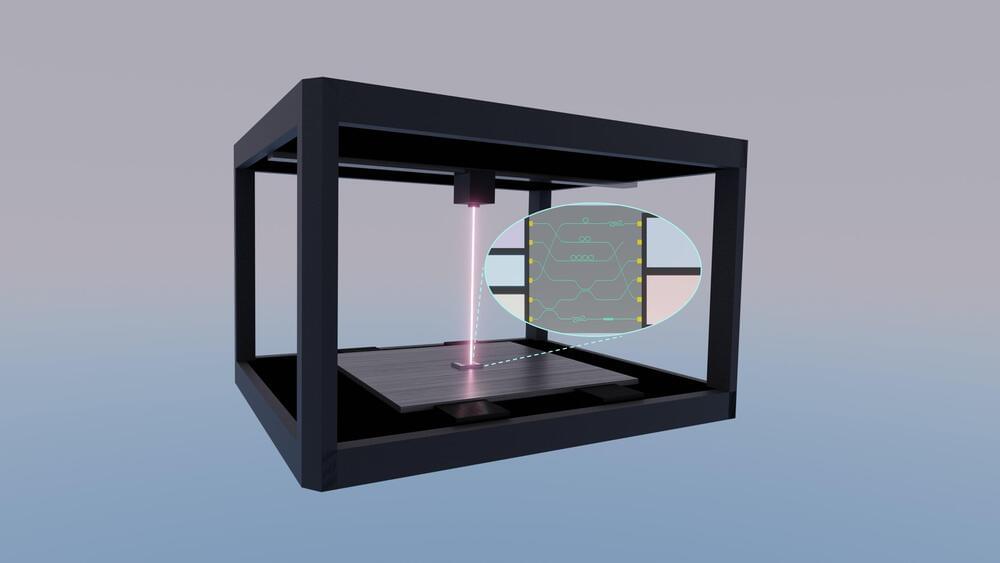
Photonic integrated circuits are an important next-wave technology. These sophisticated microchips hold the potential to substantially decrease costs and increase speed and efficiency for electronic devices across a wide range of application areas, including automotive technology, communications, health care, data storage, and computing for artificial intelligence.
Photonic circuits use photons, fundamental particles of light, to move, store, and access information in much the same way that conventional electronic circuits use electrons for this purpose. Photonic chips are already in use today in advanced fiber-optic communication systems, and they are being developed for implementation in a broad spectrum of near-future technologies, including light detection and ranging, or LiDAR, for autonomous vehicles; light-based sensors for medical devices; 5G and 6G communication networks; and optical and quantum computing.
Given the broad range of existing and future uses for photonic integrated circuits, access to equipment that can fabricate chip designs for study, research and industrial applications is also important. However, today’s nanofabrication facilities cost millions of dollars to construct and are well beyond the reach of many colleges, universities, and research labs.