Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
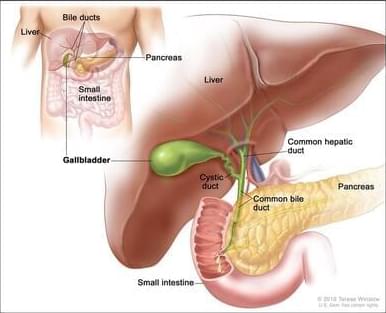
Gallbladder Cancer Treatment
Types of treatment for gallbladder cancer include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Treatment of gallbladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, cannot be removed by surgery, or has come back after treatment is often within a clinical trial. Find out about treatment options for gallbladder cancer.
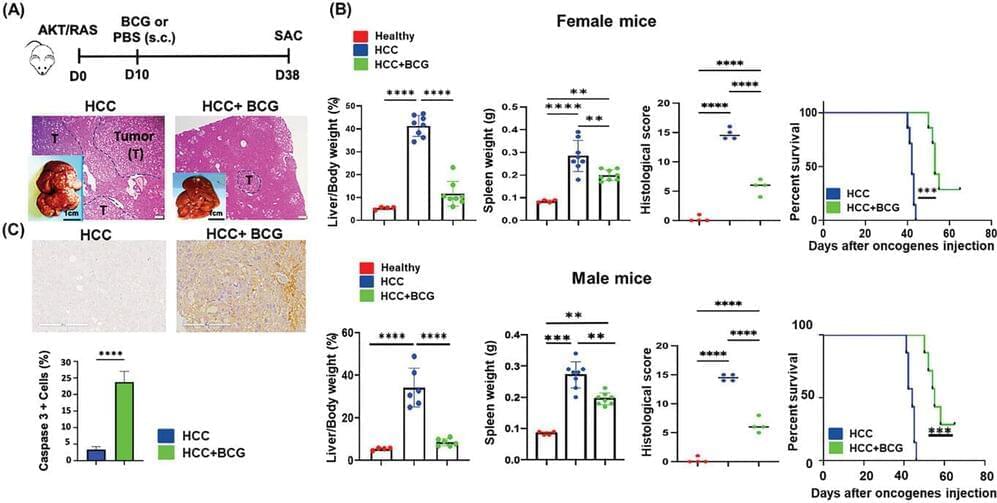
TB vaccine shrinks liver cancer tumors in mice
A UC Davis Health study found that a single dose of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), the vaccine for tuberculosis (TB), reduced liver tumor burden and extended the survival of mice with liver cancer. The study, published in Advanced Science, is the first to show the promising effects of the vaccine in treating liver cancer.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer. It is also the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Current therapies include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy and liver transplant. Yet, the therapy outcomes for liver cancer remain bleak.
BCG, the century-old TB vaccine, is derived from the live bacteria Mycobacterium bovis. It is considered safe and widely used around the world.
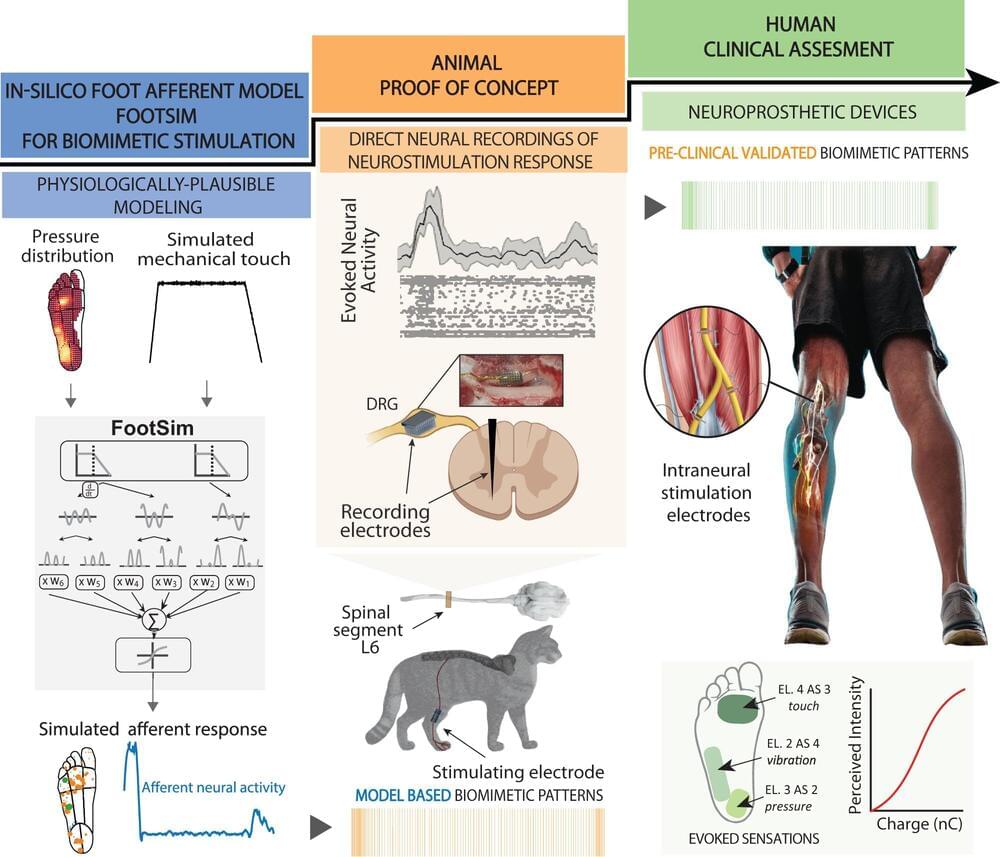
Bio-inspired neuroprosthetics: Sending signals the brain can understand
A few years ago, a team of researchers working under Professor Stanisa Raspopovic at the ETH Zurich Neuroengineering Lab gained worldwide attention when they announced that their prosthetic legs had enabled amputees to feel sensations from this artificial body part for the first time.
Unlike commercial leg prostheses, which simply provide amputees with stability and support, the ETH researchers’ prosthetic device was connected to the sciatic nerve in the test subjects’ thigh via implanted electrodes.
This electrical connection enabled the neuroprosthesis to communicate with the patient’s brain, for example relaying information on the constant changes in pressure detected on the sole of the prosthetic foot when walking. This gave the test subjects greater confidence in their prosthesis—and it enabled them to walk considerably faster on challenging terrains.
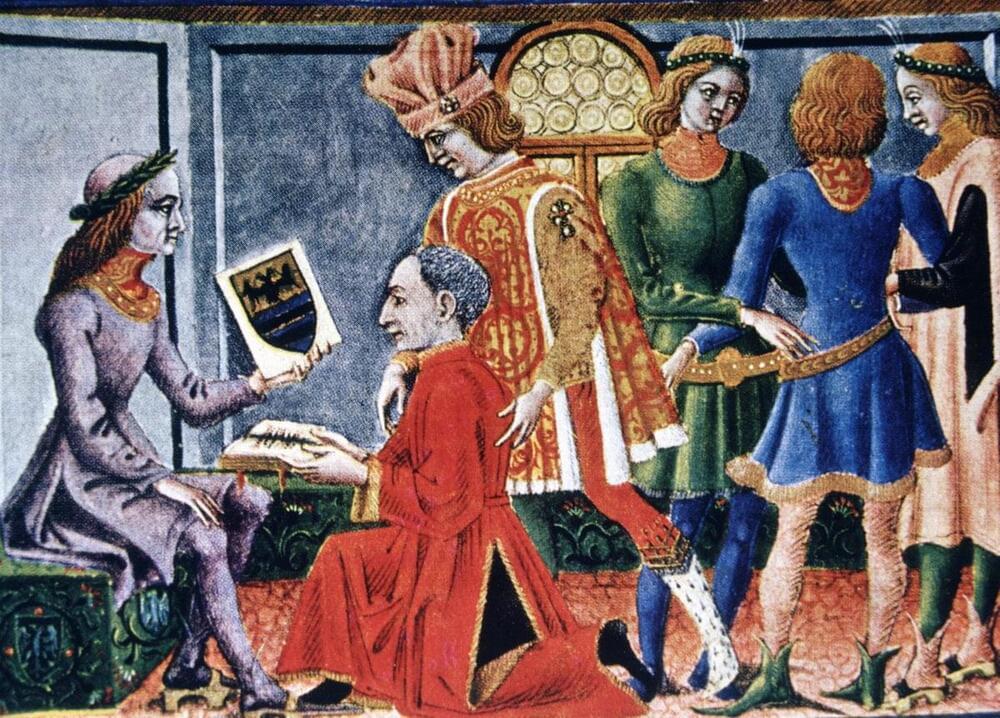
The Decimal Point Is 150 Years Older than Historians Thought
The origin of the decimal point, a powerful calculation tool, has been traced back to a mathematician who lived during the Italian Renaissance.
By Jo Marchant & Nature magazine.
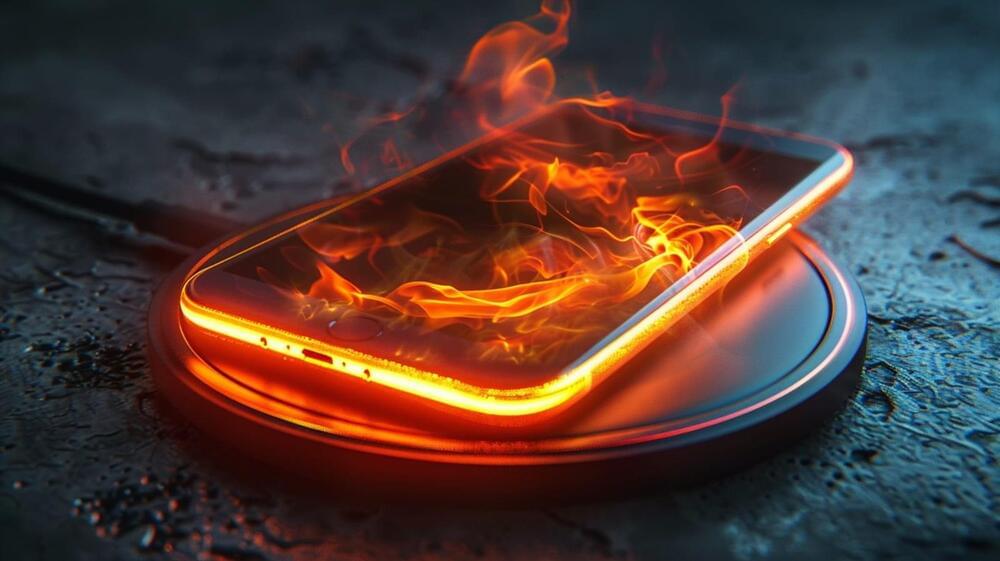

VoltSchemer attacks use wireless chargers to inject voice commands, fry phones
A team of academic researchers show that a new set of attacks called ‘VoltSchemer’ can inject voice commands to manipulate a smartphone’s voice assistant through the magnetic field emitted by an off-the-shelf wireless charger.
VoltSchemer can also be used to cause physical damage to the mobile device and to heat items close to the charger to a temperature above 536F (280C).
A technical paper signed by researchers at the University of Florida and CertiK describes VoltSchemer as an attack that leverages electromagnetic interference to manipulate the charger’s behavior.
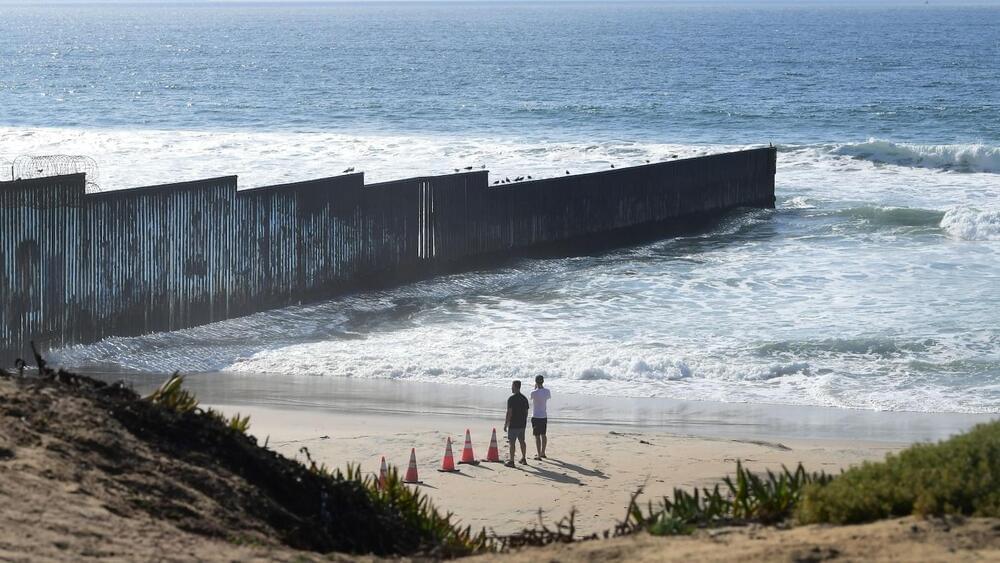

US-Mexico border: 100 billion gallons of toxic sewage creating a ‘public health crisis’
“South San Diego County is in a total state of emergency related to transboundary pollution, and this is a public health ticking time bomb,” Imperial Beach Mayor Paloma Aguirre told ABC News. “We are living in conditions that nobody in this great nation should be living in.”
The Tijuana River – which has been classified as an impaired water body, according to the U.S. Clean Water Act — flows north for 120 miles from Mexico to California before reaching the Pacific Ocean on the U.S. side of the border in the Imperial Beach, San Ysidro and Coronado coastal areas.
Over the last five years, 100 billion gallons of untreated sewage, industrial waste and urban runoff have been dumped into the Tijuana River, according to the International Boundary and Water Commission.

