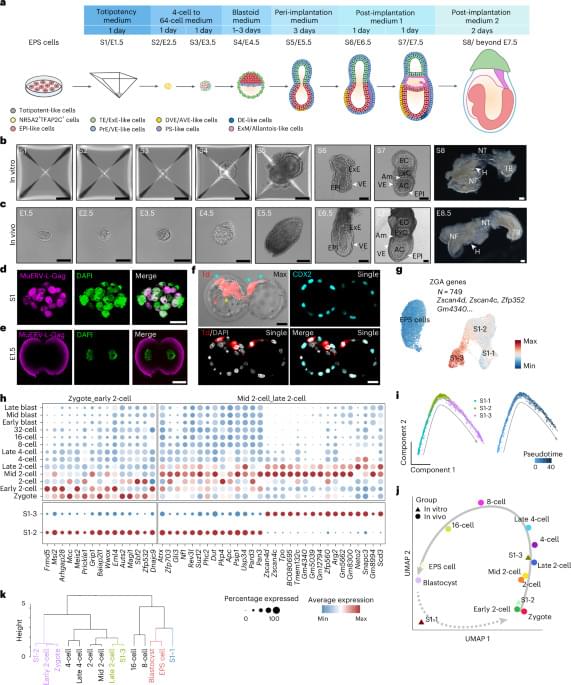
The authors identify a chemical cocktail to generate totipotent-like cells, which they then use to build an embryo model. This model captures a developmental spectrum from early embryogenesis to post-implantation events.


Manufacturing better batteries, faster electronics, and more effective pharmaceuticals depends on the discovery of new materials and the verification of their quality. Artificial intelligence is helping with the former, with tools that comb through catalogs of materials to quickly tag promising candidates.
But once a material is made, verifying its quality still involves scanning it with specialized instruments to validate its performance — an expensive and time-consuming step that can hold up the development and distribution of new technologies.
Now, a new AI tool developed by MIT engineers could help clear the quality-control bottleneck, offering a faster and cheaper option for certain materials-driven industries.



Five of Earth’s vital systems are close to a point of irreversible change, warns a new report released by a global network of scientists ahead of the upcoming U.N. climate change conference in Brazil.
The 2025 Global Tipping Points report updates a 2023 report to assess 25 Earth systems that human societies and economies depend on, including the stability of coral reefs, forests and ice sheets. It found at least one system has likely passed a tipping point, while four others are perilously close.
The Paris Agreement set a goal of limiting global warming to 1.5° Celsius (2.7° Fahrenheit) above preindustrial levels by 2100. The report notes that Earth has already reached an average increase of 1.4°C (2.5°F) over the past couple decades.

Impulse Space has already started working on the moon lander’s engine, which will “use a nitrous and ethane bipropellant — the same combination used successfully in space on Mira,” Mueller wrote.
And he reminded readers that Impulse took Mira from a mere design on paper to a functioning spacecraft in Earth orbit in less than 15 months.
“We’re confident in our ability to deliver this solution because of our strong track record of rapid success,” Mueller wrote of his company’s moon plans.
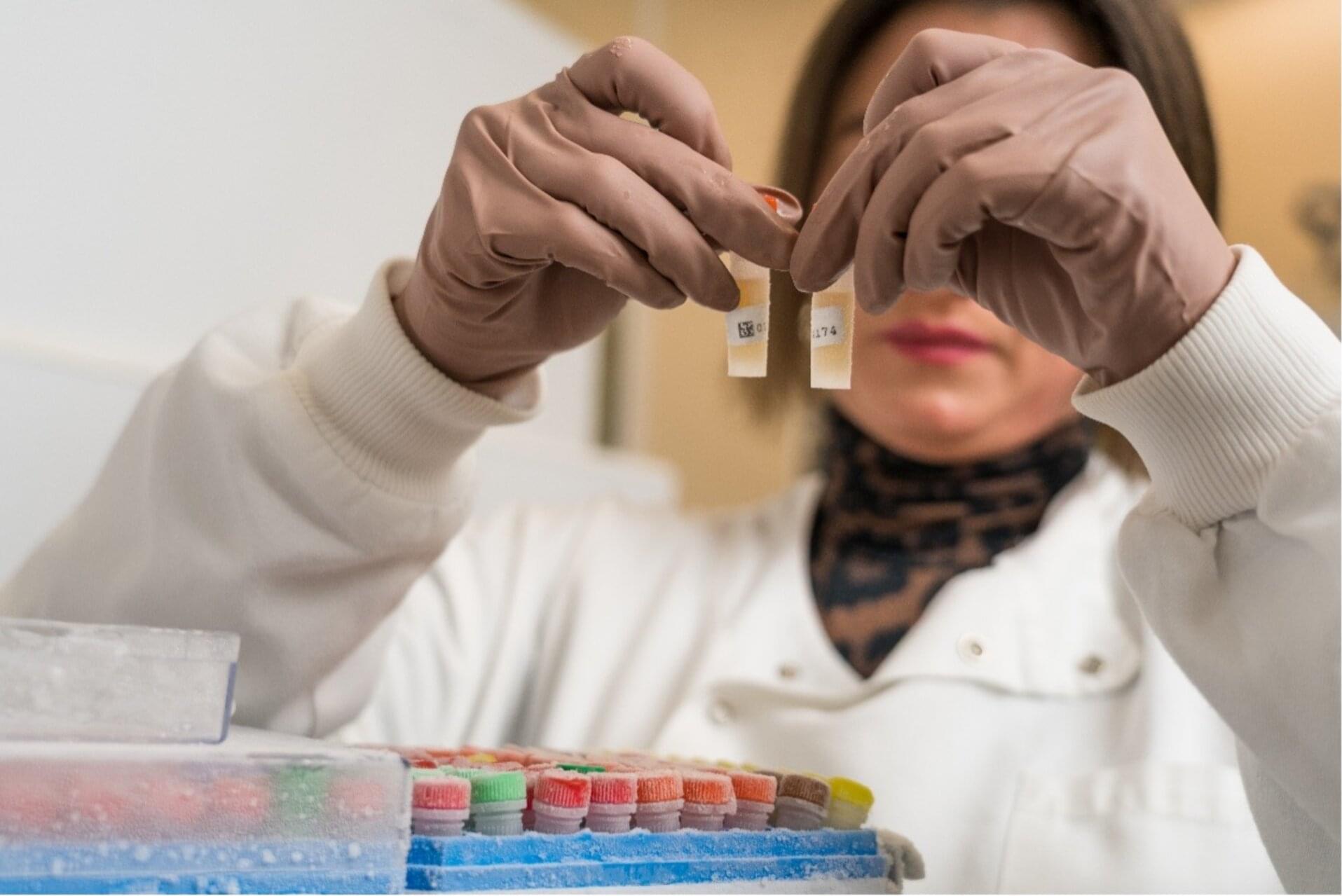

ESA’s new Exploration Biobank received its first biological samples linked to European space research in Portugal this week.
The shipment contained over 1,400 human samples from the Vivaldi III bedrest and dry-immersion campaign that took place earlier this year at Medes space clinic in Toulouse, France. Vivaldi III had a group of volunteers lying down on a waterbed and another group in bedrest for 10 days to recreate some of the effects of spaceflight on the body.
Samples of blood, saliva, urine, stool and hair from the participants arrived at the Biobank of the Gulbenkian Institute for Molecular Medicine (GIMM) in Lisbon on 14 October following strict safety, traceability and conservation protocols.
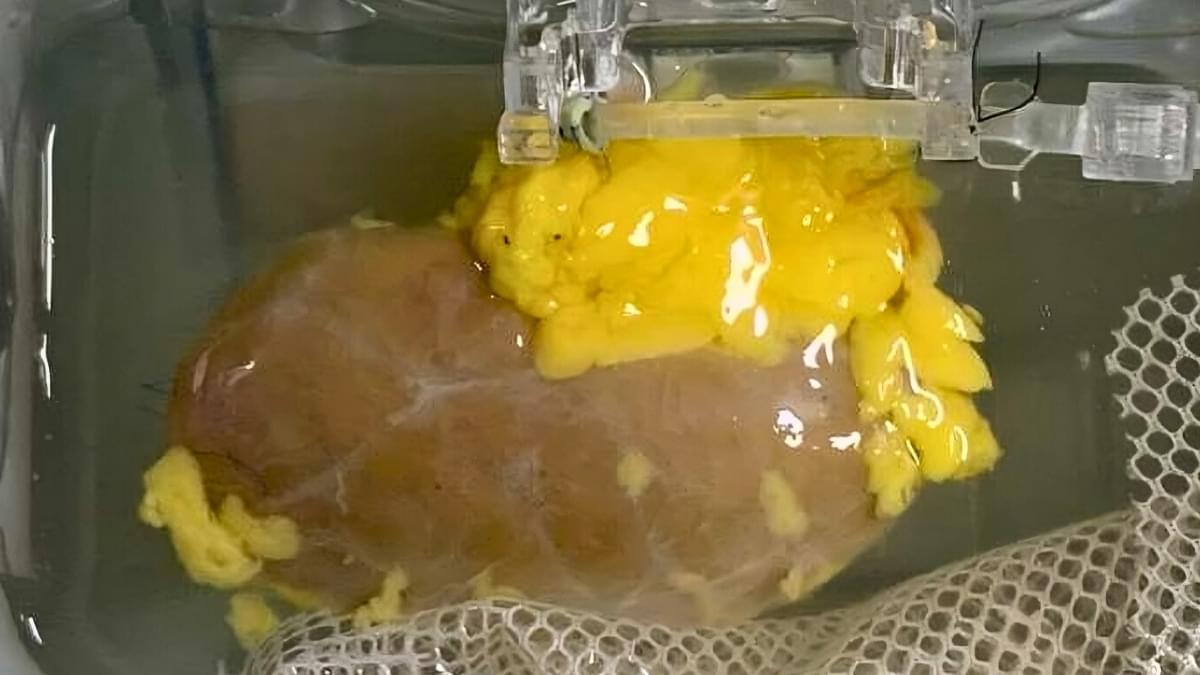
After a decade of work, researchers are closer than ever to a key breakthrough in kidney organ transplants: being able to transfer kidneys from donors with different blood types than the recipients, which could significantly speed up waiting times and save lives.
A team from institutions across Canada and China has managed to create a ‘universal’ kidney, which can, in theory, be accepted by any patient.
Their test organ survived and functioned for several days in the body of a brain-dead recipient, whose family consented to the research.

Approximately 550 employees of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) will be laid off, according to an announcement made on the agency’s website on Monday (Oct. 13).
The news comes in the midst of an ongoing U.S. government shutdown and the looming threat of the single largest funding reduction in NASA’s 66-year history. Due to those potential cuts, NASA has been forced to reshape many of its science and space exploration efforts. However, NASA has stated this latest wave of layoffs are unrelated to the government shutdown that has seen over 15,000 federal employees furloughed and is, rather, part of an agency-wide “reorganization” that began in June.