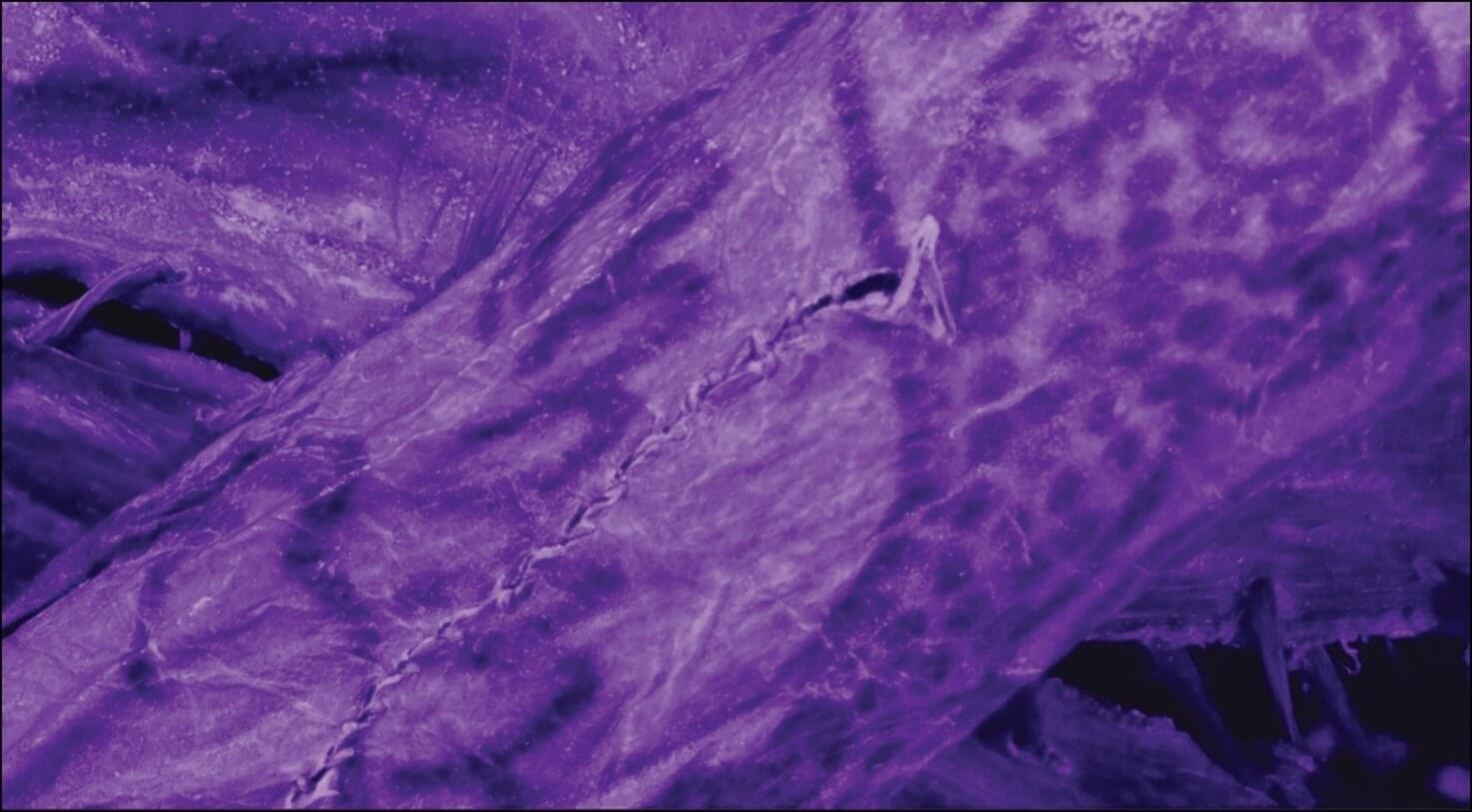
An international team of archaeologists has used high-resolution digital imaging techniques to examine tattoos on a more than 2,000-year-old ice mummy from the Pazyryk culture of Siberia, shedding light on individual craftsmanship in prehistoric Siberian tattooing for the first time.
Tattooing was likely widespread during prehistory, but the lack of surviving tattoos means it is difficult to investigate. The so-called “ice mummies” of the Altai mountains are an exception, since their deep burial chambers encased in permafrost sometimes preserve the skin (and therefore tattoos) of those buried within.
“The tattoos of the Pazyryk culture-Iron Age pastoralists of the Altai Mountains-have long intrigued archaeologists due to their elaborate figural designs,” states senior author of the research, Dr. Gino Caspari from the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology and the University of Bern.