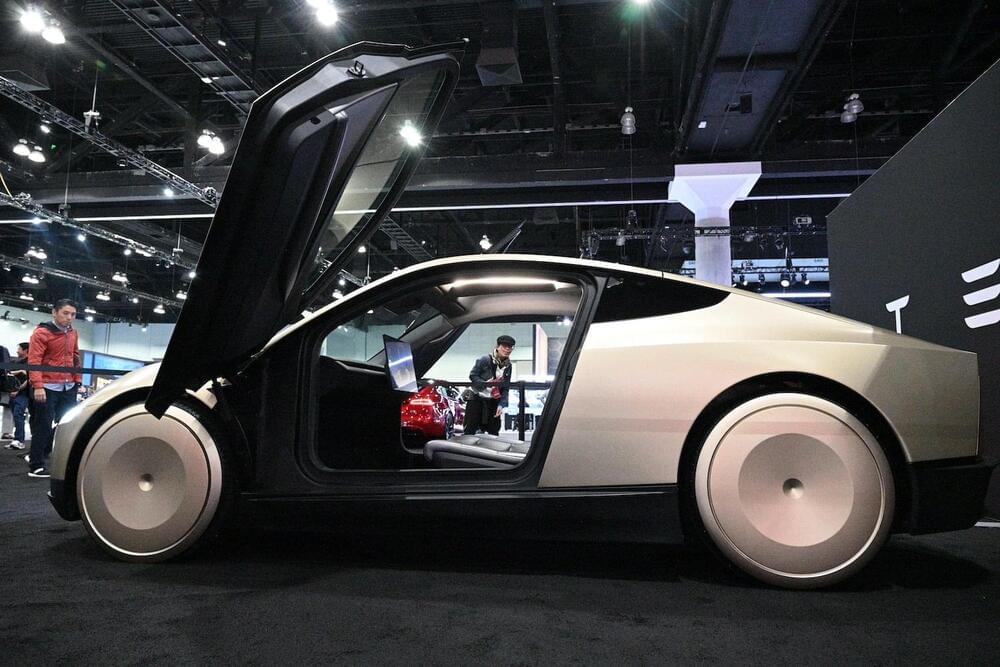
Elon Musk’s ‘fully autonomous’ cars will, like other robotaxi vehicles, rely on remote human pilots.
Summary: Researchers identified specific plant compounds that provide antioxidant and neuroprotective effects, contributing to brain health beyond basic nutrition. By analyzing plant-based foods like lemon balm, sage, and elderberry, scientists linked compounds such as phenolics and terpenes to benefits like reducing oxidative stress and scavenging harmful reactive species.
Quercetin-rich foods, such as Queen Garnet plum and clove, showed strong potential to prevent neuron-like cell damage. This study sheds light on how plant-based diets and supplements could support brain health and manage neuroinflammation-related conditions.
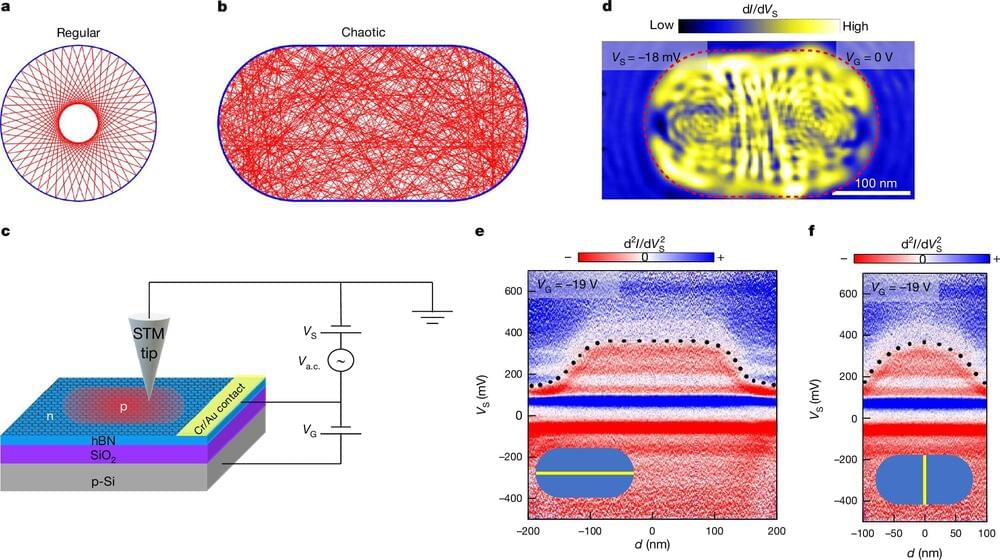
Unveiling Quantum Scars: A Window into Chaos in Graphene Quantum Dots.
In the realm of quantum physics, certain phenomena challenge our understanding of chaos and order.
Patterns in chaos have been proven, in the incredibly tiny quantum realm, by an international team co-led by UC Santa Cruz physicist Jairo Velasco, Jr. In a new paper published on November 27 in Nature, the researchers detail an experiment that confirms a theory first put forth 40 years ago stating that electrons confined in quantum space would move along common paths rather than producing a chaotic jumble of trajectories.
Electrons exhibit both particle and wave-like properties—they don’t simply roll like a ball. Electrons behave in ways that are often counterintuitive, and under certain conditions, their waves can interfere with each other in a way that concentrates their movement into certain patterns. The physicists call these common paths “unique closed orbits.”
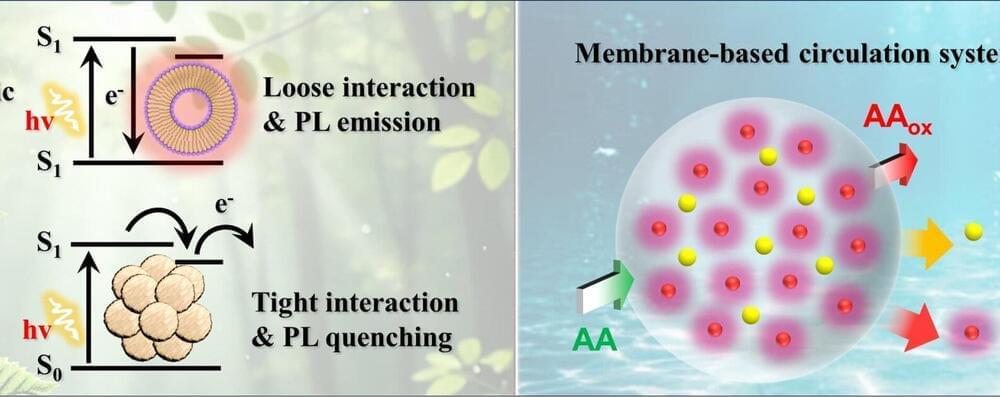
Researchers have successfully developed a supramolecular fluorophore nanocomposite fabrication technology using nanomaterials and constructed a sustainable solar organic biohydrogen production system.
The research team used the good nanosurface adsorption properties of tannic acid-based metal-polyphenol polymers to control the self-assembly and optical properties of fluorescent dyes while also identifying the photoexcitation and electron transfer mechanisms. Based on these findings, he implemented a solar-based biohydrogen production system using bacteria with hydrogenase enzymes.
The findings are published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition. The joint research was led by Professor Hyojung Cha at the Department of Hydrogen and Renewable Energy, Kyungpook National University and Professor Chiyoung Park at the Department of Energy Science and Engineering, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology.
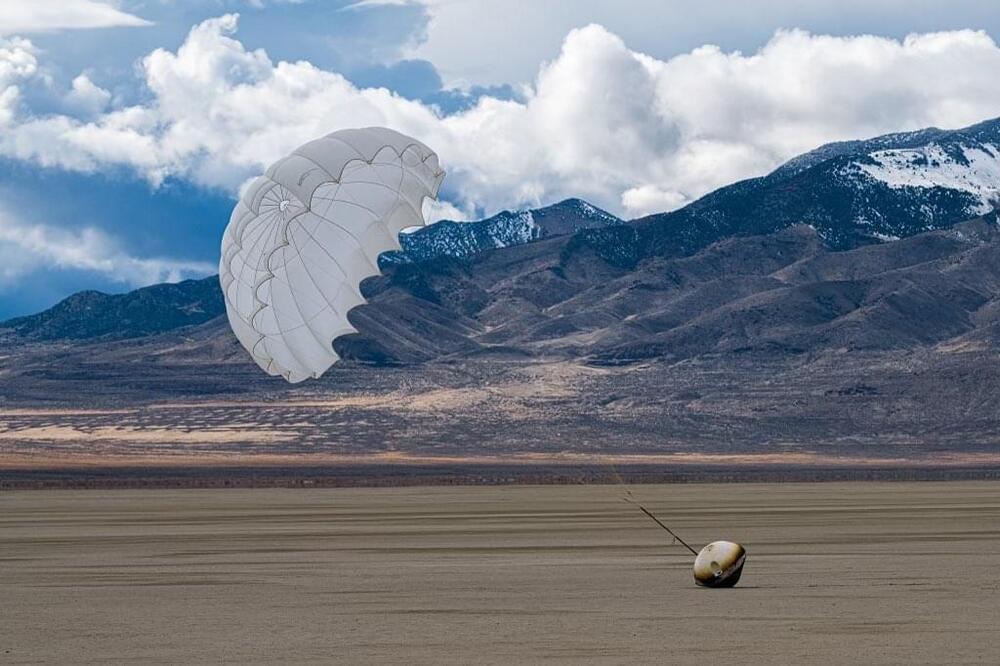
WASHINGTON — Varda Space Industries secured a $48 million contract from the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory to test military payloads on the company’s reentry capsules.
A California-based startup focused on in-space manufacturing, Varda Space developed a factory-in-orbit spacecraft — a compact, 120-kilogram satellite engineered to produce high-value materials such as pharmaceuticals in zero-gravity conditions. The materials are returned to Earth in a capsule built with advanced thermal protection materials developed by NASA to withstand reentry.
The four-year deal with AFRL, announced on Nov. 26, leverages Varda’s W-Series reentry capsules as platforms to test payloads at hypersonic speeds. The spacecraft are built on Rocket Lab’s Photon satellite bus.
The Armenians, a population in Western Asia historically native to the Armenian Highlands, were long thought to be descendants of Phrygian settlers from the Balkans. This theory, rooted primarily in the writings of the Greek historian Herodotus, stemmed from his observation that Armenians serving in the Persian army were armed in a manner similar to the Phrygians. Linguists have also bolstered this theory, noting linguistic connections between the Armenian language and the Thraco-Phrygian subgroup of Indo-European languages.
But the first whole-genome study is challenging this long-held belief, revealing no significant genetic link between Armenians and the populations in the Balkan region. The study compares newly generated modern Armenian genomes and published genetic data of ancient individuals from the Armenian highlands with both modern and ancient genomes from the Balkans.
A new quantum algorithm developed by University of Georgia statisticians addresses one of the most complex challenges in single-cell analysis, signaling significant impact in both the fields of computational biology and quantum computing.
The study, “Bisection Grover’s Search Algorithm and Its Application in Analyzing CITE-seq Data,” was published in the Journal of the American Statistical Association on Sept. 20.
While traditional approaches struggle to handle the immense amount of data generated from measuring both RNA and protein expression in individual cells, the new quantum algorithm enables analysis of data from a single-cell technology known as CITE-seq. It allows for selection of the most important markers from billions of possible combinations—a task that would be formidable using classical methods.
How will NASA and SpaceX establish a permanent presence on the Moon? Dive into the details of the Artemis program, the Starship lunar lander, and the ambitious plans to create a lunar base. It’s the dawn of a new era in space exploration!