Homeowners get the best heloc rates by using lendgo. Takes 2 minutes.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Max Tegmark: Life 3.0
Take courses developed and taught by the same tenured & tenure-track faculty as on campus.
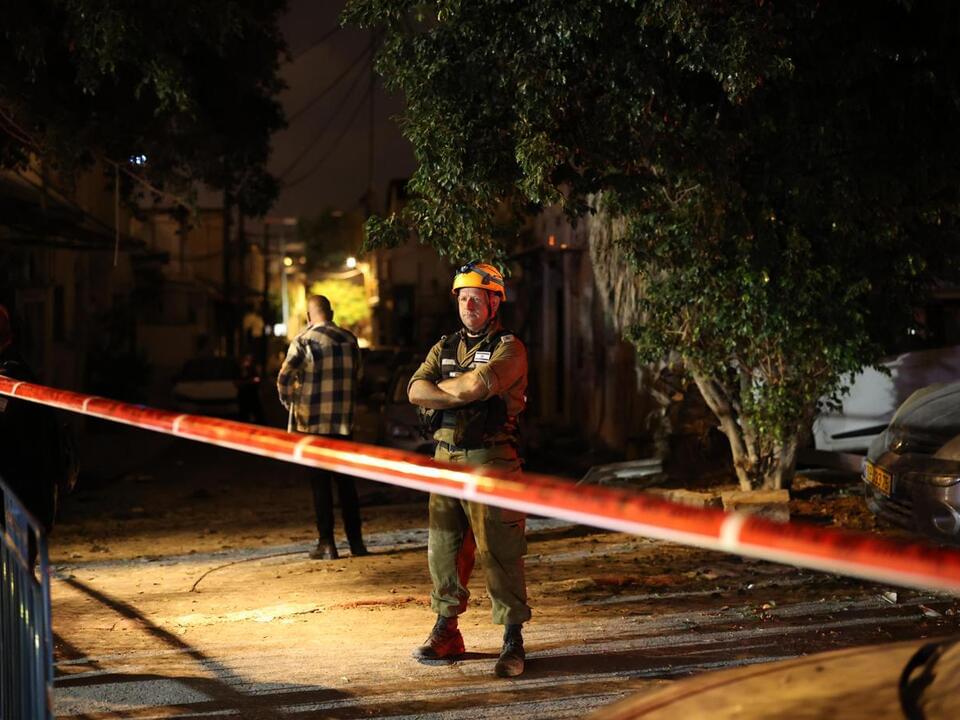

Hamas gunmen open fire on hundreds at music festival in southern Israel
During the surprise assault on Israel by Palestinian militant group Hamas Saturday, gunmen opened fire on hundreds of young people during a dance music festival in the southern Israeli kibbutz of Re’im near the Gaza Strip, according to the Associated Press and multiple Israeli media outlets.
Witnesses told the Times of Israel that rocket fire was followed by gunshots fired into the crowd, as hundreds tried to flee.
“The music stopped and there was a rocket siren,” a young woman called Ortal told Israel’s Channel 12, according to Reuters. “Suddenly out of nowhere, they started shooting.”
Dive into anything
We are a community of machine learning enthusiasts/researchers/journalists/writers who share interesting news and articles about the applications of AI. You will never miss any updates on ML/AI/CV/NLP fields because we post them daily. We hope that you subscribe to us so that you’ll be up-to-date with the latest developments around the world in terms of machine learning and related areas.
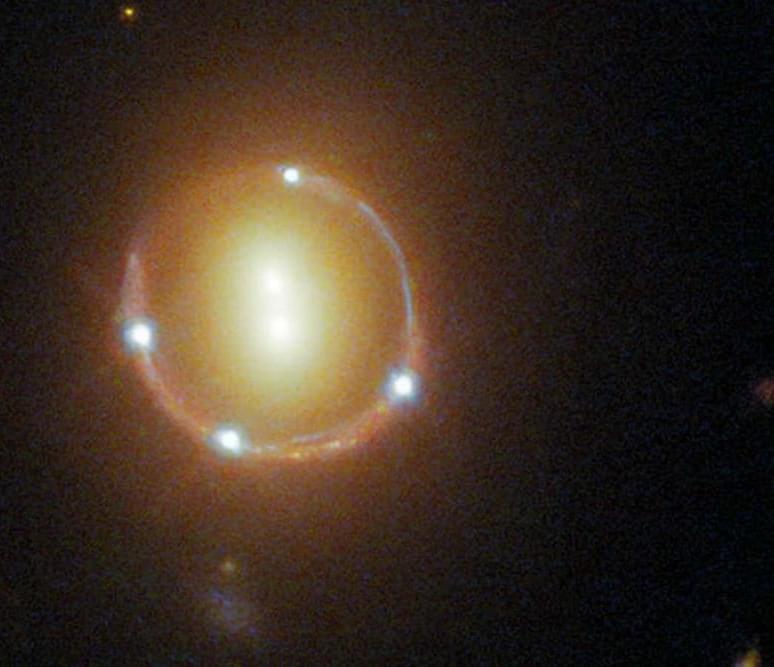
Weird dark matter waves seem to warp the light from distant galaxies
Ultralight dark matter particles that behave like waves, called axions, seem to be a better match for gravitational lensing measurements than more traditional explanations for dark matter.
By Leah Crane
A Scanner Darkly
America in the near future has lost the war against drugs. Paranoia reigns as 2 out of every 10 Americans have been hired by the government to spy on the other 8 in the name of national security and drug enforcement. Enter Fred, a reluctant undercover cop recruited by the government. To maintain his cover, Fred regularly ingests the popular Substance D. The drug has caused Fred to develop a split personality, of which he is unaware; his alter ego is Bob Arctor, a drug dealer. Fred’s superiors set up a hidden holographic camera in his home as part of a sting operation to snare Bob. A “scramble suit” that changes his appearance allows Fred to appear on camera as Bob and prevents his colleagues from knowing his true identity. The camera in Fred/Bob’s apartment reveals that Bob’s friends regularly betray one another for the chance to score more drugs.
2010: The Year We Make Contact
In the year 2001, the spaceship Discovery is betrayed by its on-board computer, HAL, while on a mission to Jupiter. Nine years later, with the United States and Russia on the brink of war, the superpowers launch a joint mission to return to the Discovery in 2010: The Year We Make Contact. During the three-year voyage to Jupiter, world war breaks out on Earth, threatening to extend to the spaceship. But the ghostly presence of Dave Bowman (Keir Dullea) of the Discovery crew intervenes, warning that something grand, dangerous and wonderful is about to occur…
Maria Entraigues Abramson’s abbreviated presentation @RAADfest 2023
Here’s a quick look at Maria Entraigues Abramson’s presentation at RAADfest 2023 in California. Our Director of Develpoment gives an overview of SRF’s work and misison. You can watch the full presentation by renting the video program for the full event from the Coalition for Radical Life Extension here: https://vimeo.com/ondemand/raadfest2023/
In her full presentation, she highlights that adopting a better lifestyle to enhance our health is always a good idea and we should all do this. She personally advocates for everyone to utilize all scientifically supported resources to achieve optimized health. However, she reminds the audience that the mission of SRF is not about lifestyle changes but to transform the aging process completely, aiming to significantly extend our healthspan by repairing our bodies at a cellular level. SRF’s damage-repair approach will lead to a much longer and healthier lifespan—a feat not yet accomplished, regardless of the excellent care we may take of ourselves through lifestyle changes, supplement intake, etc.
She also underscores the importance of SRF’s work being on applied research, with the explicit goal to translate their science into therapies for everyone.
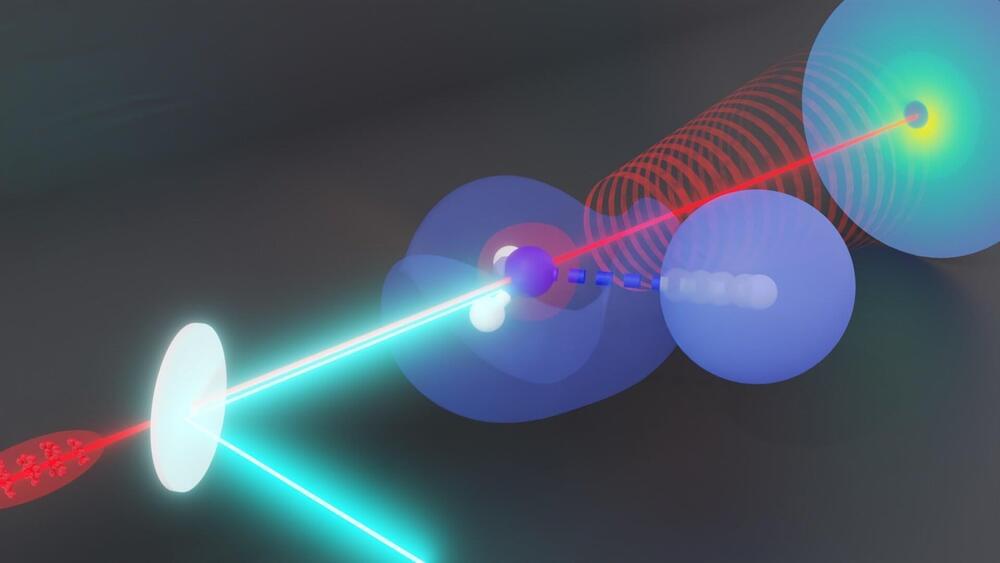
Researchers catch protons in the act of dissociation with ultrafast ‘electron camera’
Scientists have caught fast-moving hydrogen atoms—the keys to countless biological and chemical reactions—in action.
A team led by researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University used ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) to record the motion of hydrogen atoms within ammonia molecules. Others had theorized they could track hydrogen atoms with electron diffraction, but until now nobody had done the experiment successfully.
The results, published in Physical Review Letters, leverage the strengths of high-energy Megaelectronvolt (MeV) electrons for studying hydrogen atoms and proton transfers, in which the singular proton that makes up the nucleus of a hydrogen atom moves from one molecule to another.
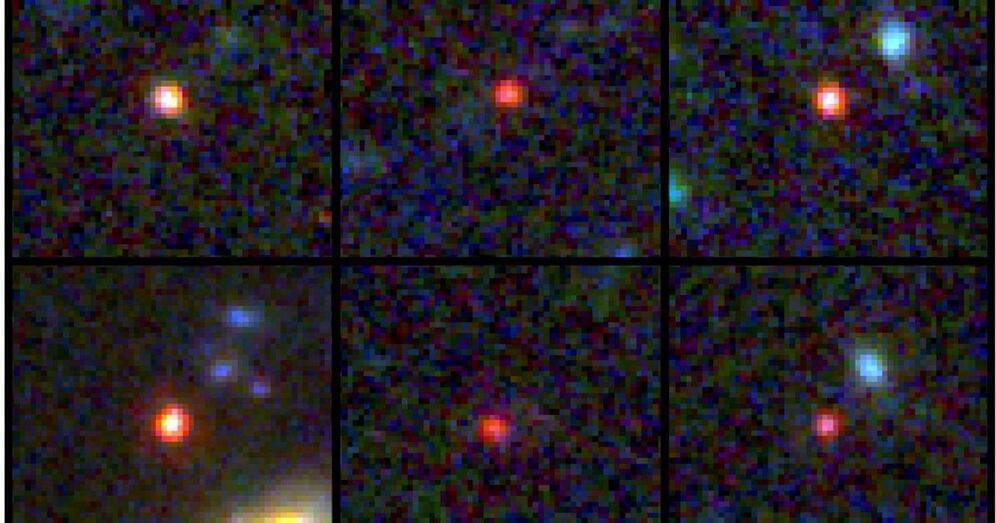

Scientists untangle mystery about the universe’s earliest galaxies
WASHINGTON, Oct 6 (Reuters) — Since beginning operations last year, the James Webb Space Telescope has provided an astonishing glimpse of the early history of our universe, spotting a collection of galaxies dating to the enigmatic epoch called cosmic dawn.
But the existence of what appear to be massive and mature galaxies during the universe’s infancy defied expectations — too big and too soon. That left scientists scrambling for an explanation while questioning the basic tenets of cosmology, the science of the origin and development of the universe. A new study may resolve the mystery without ripping up the textbooks.
The researchers used sophisticated computer simulations to model how the earliest galaxies evolved. These indicated that star formation unfolded differently in these galaxies in the first few hundred million years after the Big Bang event 13.8 billion years ago that initiated the universe than it does in large galaxies like our Milky Way populating the cosmos today.