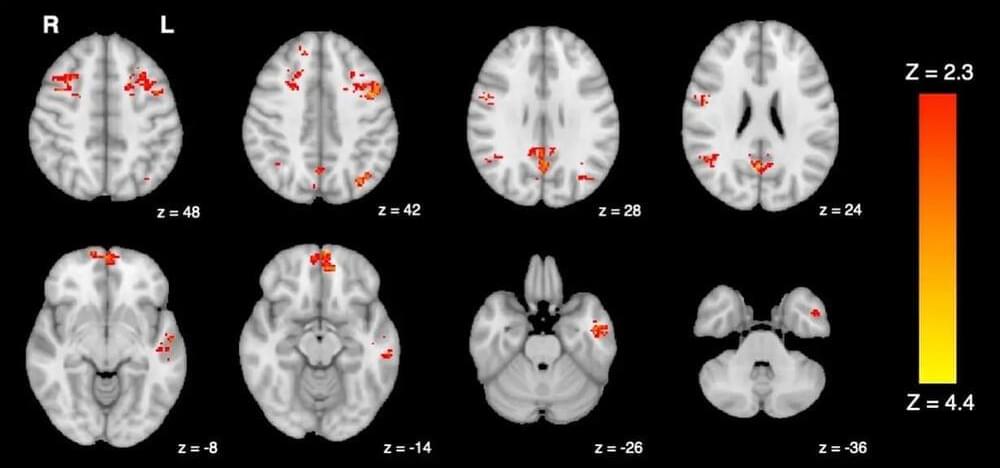
The study conducted by researchers at the University of British Columbia and the University of Victoria reveals that exposure to common levels of traffic pollution can impair brain function within hours.
The peer-reviewed study published in Environmental Health found that only two hours of exposure to diesel exhaust leads to a decrease in brain functional connectivity, which is a measure of how different areas of the brain interact and communicate with each other. This study is the first controlled experiment to provide evidence of air pollution altering brain connectivity in humans.
“For many decades, scientists thought the brain may be protected from the harmful effects of air pollution,” said senior study author Dr. Chris Carlsten, professor and head of respiratory medicine and the Canada Research Chair in occupational and environmental lung disease at UBC. “This study, which is the first of its kind in the world, provides fresh evidence supporting a connection between air pollution and cognition.”