The latest open large language model from Meta — built with NVIDIA technology — is optimized to run on NVIDIA GPUs from the cloud and data center to the edge and the PC.


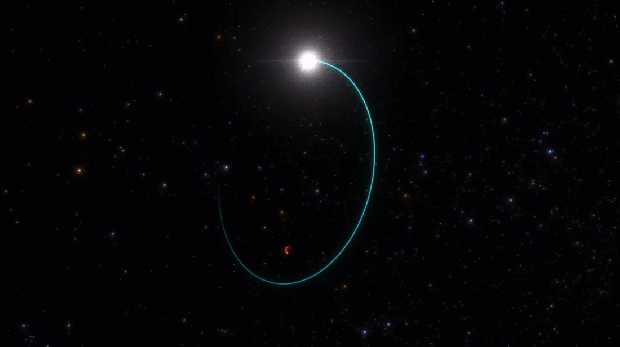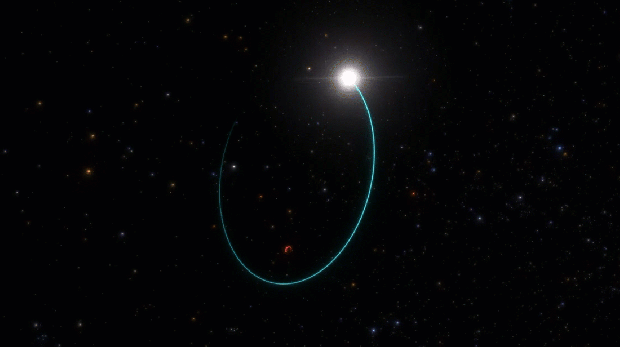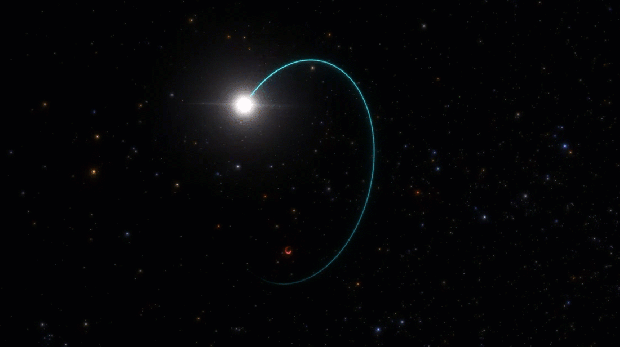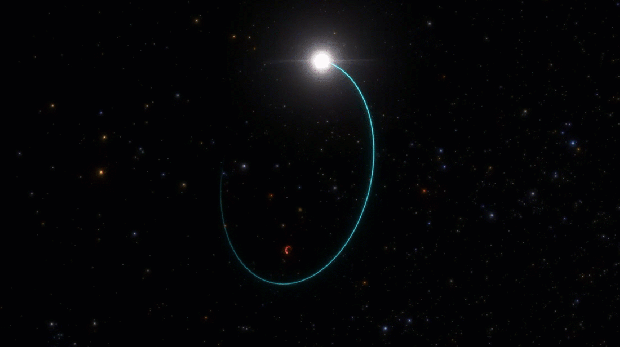
The newfound black hole, an intense, light-trapping abyss which has been named Gaia BH3, lurks just 1,926 light-years from Earth in the Aquila constellation. (That makes it the second closest black hole to Earth after Gaia BH1, which resides at 1,500 light-years away and is three times lighter than Gaia BH3.) The so-called “sleeping giant” — so named because unlike its ilk, the dormant black hole doesn’t appear to be shredding its companion star to pieces — birthed out of the imminent collapse of a once-massive star. It is the first direct link between a black hole and a progenitor star that was deprived of metals heavier than hydrogen and helium, according to the new study published in April in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
The discovery confirms a leading theory of stellar evolution that posits high-mass black holes are remnants of stars that are low on metals. Such metal-poor stars have damped mass-eroding winds compared to their metal-rich counterparts, and thus have more material available to form heavier black holes. Astronomers normally time announcements of science discoveries at the same time as data release, in this case no sooner than early 2026, but “you cannot hide this kind of discovery from the community for two years,” says Panuzzo. “It is a unique case of publication based on the preliminary data because the data is exceptional and also something that’s very interesting for the community.”

Depression and cardiovascular disease (CVD) are serious concerns for public health. Approximately 280 million people worldwide have depression, while 620 million people have CVD.
It has been known since the 1990s that the two diseases are somehow related. For example, people with depression run a greater risk of CVD, while effective early treatment for depression cuts the risk of subsequently developing CVD by half. Conversely, people with CVD tend to have depression as well. For these reasons, the American Heart Association (AHA) advises to monitor teenagers with depression for CVD.
What wasn’t yet known is what causes this apparent relatedness between the two diseases. Part of the answer probably lies in lifestyle factors common in patients with depression and which increase the risk of CVD, such as smoking, alcohol abuse, lack of exercise, and a poor diet. But it’s also possible that both diseases might be related at a deeper level, through shared developmental pathways.
What influences mental health, academic achievement, and cognitive growth? A recent review published in De Gruyter’s Reviews in the Neurosciences indicates that poverty and low socioeconomic status (SES) are significant contributing factors. While previous research has explored the individual impacts of poverty on the brain and behavior, this review introduces the first integrated framework. It synthesizes evidence from various studies to directly connect brain alterations caused by low SES with behavioral, pathological, and developmental outcomes.
SES refers to the social standing of an individual or family, and involves factors such as wealth, occupation, educational attainment, and living conditions. As well as affecting day-to-day life, perhaps surprisingly SES can also have far-reaching consequences for our brains that begin in childhood and persist into adulthood.
So, how can poverty and low SES change the brain? The review examines the negative effects of poor nutrition, chronic stress, and environmental hazards (such as pollution and inadequate housing conditions), which are more likely to affect low-SES families. These factors can impair the brain development of children, which in turn can influence their language skills, educational attainment, and risk of psychiatric illness.


WASHINGTON — Redwire Space is doubling down on interest in the emerging market for very low Earth orbit (VLEO) satellites by offering a second spacecraft platform from its European subsidiary.
In a May 9 earnings call, Redwire announced a VLEO satellite platform called Phantom, developed by the company’s European business unit in Belgium. Phantom is being developed for the European Space Agency’s Skimsat mission, on which Redwire is partnered with Thales Alenia Space, and is now being offered for European and international customers.
Phantom joins SabreSat, a VLEO satellite Redwire announced in its previous earnings call in March that is being developed by the company in the United States. The two designs use different technologies.


A study focusing on childhood maltreatment in Australia has uncovered its alarming impact, estimating it causes up to 40 percent of common, life-long mental health conditions.
The mental health conditions examined were anxiety, depression, harmful alcohol and drug use, self-harm, and suicide attempts. Childhood maltreatment is classified as physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, and emotional or physical neglect before the age of 18. Childhood maltreatment was found to account for 41 percent of suicide attempts in Australia, 35 percent for cases of self-harm, and 21 percent for depression.
The analysis, published in JAMA Psychiatry is the first study to provide estimates of the proportion of mental health conditions in Australia that arise from childhood maltreatment. The researchers said the results are a wake-up call for childhood abuse and neglect to be treated as a national public health priority.