In our latest video, “Has The Future Already Happened? Is the Universe Predetermined?” we embark on a cosmic journey that challenges the very fabric of our u…
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
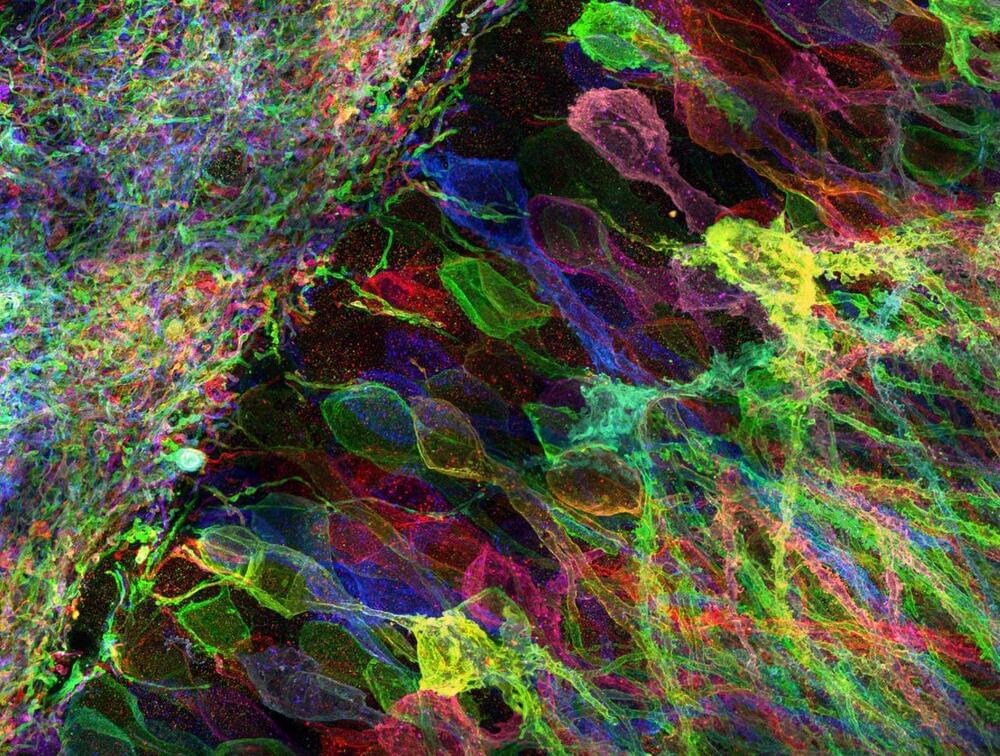
New study provides genomic insights into kidney cancer risk
MEDIA ADVISORY: An international team of researchers, led by NCI scientists, has identified 50 new areas across the human genome that are associated with the risk of developing kidney cancer.
In a new analysis of genetic susceptibility to kidney cancer, an international team of researchers has identified 50 new areas across the genome that are associated with the risk of developing kidney cancer. These insights could one day be used to advance our understanding of the molecular basis of kidney cancer, inform screening efforts for those at highest risk, and identify new drug targets. The study was led by scientists at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
A previous genome-wide association study (GWAS) of people of European ancestry identified 13 regions of the genome that are associated with kidney cancer risk. However, the study population was not diverse. To identify additional regions, researchers conducted a GWAS in participants of many different genetic ancestries that included 29,020 people with kidney cancer and 835,670 people without kidney cancer. Analysis of the data, which came from published studies, biobanks, and a new study, resulted in the identification of 50 new regions associated with the risk of developing kidney cancer, bringing the total number of such regions to 63.
Among the newly identified genetic variants were several associated with a risk of developing papillary renal cell carcinoma, the second most common subtype of renal cell carcinoma. Another variant, in the VHL gene, was common in individuals of African ancestry and was associated with an estimated three times higher risk of developing clear cell renal cell carcinoma, the most common type of kidney cancer.
In a first, scientists use new tech to see inside cancer cells
Technology views living cancer cell:
This technique could provide valuable insights into how different types of cancer respond to treatments. It might also help doctors understand the impact of irradiation on cells, specifically how some cancer cells resist radiation treatment. This resistance may result in relapse of the cancer.
A deeper understanding of cancer biology may lead to the development of more effective treatments in the future.
Moreover, the researchers state that studying lipids inside single cells may help various health areas, including immunity, and infectious diseases.
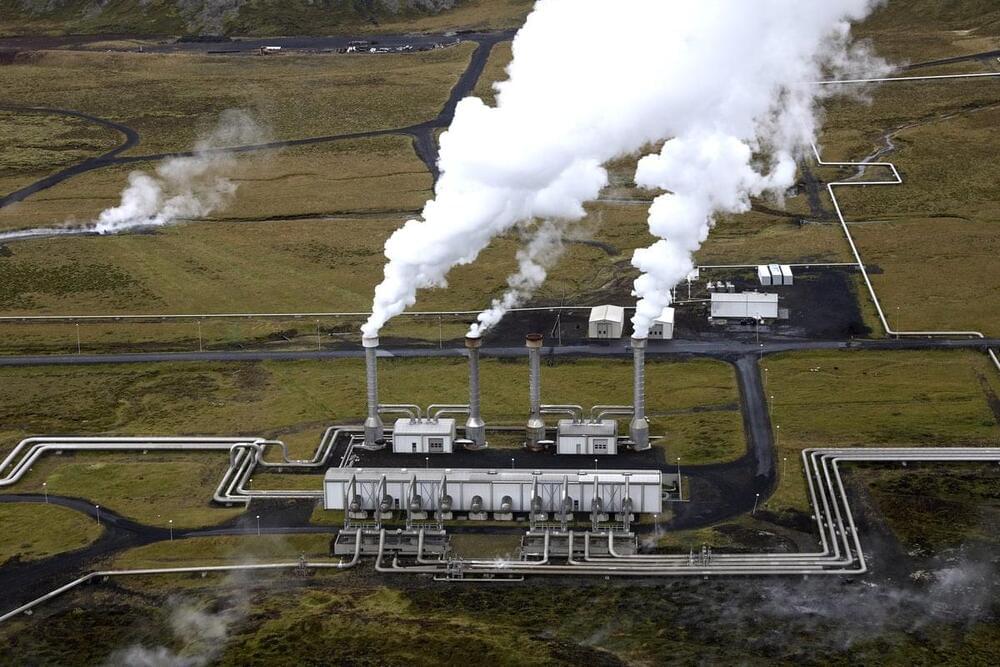


New Geothermal Technology Could Expand Clean Power Generation
Long confined to regions with volcanic activity, geothermal promises to become a much more versatile energy source thanks to new technologies.
By Katarina Zimmer & Knowable Magazine
Glistening in the dry expanses of the Nevada desert is an unusual kind of power plant that harnesses energy not from the sun or wind, but from the Earth itself.

SETI Scientist Says Announcement of Alien Life Could Be Imminent
One of the world’s foremost experts in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) believes that with the help of the James Webb Space Telescope, humans are closer to discovering life outside our planet than ever before.
Lisa Kaltenegger, who directs the Carl Sagan Institute at Cornell, told The Telegraph this week that because the Webb Telescope is designed to detect biosignatures — the scientific word for “signs of life,” including organism-produced methane gas — we may well find ETs very soon.
Kaltnegger, whose new book “Alien Earths: Planet Hunting in the Cosmos” was published this month, waxed enthusiastic when discussing the JWST, bragging that with its technological leaps, humanity is now in “this era of golden exploration, with thousands of other worlds on our doorstep, that we now can actually explore.”
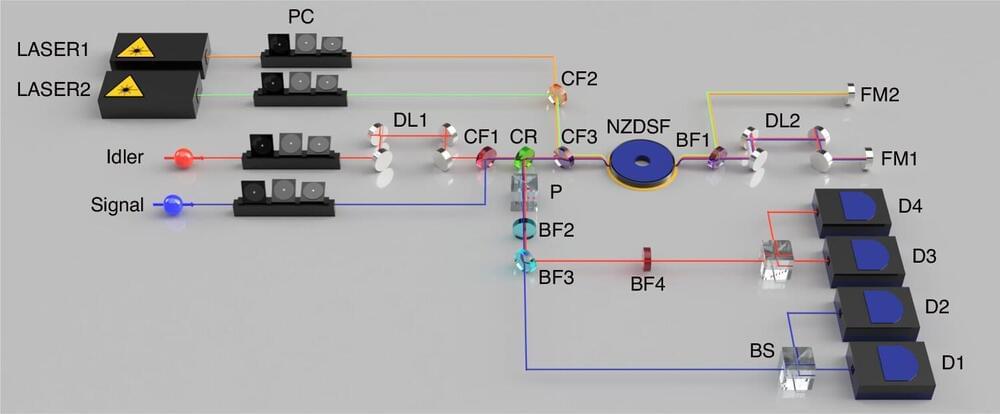
Unveiling a new quantum frontier: Frequency-domain entanglement
Scientists have introduced a form of quantum entanglement known as frequency-domain photon number-path entanglement. This advance in quantum physics involves an innovative tool called a frequency beam splitter, which has the unique ability to alter the frequency of individual photons with a 50% success rate.
For years, the scientific community has delved into spatial-domain photon number-path entanglement, a key player in the realms of quantum metrology and information science.
This concept involves photons arranged in a special pattern, known as NOON states, where they’re either all in one pathway or another, enabling applications like super-resolution imaging that surpasses traditional limits, the enhancement of quantum sensors, and the development of quantum computing algorithms designed for tasks requiring exceptional phase sensitivity.

Breakthrough: Rare Gene Mutation Offers Clues to Preventing Type 1 Diabetes
A unique genetic mutation in two siblings – that has never been seen in anyone else – has been discovered by UK researchers at the University of Exeter, pointing the way towards new treatment options for type 1 diabetes.
The mutation is in the gene for a protein called programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), and a new study explains how it may be responsible for the autoimmune form of diabetes that the children developed at a very young age.
“We searched the globe, looking at all the large-scale datasets that we know of, and we haven’t been able to find another family,” says molecular geneticist Matthew Johnson, from the University of Exeter in the UK.