Connectionism eliminativism and the future of folk psychology.
Shared with Dropbox.


In the age of rapid technological advancements, a new player has emerged on the scene, promising to revolutionize the way we transmit data wirelessly. Li-Fi, or Light Fidelity, is a cutting-edge technology that employs visible light to transmit information, offering an innovative alternative to traditional radio frequency-based wireless communication systems.
The IEEE published the 802.11bb standard for light-based networking in July 2023, an extension of the Wi-Fi specification enabling wireless networking using visible and infrared light rather than the radio spectrum. The standard outlines adjustments to the physical and medium access control layers, allowing wireless networking through light source modulation imperceptible to the human eye.
The Li-Fi specification mandates bidirectional transmission within the 800nm to 1,000nm electromagnetic spectrum range, ensuring a minimum throughput of 10 Mb/s and a maximum of 9.6 Gb/s at the MAC data service access point. By comparison, Wi-Fi operates within wavelengths of 120mm (2.4 GHz) and 60mm (5 GHz), with speeds that vary across versions, including Wi-Fi 6, which reaches up to 9.6 Gb/s, akin to Li-Fi capabilities.


AI with image recognition opens up new possibilities for designers and developers to quickly turn an idea into a prototype. There are several approaches based on OpenAI technology.
The introduction of multimodal capabilities in GPT-4 has laid an important foundation for future software development. Thanks to GPT-4V, the AI model accepts both text and images as input. This allows it to generate working code from screenshots or rudimentary drawings.
Recently, several products have been developed around this idea. The collaborative whiteboard tool tldraw has set up a playground on the website makereal.tldraw.com, where mockups of website elements can be created in the browser. GPT-4V converts these into code using the OpenAI API. A separate API key is required.

Insider Brief.
Scientists report on a new approach that can significantly improve the study and understanding of entanglement in quantum materials.
The researchers were led by Peter Zoller at the University of Innsbruck and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information of the Austrian Academy of Sciences.

Will artificial intelligence serve humanity — or will it spawn a new species of conscious digital beings with their own agenda?
It’s a question that has sparked scores of science-fiction plots, from “Colossus: The Forbin Project” in 1970, to “The Matrix” in 1999, to this year’s big-budget tale about AI vs. humans, “The Creator.”
The same question has also been lurking behind the OpenAI leadership struggle — in which CEO Sam Altman won out over the nonprofit board members who fired him a week earlier.

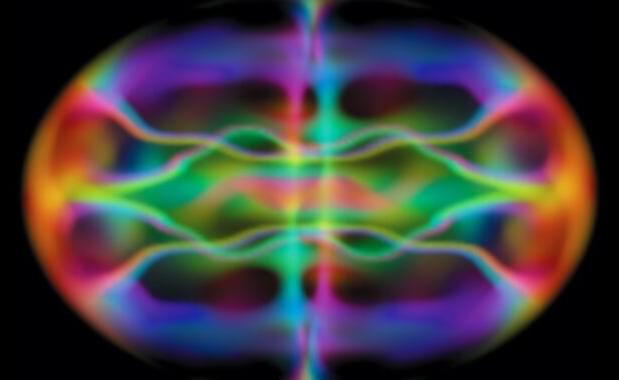
In the basement of Kirchhoff-Institut für Physik in Germany, researchers have been simulating the Universe as it might have existed shortly after the Big Bang. They have created a tabletop quantum field simulation that involves using magnets and lasers to control a sample of potassium-39 atoms that is held close to absolute zero. They then use equations to translate the results at this small scale to explore possible features of the early Universe.
The work done so far shows that it’s possible to simulate a Universe with a different curvature. In a positively curved universe, if you travel in any direction in a straight line, you will come back to where you started. In a negatively curved universe, space is bent in a saddle shape. The Universe is currently flat or nearly flat, according to Marius Sparn, a PhD student at Kirchhoff-Institut für Physik. But at the beginning of its existence, it might have been more positively or negatively curved.
New SpaceX renderings reveal that the design of the company’s Starship lunar lander has evolved significantly. We analyze the numerous improvements to the vehicle, including stretched fuel tanks, rotating solar arrays, and a new docking port.