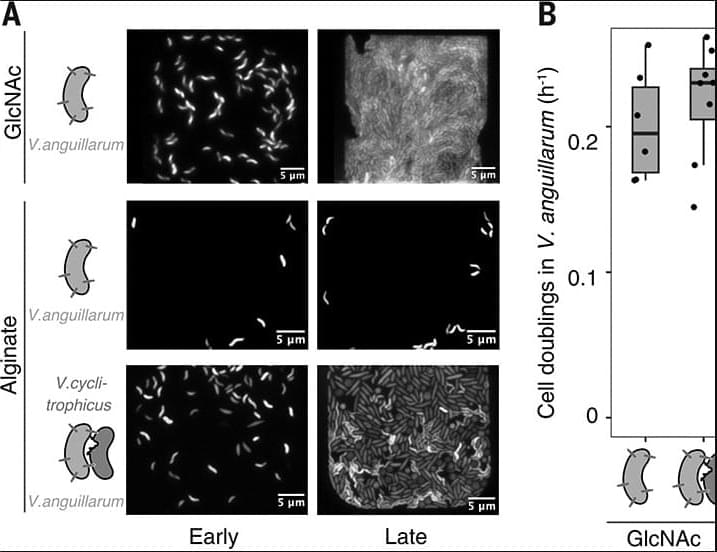
Fascinating paper where the authors show that many bacteria can attack other ‘prey’ bacteria (using T6SS as a weapon) and feed on the nutrients released by the destroyed prey. This behavior appears widespread across environments such as soil, ocean, etc.
In natural habitats, nutrient availability limits bacterial growth. We discovered that bacteria can overcome this limitation by acquiring nutrients by lysing neighboring cells through contact-dependent antagonism. Using single-cell live imaging and isotopic markers, we found that during starvation, the type VI secretion system (T6SS) lysed neighboring cells and thus provided nutrients from lysing cells for growth. Genomic adaptations in antagonists, characterized by a reduced metabolic gene repertoire, and the previously unexplored distribution of the T6SS across bacterial taxa in natural environments suggest that bacterial antagonism may contribute to nutrient transfer within microbial communities in many ecosystems.