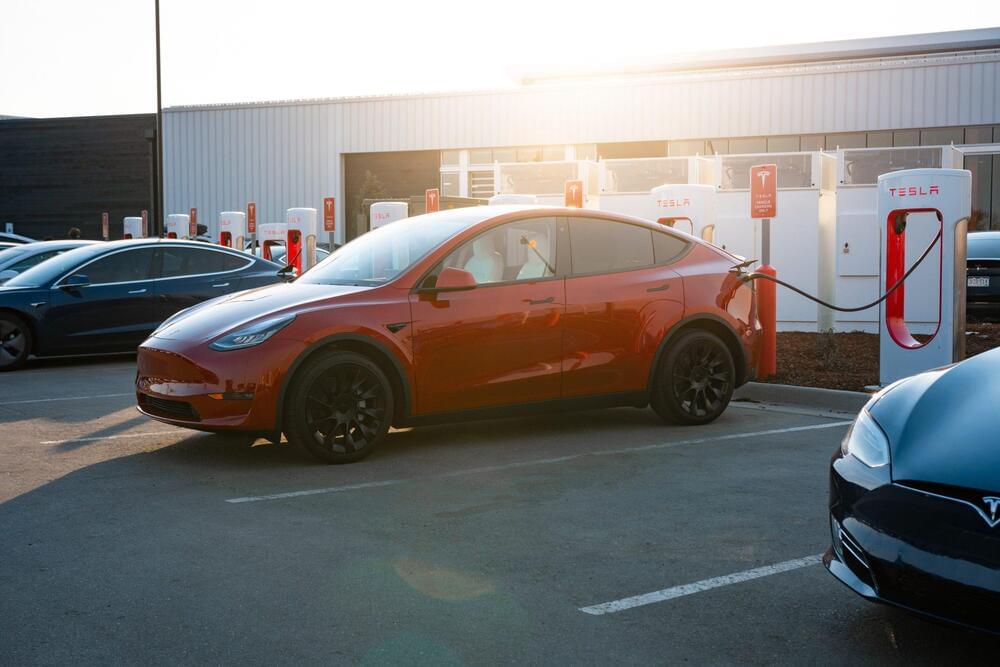
Tesla executive Rohan Patel clarified some facts about Supercharger NACS access for non-Tesla vehicles like Rivian and Ford.
Patel—Tesla’s Vice President of Public Policy and Business Development—recently replied to a question from Teslavangelist, who questioned the number of Supercharger stalls non-Tesla owners actually had access to with NACS connectors.
Tesla recently opened the Supercharger Network to Ford and Rivian electric vehicles (EVs) through its NACS connecter. Both automakers claim that NACS connectors provide Ford and Rivian owners access to over 15,000 Tesla Supercharger locations. Teslavangelist pointed out that non-Tesla EV owners only have access to V3 and V4 Superchargers, doubting they have access to 15,000 Supercharger stalls.