While the artificial intelligence revolution has just begun, it is transforming healthcare, speeding drug discovery, improving both diagnosis and patient communication.



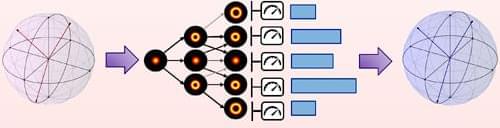
A quantum squeezing method can enhance interactions between quantum systems, even in the absence of precise knowledge of the system parameters.
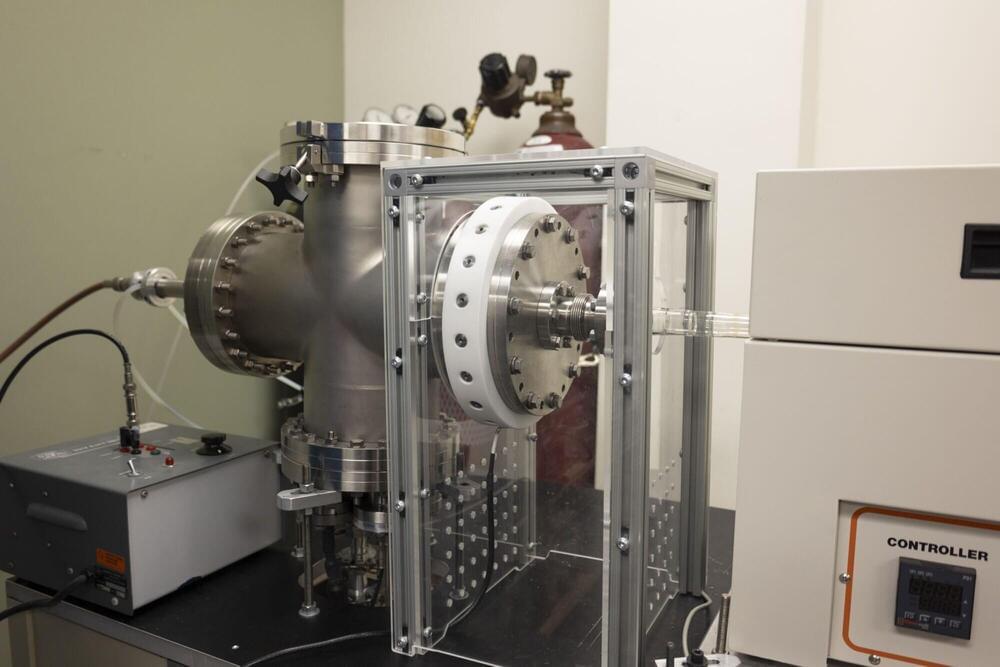
Squeezed states are an important class of nonclassical states, where quantum fluctuations can be reduced in one property of a system, such as position. However, at the same time, according to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, quantum fluctuations increase in the conjugate property, in this case momentum. The ability to suppress noise in at least one variable is valuable in a wide range of areas in quantum technologies. Now Shaun Burd at the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Colorado, and colleagues have experimentally demonstrated a squeezing-based enhancement method that requires no preknowledge of the system’s parameters [1]. The researchers use a trapped-ion system (Fig. 1) and show that they can amplify the motion of the ion using a combination of squeezing procedures. This experimental research can stimulate other novel applications of squeezing, for example, in dark matter searches.
For decades, quantum squeezing has played a central role in high-precision quantum measurements, such as gravitational-wave detection [2, 3] and nondemolition qubit readout [4– 6]. The methods typically involve applying a field or inserting an optical element that reduces the fluctuations in one observable. The measurements of this squeezed observable can beat the standard quantum limit and thus enable a significant improvement in the detection sensitivity or the readout signal-to-noise ratio.
It is a common hack to stretch a balloon out to make it easier to inflate. When the balloon stretches, the width crosswise shrinks to the size of a string. Noah Stocek, a Ph.D. student collaborating with Western physicist Giovanni Fanchini, has developed a new nanomaterial that demonstrates the opposite of this phenomenon.
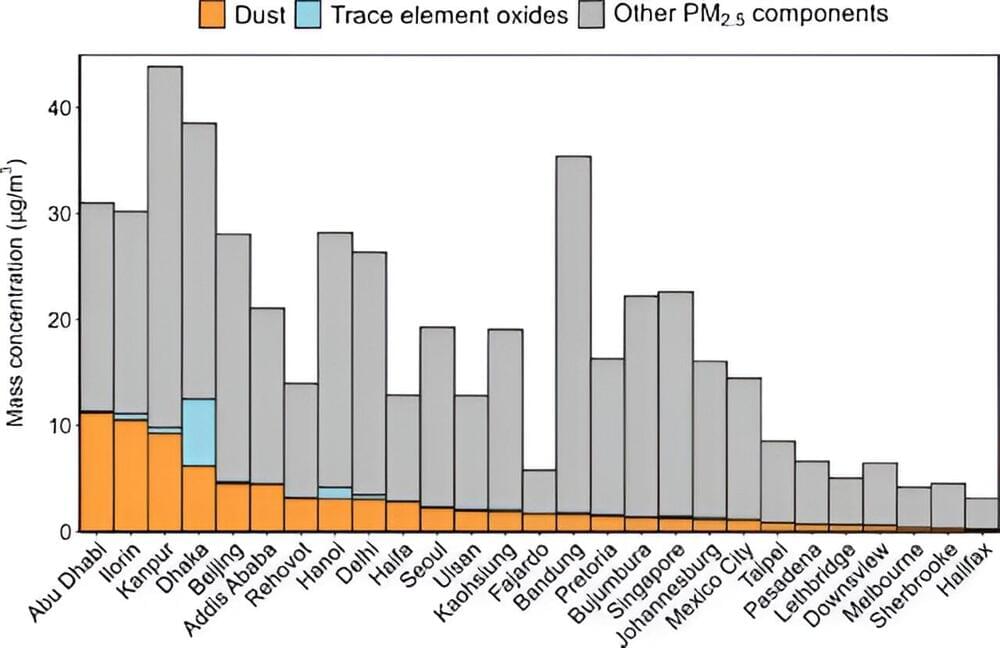
As anyone with seasonal allergies knows, unseen airborne particles can really wreck a person’s day. Like the tree pollen that might be plaguing you this spring, small concentrations of trace elements in the air can have significant negative impacts on human health. However, unlike pollen counts and other allergy indices, which are carefully tracked and widely available, limited knowledge exists about the ambient concentrations of cancer-causing trace elements like lead and arsenic in urban areas of developing countries.
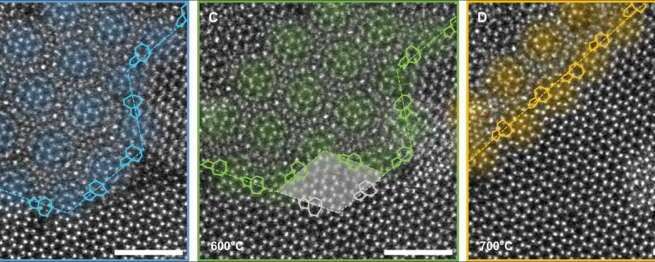
Silicon-based electronics are approaching their physical limitations and new materials are needed to keep up with current technological demands. Two-dimensional (2D) materials have a rich array of properties, including superconductivity and magnetism, and are promising candidates for use in electronic systems, such as transistors. However, precisely controlling the properties of these materials is extraordinarily difficult.
A numerical investigation has revealed a surprising correspondence between a lattice spin model and a quantum field theory.
The search for a quantum spin liquid (QSL) in a real magnetic material has been at the forefront of condensed-matter physics since this exotic quantum state was first proposed over half a century ago. Meanwhile, theorists continue to grapple with understanding what rich physics might emerge from this state. Now Alexander Wietek of the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems in Germany and his collaborators have made a significant advance toward that goal. Through numerical simulations, they have presented a compelling numerical case that the spectrum of elementary excitations of a well-studied QSL has a one-to-one correspondence with the spectrum of excitations of a well-studied quantum field theory [1]. If a real QSL is discovered or fabricated, the correspondence opens the prospect of testing theories from particle physics with condensed-matter systems.