AI is hot – literally.
The chips that datacenters use to run the latest AI breakthroughs generate much more heat than previous generations of silicon. Anybody whose phone or laptop has overheated knows that electronics don’t like to get hot. In the face of rising demand for AI and newer chip designs, the current cooling technology will put a ceiling on progress in just a few years.
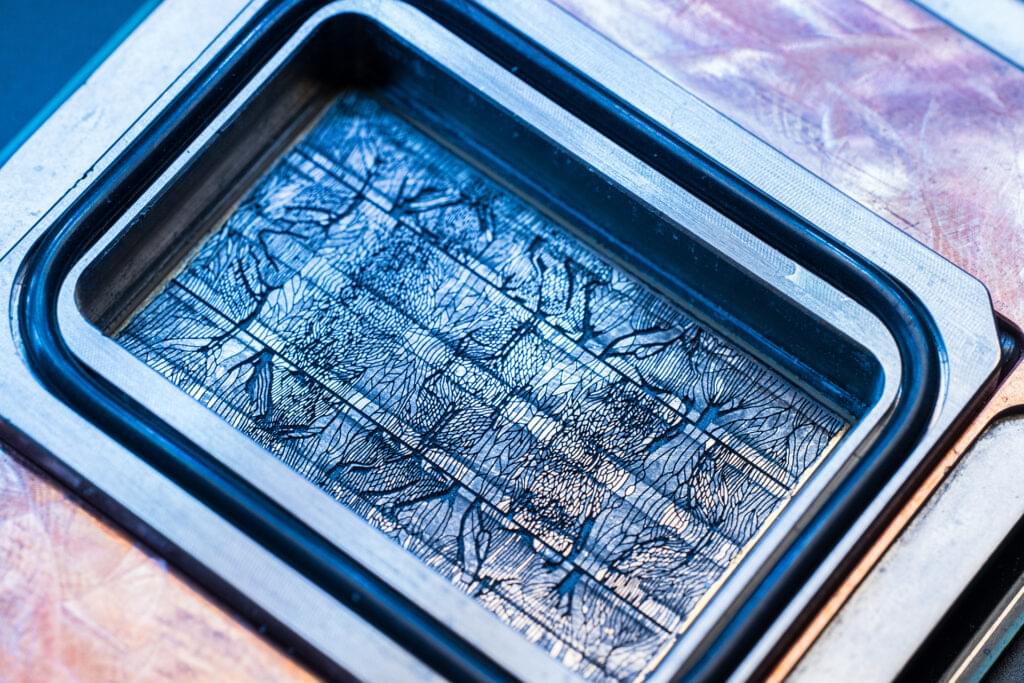
To help address this problem, Microsoft has successfully tested a new cooling system that removed heat up to three times better than cold plates, an advanced cooling technology commonly used today. It uses microfluidics, an approach that brings liquid coolant directly inside the silicon – where the heat is. Tiny channels are etched directly on the back of the silicon chip, creating grooves that allow cooling liquid to flow directly onto the chip and more efficiently remove heat. The team also used AI to identify the unique heat signatures on a chip and direct the coolant with more precision.