A defense of strong AI.
Shared with Dropbox.
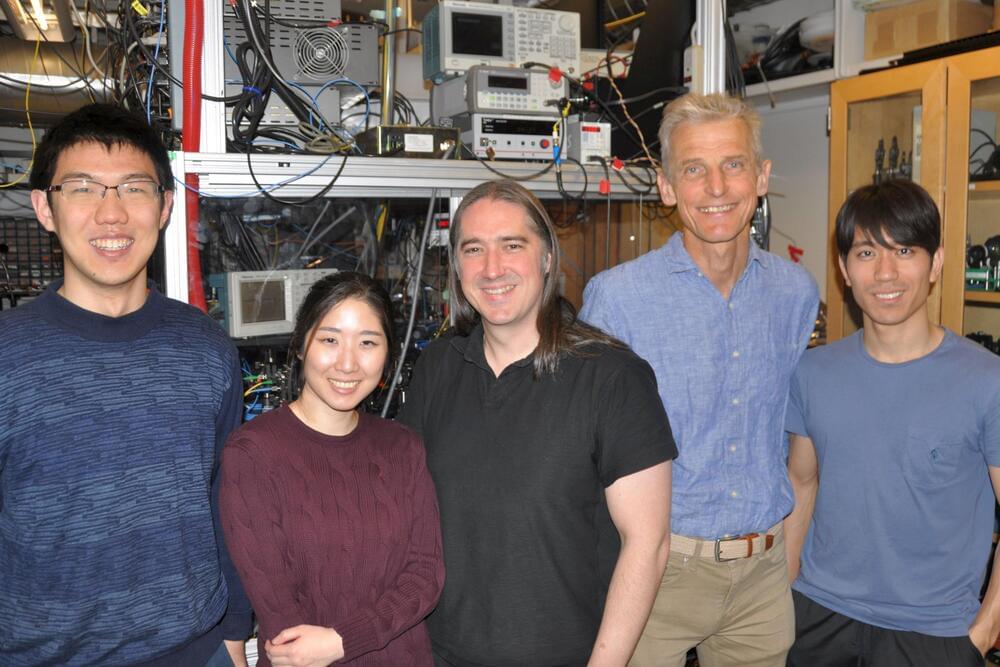

Physicists in the MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms (CUA) have developed a new approach to control the outcome of chemical reactions. This is traditionally done using temperature and chemical catalysts, or more recently with external fields (electric or magnetic fields, or laser beams).
MIT CUA physicists have now added a new twist to this: They have used minute changes in a magnetic field to make subtle changes to the quantum mechanical wavefunction of the colliding particles during the chemical reaction. They show how this technique can steer reactions to a different outcome: enhancing or suppressing reactions.
This was only possible by working at ultralow temperatures at a millionth of a degree above absolute zero, where collisions and chemical reactions occur in single quantum states. Their research was published in Science on March 4.


University of Wyoming researchers have gained further insight into how tardigrades survive extreme conditions and shown that proteins from the microscopic creatures expressed in human cells can slow down molecular processes.
This makes the tardigrade proteins potential candidates in technologies centered on slowing the aging process and in long-term storage of human cells.
The new study, published in the journal Protein Science, examines the mechanisms used by tardigrades to enter and exit from suspended animation when faced by environmental stress. Led by Senior Research Scientist Silvia Sanchez-Martinez in the lab of UW Department of Molecular Biology Assistant Professor Thomas Boothby, the research provides additional evidence that tardigrade proteins eventually could be used to make life-saving treatments available to people where refrigeration is not possible — and enhance storage of cell-based therapies, such as stem cells.
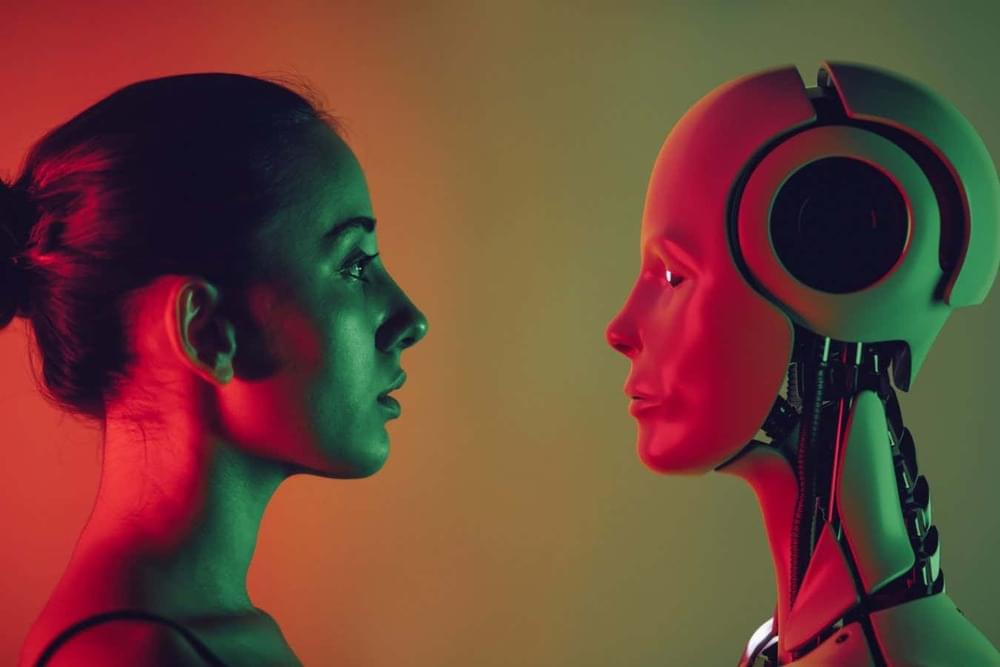


When people were challenged to debate contentious topics with a human or GPT-4, they were more likely to be won over by the artificial intelligence.

“I think of [the agreement] as marking the next chapter in our journey on AI safety, working hand in glove with the United States government,” Donelan told TIME in an interview at the British Embassy in Washington, D.C. on Monday. “I see the role of the United States and the U.K. as being the real driving force in what will become a network of institutes eventually.”
The U.K. and U.S. AI Safety Institutes were established just one day apart, around the inaugural AI Safety Summit hosted by the U.K. government at Bletchley Park in November 2023. While the two organizations’ cooperation was announced at the time of their creation, Donelan says that the new agreement “formalizes” and “puts meat on the bones” of that cooperation. She also said it “offers the opportunity for them—the United States government—to lean on us a little bit in the stage where they’re establishing and formalizing their institute, because ours is up and running and fully functioning.”
The two AI safety testing bodies will develop a common approach to AI safety testing that involves using the same methods and underlying infrastructure, according to a news release. The bodies will look to exchange employees and share information with each other “in accordance with national laws and regulations, and contracts.” The release also stated that the institutes intend to perform a joint testing exercise on an AI model available to the public.
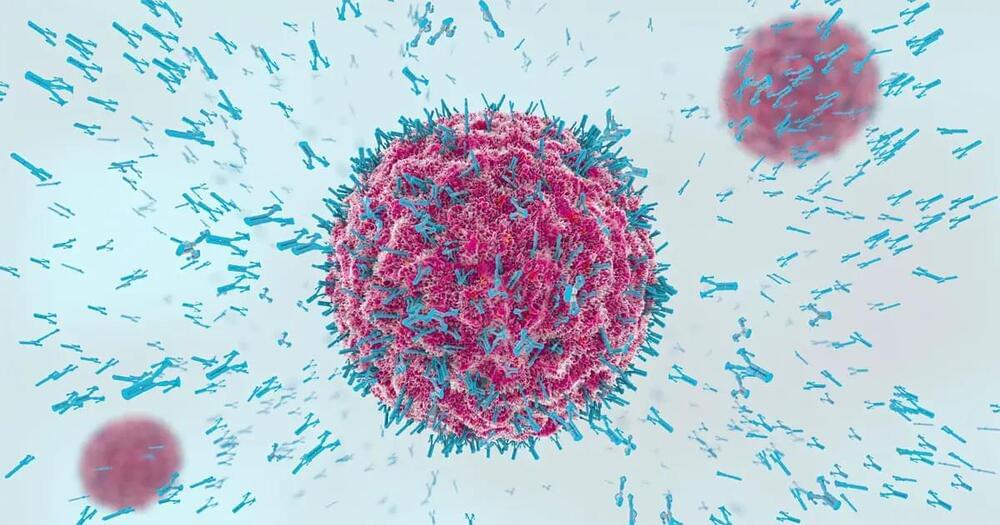
In a study published by Stanford University, old mice developed more youthful immune systems after treatment with an antibody targeting abnormal stem cells.
As we age, so too does our immune system. This decline, known as immunosenescence, makes us more susceptible to infections, chronic inflammation, and diseases like cancer.
Black holes are one of the most elusive objects in the space, but this simulation created by researchers in Netherlands might help us know more about their mysteries.
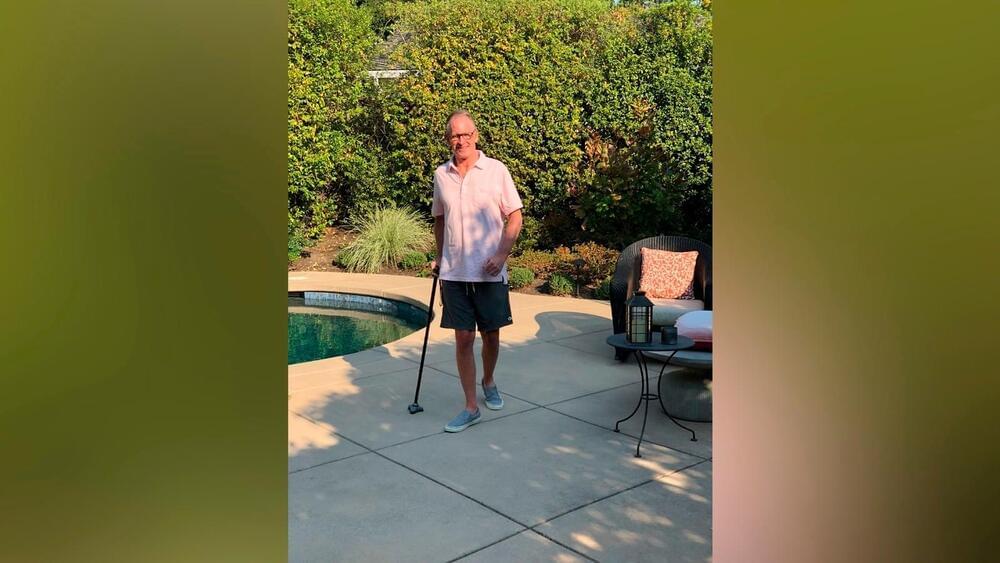

A man who was paralyzed from the neck down after a surfing accident seven years ago is now able to stand and walk on his own, thanks in part to a potentially groundbreaking stem cell treatment.
Chris Barr was the very first patient in a Mayo Clinic study that collected stem cells from his own stomach fat, expanded them in a laboratory to 100 million cells and then injected the cells into Barr’s lumbar spine.
Over five years after undergoing the therapy, Barr said he is continuing to gain more independence and get faster at walking.