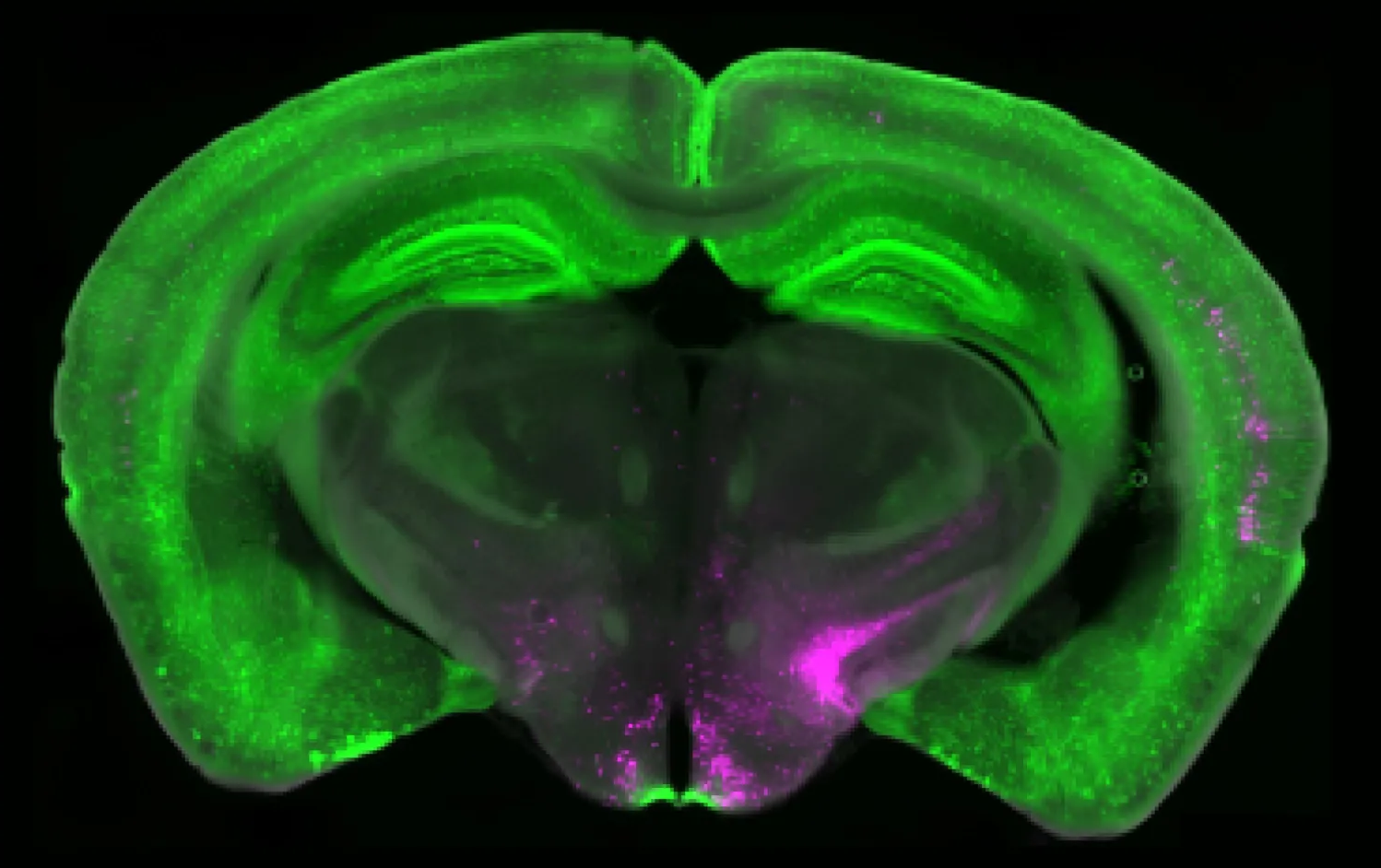
Researchers at Ruhr University Bochum, Germany, identified a receptor that plays a crucial role in stress-induced motor incoordination associated with ataxias. These hereditary motor disorders have long been linked to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine.
The team, led by Dr. Pauline Bohne and Professor Melanie Mark from the Behavioral Neurobiology Working Group in Bochum, has now shown that the α1D norepinephrine receptor in the cerebellum is responsible for the symptoms. The team published these findings in the journal Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences on October 6, 2025.
People with ataxia experience recurring episodes of motor incoordination, also known as dystonia. These phases are triggered by various factors, such as physical or emotional stress, fever, alcohol, or caffeine. The episodes are triggered by the release of norepinephrine in the cerebellum, which is the most important brain region for coordinating movement. Currently, there is no cure for ataxia. Therefore, researchers want to gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms to find new treatment approaches.