Plans are already under way to roll it out for the public sector too by the end of the year. With a 2–3 million dose production capacity, a single dose of the two-dose vial is priced at Rs 2,000 currently. Vaccine effective against high risk types of the cancer-causing virus, say oncologists.
The researchers also found a spot in the brain’s temporal lobe that reacted when volunteers heard the 16th notes of the song’s guitar groove. They proposed that this particular area might be involved in our perception of rhythm.
The findings offer a first step toward creating more expressive devices to assist people who can’t speak. Over the past few years, scientists have made major breakthroughs in extracting words from the electrical signals produced by the brains of people with muscle paralysis when they attempt to speak.
But a significant amount of the information conveyed through speech comes from what linguists call “prosodic” elements, like tone — “the things that make us a lively speaker and not a robot,” Dr. Schalk said.
Kranthi Mandadapu.
This is according to a press release by the institution published on Tuesday.
No, it’s not dark matter.
Gravity is the force that attracts objects toward the Earth and maintains the orbital motion of planets around the Sun. Our scientific understanding of gravity was established by Isaac Newton.
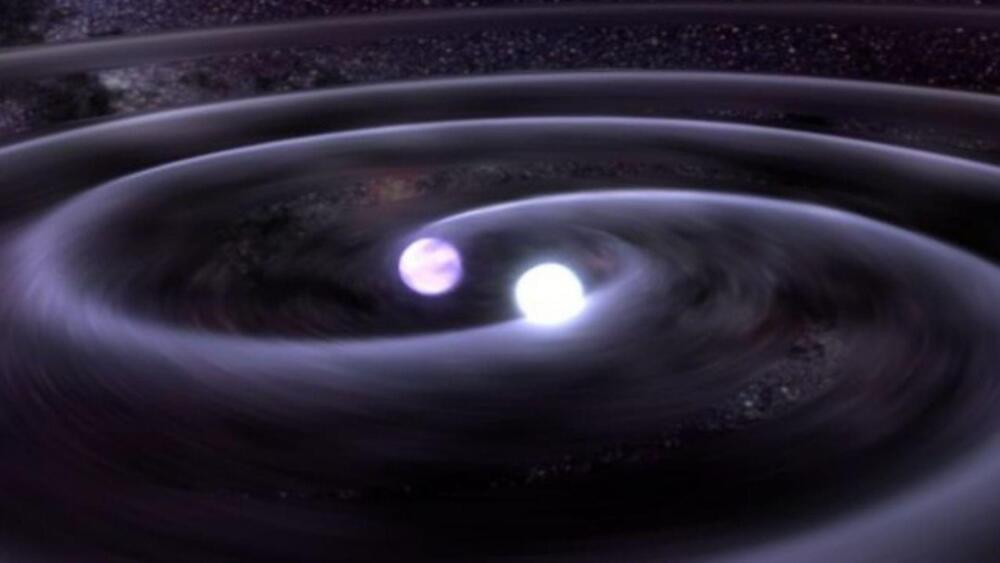
Despite the many successes of Einstein’s theory of gravity, many phenomena, such as gravity inside a black hole and gravitational waves, can’t be explained.
Tod Strohmayer (GSFC), CXC, NASA — Illustration: Dana Berry (CXC)
Our scientific understanding of gravity was established by Isaac Newton in 1687. Newton’s theory of gravity stood the test of time for two centuries until Albert Einstein proposed his ‘General Theory of Relativity,’ filling in the gaps left by Newton’s theory of gravity.
Venture capitalist a16z rebuilds a research paper with “AI Town” and releases the code. AI Town uses a language model to simulate a Sims-like virtual world in which all characters can flexibly pursue their motives and make decisions based on prompts.
In April, a team of researchers from Google and Stanford published the research paper Smallville. OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 simulates AI agents in a small digital town based solely on prompts.
Each character has an occupation, personality, and relationships with other characters, which are specified in an initial description. With further prompts, the AI agents begin to observe, plan, and make decisions.
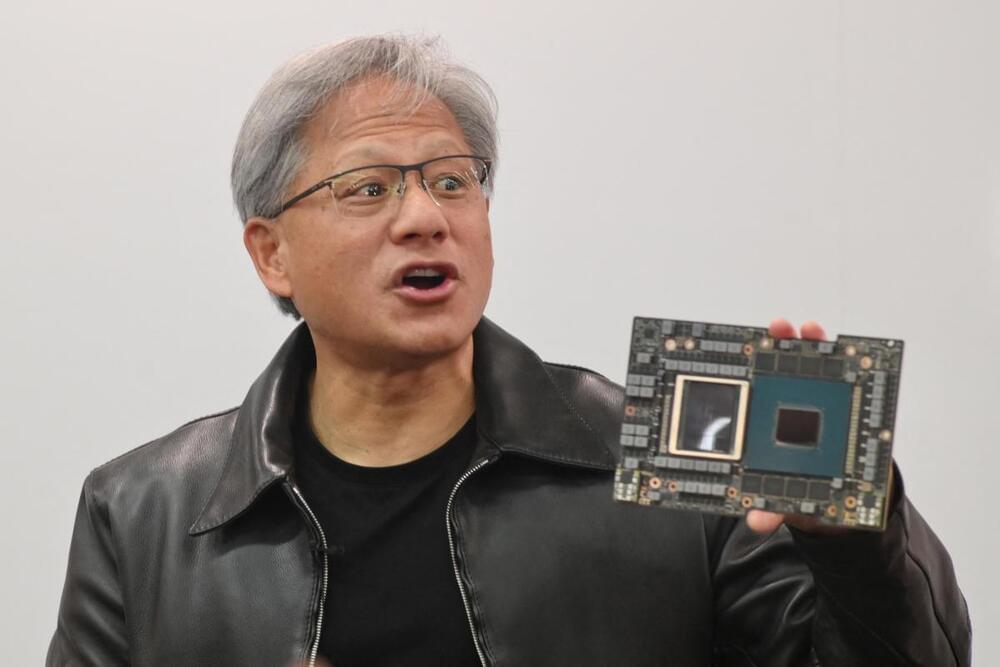
Nvidia (NVDA) will report its second quarter earnings after the closing bell next Wednesday, setting up what will be the AI hype cycle’s biggest test yet. During this AI gold rush, companies around the world looking to profit have turned to Nvidia’s graphics processors to power new AI software and platforms.
Currently, tech firms of all sizes are doing everything they can to get their hands on Nvidia chips. During Tesla’s (TSLA) Q2 earnings call, CEO Elon Musk told analysts that the automaker will take as many Nvidia graphics processors as the company can produce.
Nvidia is widely expected to have a blowout earnings report. A miss could derail the AI hype train.
Called “Pibot,” this humanoid robot integrates large language models to help it fly any aircraft as well as, if not better than, a human pilot.
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology (KAIST) are working to develop a humanoid pilot that can fly an aircraft without modifying the cockpit. Called “Pibot,” the robot has articulated arms and fingers that can interact with flight controls with great precision and dexterity. It also comes with camera “eyes” that help the robot monitor the internal and external conditions of the aircraft while in control.
Korea Herald.
Real robot-pilot.
The Japanese have created an uncanny AI model that can estimate your true age from the looks of your chest X-ray. It can help doctors in the early detection of chronic disorders.
Have you ever wondered why some people look much older than their chronological age? A new study from Japan’s Osaka Metropolitan University (OMU) suggests this could be a sign of a disease they don’t know yet.
The study authors have developed an AI program that can accurately calculate an individual’s age by reading their chest X-ray. This model estimates age, unlike various previously reported AI programs that examine radiographs to detect lung anomalies. Then researchers use this information to predict body ailments further.
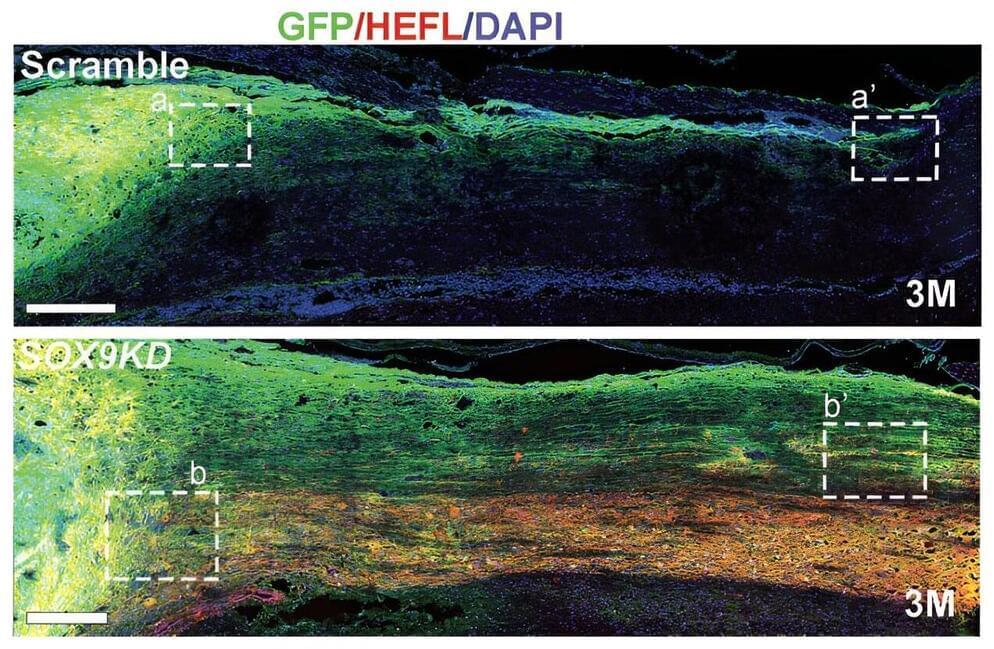
A research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently made a significant advancement in spinal cord injury treatment by using genetically-modified human neural stem cells (hNSCs).
They found that specifically modulating a gene expression to a certain level in hNSCs can effectively promote the reconstruction of damaged neural circuits and restore locomotor functions, offering great potential for new therapeutic opportunities for patients with spinal cord injury. The findings were published in the journal Advanced Science under the title “Transplanting Human Neural Stem Cells with ≈50% Reduction of SOX9 Gene Dosage Promotes Tissue Repair and Functional Recovery from Severe Spinal Cord Injury.”
Traumatic spinal cord injury is a devastating condition that commonly results from accidents such as falls, car crashes or sport-related injuries.