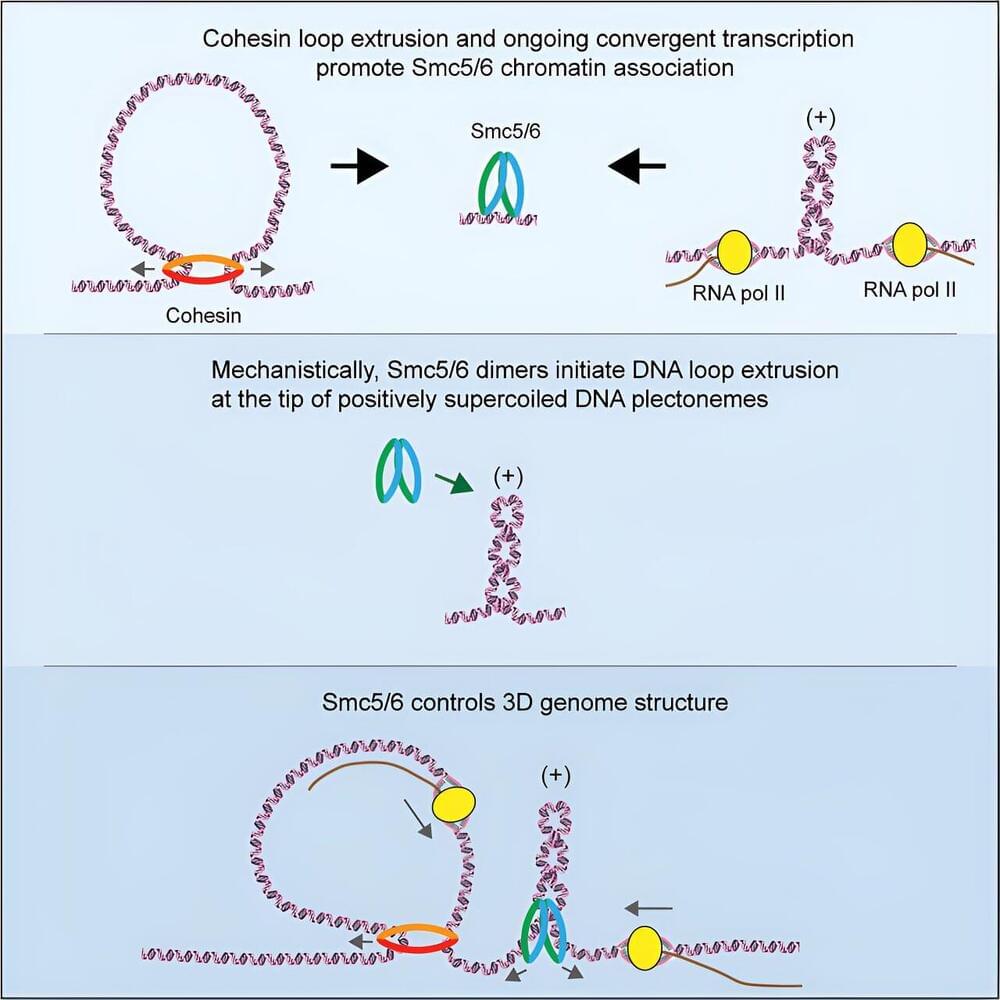
“Soilless biofortification of vegetables has opened the door to the potential for adapting vegetable production to specific dietary requirements,” said Dr. Massimiliano Renna.
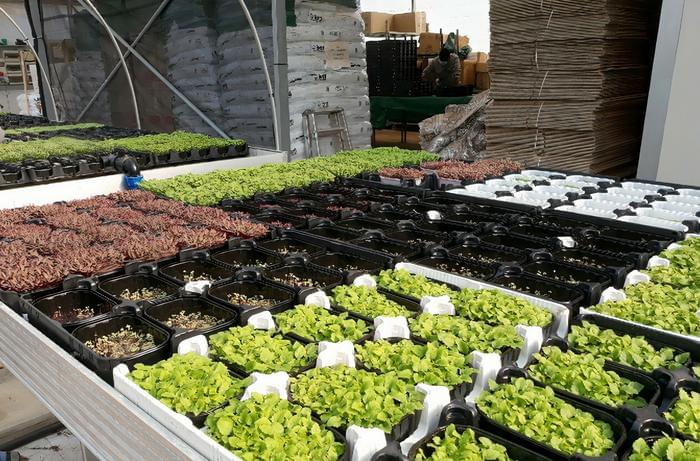
Can microgreen be customized based on dietary and medical needs? This is what a recent study published in the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture hopes to address as a collaborative team of Italian researchers investigated the potential for customizing microgreens via soilless growing methods designed to suit specific dietary needs based on medical concerns. This study holds the potential to help scientists and patients better understand the available nutritional options, specifically for medical reasons.
“Propelled by an ever-growing awareness of the importance of following dietary recommendations, interest in personalized nutrition is on the rise. Soilless biofortification of vegetables has opened the door to the potential for adapting vegetable production to specific dietary requirements,” said Dr. Massimiliano Renna, who is a professor of agricultural and environmental science at the University of Bari Aldo Moro and a co-author on the study.
For the study, the researchers focused on growing customized microgreens that could meet the needs of individuals who suffer from an iodine deficiency or need less potassium. Iodine deficiency impacts approximately two billion people around the world and reduced potassium is required for individuals suffering from chronic kidney disease, which impacts more than 800 million people around the world, as well. In the end, the researchers were able to grow microgreens in iodine solution that resulted in up to 14 times increase in iodine levels, plus they successfully reduced potassium levels by an average of 45 percent.