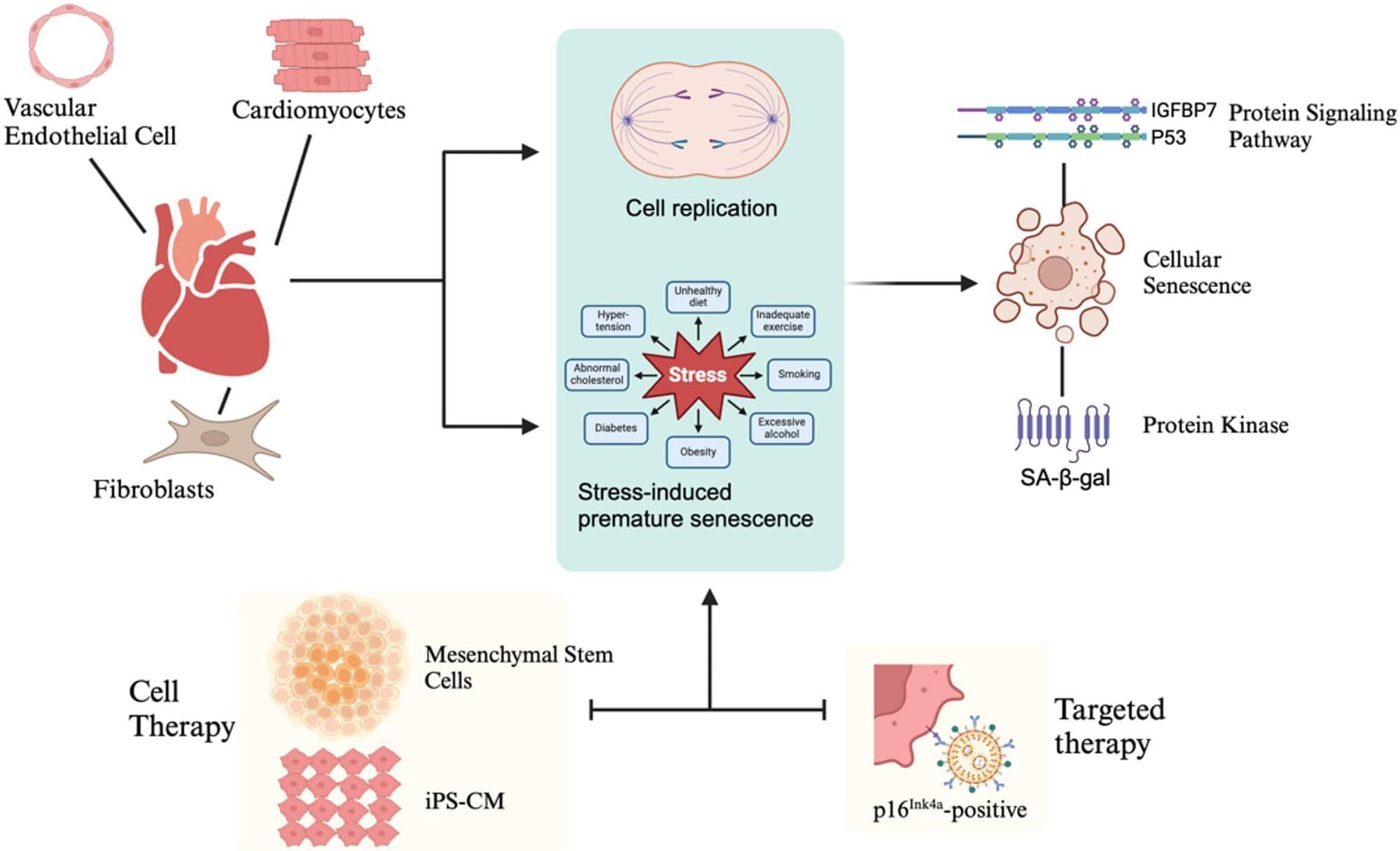
Hayflick and Moorhead initially defined cellular senescence in 1961 [10]. As senescent cells become enlarged with a flattened morphology, they exhibit an irreversible loss of proliferative potential. Changes in the expression of genetic profiles in these cells result in the secretion of pro-inflammatory molecules [11]. Senescent cells accumulate in various tissues and organs associated with aging and age-related disorders, and they are believed to become pathogenic by introducing chronic inflammation and tissue remodeling. Two major senescence-associated pathways have been highlighted in the recent literature. Telomeres are situated at both ends of a chromosome and replicate incompletely during cell division, leading to telomere shortening. When telomere shortening goes beyond the physiological range, it is recognized as DNA damage and activates replicative cellular senescence, primarily through the p53 or p16INK4a signaling pathways. p16INK4a also plays a crucial role in the mitotic process. It regulates the G1/S-phase transition of the cell cycle, helping to maintain the accuracy of cell proliferation. Normal cell division requires smooth progression through the cell cycle, and p16INK4a ensures that cells halt proliferation in the presence of DNA damage or unfavorable division conditions, thereby preserving genomic stability and preventing errors or malignancies during mitosis. Another form of cellular senescence is stress-induced premature senescence, triggered by various external and internal stress signals, including oxidative stress, irradiation, oncogenic activation, and metabolic stress. Research indicates that p53/p21 and p16INK4a signaling are primarily activated in response to DNA damage and telomere dysfunction. In contrast, p16INK4a signaling is mainly associated with mitogenic and general cellular stress [12, 13]. IGFBP7 is a member of the IGFBP family. It is a stress-responsive gene that can be upregulated in response to oxidative stress and DNA damage. The IGFBP7–p53 pathway is a critical stress–senescence pathway essential for regulating cell fate, such as cell cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis. This pathway may be a target for anti-tumor and anti-fibrotic therapies; however, its inhibitory effect on tissue regeneration should also be considered [14]. Senescent cells exhibit various morphological and biochemical characteristics that aid their detection [15]. Currently, no single marker can definitively identify a senescent cell; instead, combinations of markers and analytical techniques are commonly employed to improve detection specificity. Table 1 displays some widely used markers for this purpose. Many stressors that induce senescence activate the p53/p21 or p16INK4a pathways. However, it’s important to note that activating these signaling pathways does not provide conclusive evidence that the cells are senescent [16]. Currently, senescence-associated ß-galactosidase (SA-ß-galactosidase) is widely used to identify senescent cells as a marker of senescence, which has a pH optimum of 6.0; however, the SA-ß-gal activity is also known to increase in fibroblasts cultured under serum starvation [17,18,19]. Another category of sensitive senescence indicators includes DNA damage response (DDR) gene products, which are usually visualized through immunofluorescence. The DDR protein most commonly used for this purpose is γH2AX phosphorylated at Ser-139, which accumulates at sites of double-stranded DNA breaks and facilitates the detection of proteins involved in the double-strand break repair pathway [20, 21]. DNA damage at telomeres suggests that both cardiomyocytes and various non-cardiomyocytes, including myofibroblasts, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells, contribute to the senescence of the cardiovascular system. These cells interact within the microenvironment, altering cardiovascular function and promoting disease progression. Additionally, some studies have monitored cytokine secretion related to the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), characterized by the extensive release of pro-inflammatory compounds. Common SASP factors secreted by senescent cells include signaling molecules such as interleukins (IL-6, IL-1ß, IL-8) and other factors [22, 23]. The cell makers mentioned above are all related to senescence, but do not exist in isolation.
In summary, cells that show positive senescent markers are well recognized for their causal roles in the progression of pathologies associated with age-related diseases [24, 25]. Investigating biological markers that provide direct evidence of cellular senescence continues to be a significant area of research. In this review article, we aim to outline the role of senescence in cardiovascular disease and explore the potential of therapies targeting senescent cells.
Cardiomyocytes comprise 25–35% of the total number of cells in the heart [26]. Their cell cycle arrest cannot easily define the senescence of cardiomyocytes because they are terminally differentiated cells. Cardiomyocytes undergo cell cycle arrest due to the activation of the DNA damage response triggered by exposure to higher oxygen concentrations in the postnatal environment [27]. The accumulating environment indicates these cells retain proliferative capacity. It was reported that cardiomyocyte turnover was < 1% per year [28]. Senescent cardiomyocytes exhibit significant functional, morphological, and metabolic differences compared to normal cardiomyocytes. Hallmarks of senescent cardiomyocytes include mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage, contractile dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, SASP, and hypertrophic growth [29].