George TheTinMen is a content creator, pro-men’s advocate and social media influencer. Men’s mental health is in the toilet. 80% of 18–24 year old suicides are men. 15% of men say they have 0 close friends to call on in an emergency. So why does it seem like the world doesn’t care and just thinks that men are still the benefactors of a patriarchy they no longer feel a part of?
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
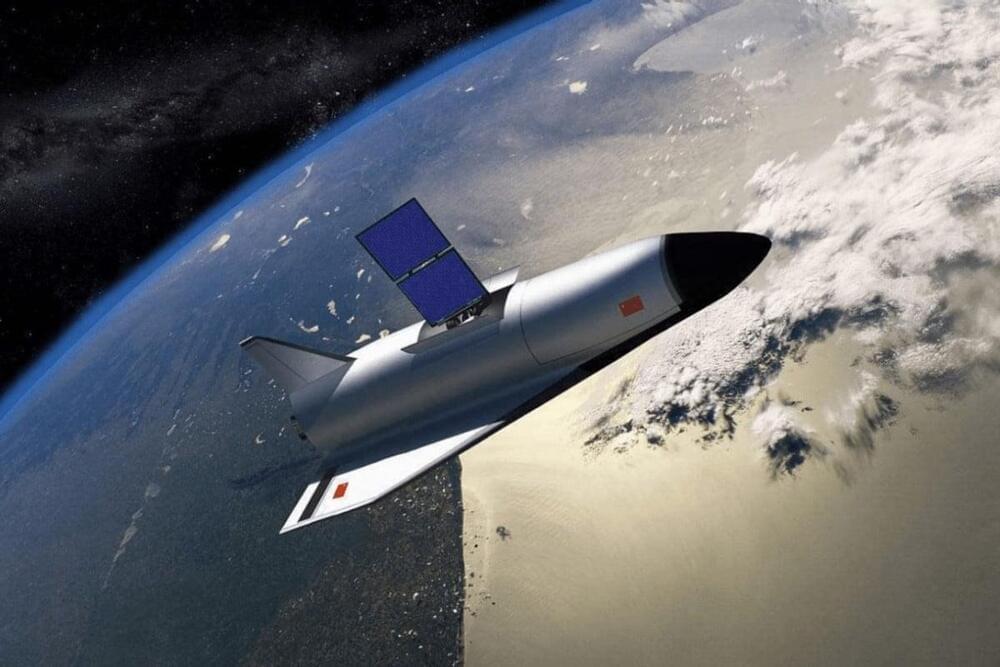

China is building a railgun that can hurl crewed spacecraft into orbit
And the g-forces???
Rockets being passé, China is working on using an electromagnetic railgun to launch crewed spacecraft the size of a Boeing 737, weighing 50 tonnes, into orbit. This remarkably ambitious project is even more ambitious than it seems at first glance.
Call it a railgun, a catapult, or a mass driver, the idea of replacing rockets with an electromagnetic accelerator is a very attractive option. Instead of lifting off on chemical rockets that have to carry fuel and fuel to lift the fuel and fuel to lift the fuel and the additional fuel, it makes more sense to keep as much of the launching system on the ground while leaving the vehicle as light as possible.
The principle behind such a space railgun is simple, but the details are surprisingly complex and the numbers involved very quickly become daunting. If China can carry off using such a system to launch a spaceplane as part of its Tengyun project that began in 2016, it would be one of history’s major engineering achievements.

A Digital Twin Might Just Save Your Life
In the last decade, thanks to advances in AI, the internet of things, machine learning and sensor technologies, the fantasy of digital twins has taken off. BMW has created a digital twin of a production plant in Bavaria. Boeing is using digital twins to design airplanes. The World Economic Forum hailed digital twins as a key technology in the “fourth industrial revolution.” Tech giants like IBM, Nvidia, Amazon and Microsoft are just a few of the big players now providing digital twin capabilities to automotive, energy and infrastructure firms.
The inefficiencies of the physical world, so the sales pitch goes, can be ironed out in a virtual one and then reflected back onto reality. Test virtual planes in virtual wind tunnels, virtual tires on virtual roads. “Risk is removed” reads a recent Microsoft advertorial in Wired, and “problems can be solved before they happen.”
All of a sudden, Dirk Helbing and Javier Argota Sánchez-Vaquerizo wrote in a 2022 paper, “it has become an attractive idea to create digital twins of everything.” Cars, trains, ships, buildings, airports, farms, power plants, oil fields and entire supply chains are all being cloned into high-fidelity mirror images made of bits and bytes. Attempts are being undertaken to twin beaches, forests, apple orchards, tomato plants, weapons and war zones. As beaches erode, forests grow and bombs explode, so too will their twins, watched closely by technicians for signals to improve outcomes in the real world.
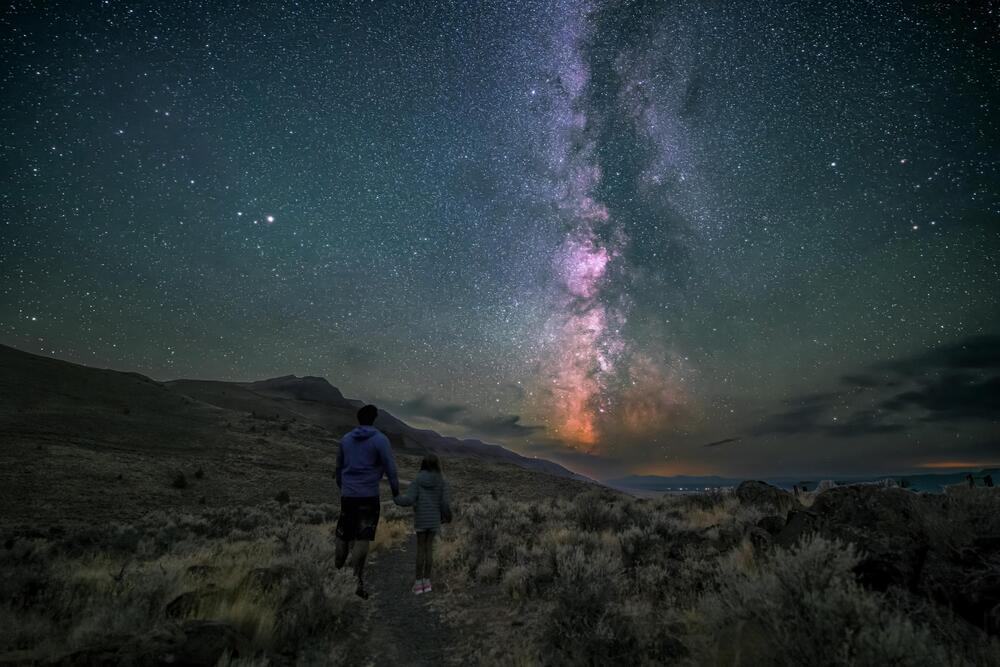

Oregon Is Now Home to the World’s Largest Dark Sky Sanctuary
Calling all stargazers: Oregon is now home to the largest Dark Sky Sanctuary in the world.
Earlier this month, DarkSky International certified a remote, 2.5 million-acre area in the southeastern part of the state. From this rugged swath of high desert landscape dotted with sagebrush, visitors who stay up late can see large numbers of stars, planets and other celestial bodies.
“It’s surprising sometimes to see that many stars all at once,” says Bob Hackett, executive director of Travel Southern Oregon, to the Guardian’s Dani Anguiano. “It catches you, and it makes you pause because you feel like you can touch it … That vastness of the whole cosmos up there—it almost makes you get closer to the people you’re with on the ground.”
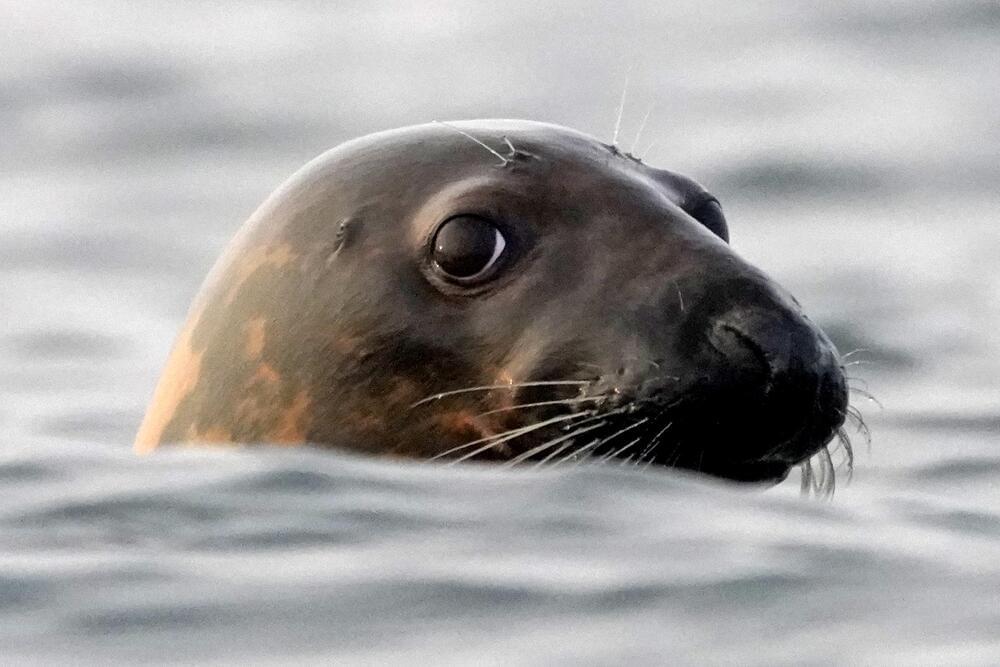

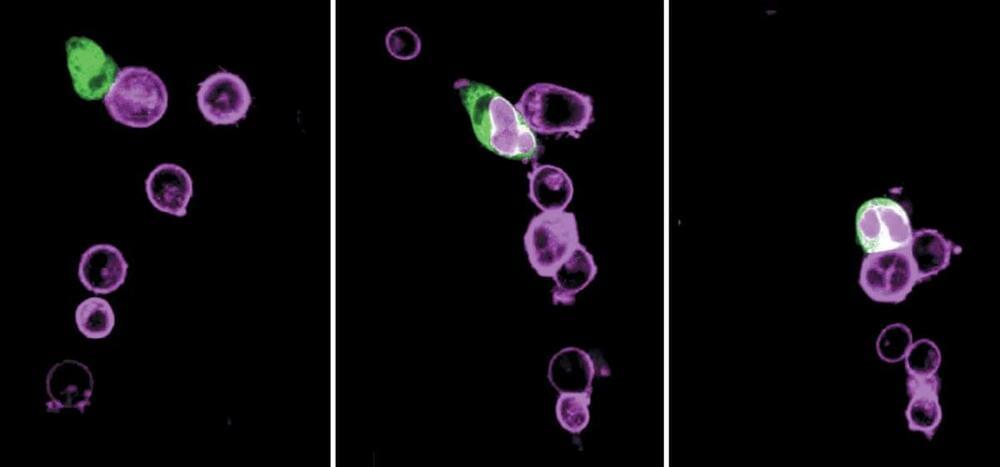
Bird flu is decimating seal colonies. Scientists don’t know how to stop it
PORTLAND, Maine (AP) — Avian influenza is killing tens of thousands of seals and sea lions in different corners of the world, disrupting ecosystems and flummoxing scientists who don’t see a clear way to slow the devastating virus.
The worldwide bird flu outbreak that began in 2020 has led to the deaths of millions of domesticated birds and spread to wildlife all over the globe. This virus isn’t thought to be a major threat to humans, but its spread in farming operations and wild ecosystems has caused widespread economic turmoil and environmental disruptions.
Seals and sea lions, in places as far apart as Maine and Chile, appear to be especially vulnerable to the disease, scientists said. The virus has been detected in seals on the east and west coasts of the U.S., leading to deaths of more than 300 seals in New England and a handful more in Puget Sound in Washington. The situation is even more dire in South America, where more than 20,000 sea lions have died in Chile and Peru and thousands of elephant seals have died in Argentina.
These ‘Strange Metals’ Bend the Rules of Physics
Electrons swarm in a soup of quantum entanglement in a new class of materials called strange metals.

Paper page — Efficient Video Diffusion Models via Content-Frame Motion-Latent Decomposition
From NVIDIA efficient video diffusion models via content-frame motion-latent decomposition.
From NVIDIA
Efficient video diffusion models via content-frame motion-latent decomposition.
Video diffusion models have recently made great progress in generation quality, but are still limited by the high memory and computational requirements.
Join the discussion on this paper page.