Could this one be the first water battery ever produced in history? Scientists believe so, and you can carry it in your car.
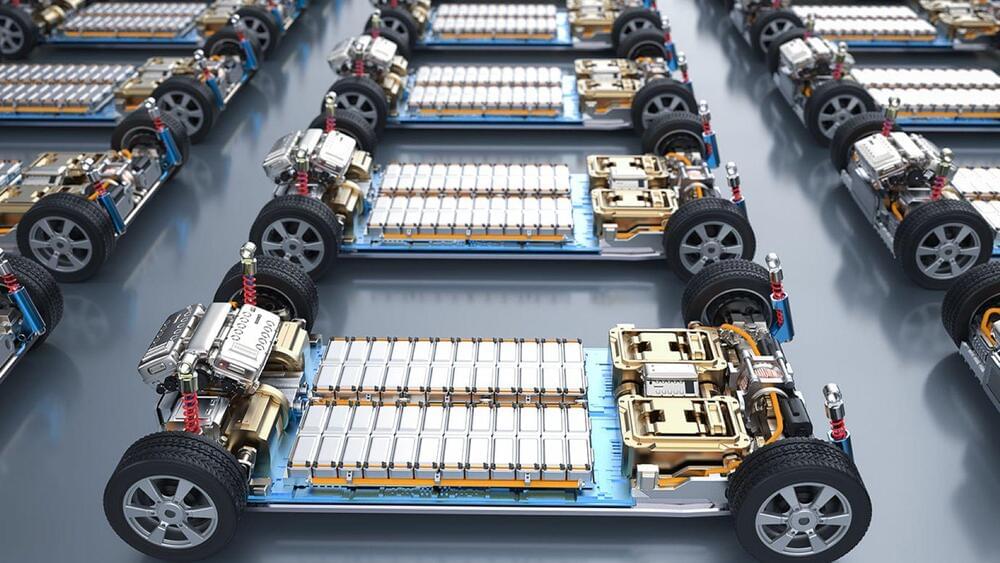


A global team of researchers and industry collaborators led by RMIT University has invented recyclable ‘water batteries’ that won’t catch fire or explode.
Lithium-ion energy storage dominates the market due to its technological maturity, but its suitability for large-scale grid energy storage is limited by safety concerns with the volatile materials inside.
Lead researcher Distinguished Professor Tianyi Ma said their batteries were at the cutting edge of an emerging field of aqueous energy storage devices, with breakthroughs that significantly improve the technology’s performance and lifespan.
Small businesses are an important part of society and AI is becoming just as important. Here is how artificial intelligence can help them.
Hackers are utilizing code from a Python clone of Microsoft’s venerable Minesweeper game to hide malicious scripts in attacks on European and US financial organizations.
Ukraine’s CSIRT-NBU and CERT-UA attribute the attacks to a threat actor tracked as ‘UAC-0188,’ who is using the legitimate code to hide Python scripts that download and install the SuperOps RMM.
Superops RMM is a legitimate remote management software that gives remote actors direct access to the compromised systems.
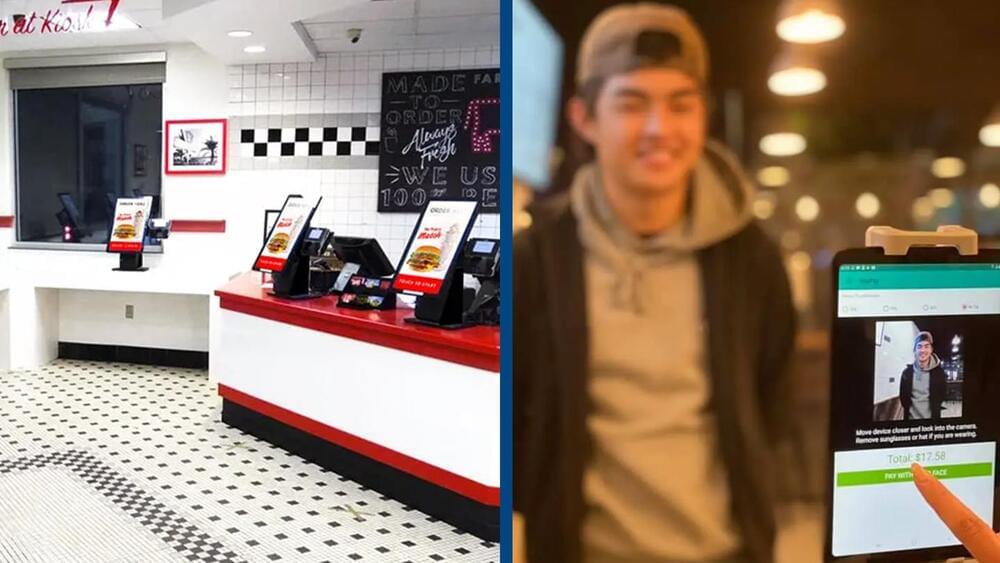


Users simply register by taking a selfie and then verify their identity and payment transaction by looking at the restaurant’s camera, according to CNBC.
In essence, it acts very similar to Apple’s Face ID.
The Cali-based software company explained the tech on its website, reading: ‘PopID is the universal gateway for verifying an individual’s identity based on their face for applications such as loyalty and payment.’
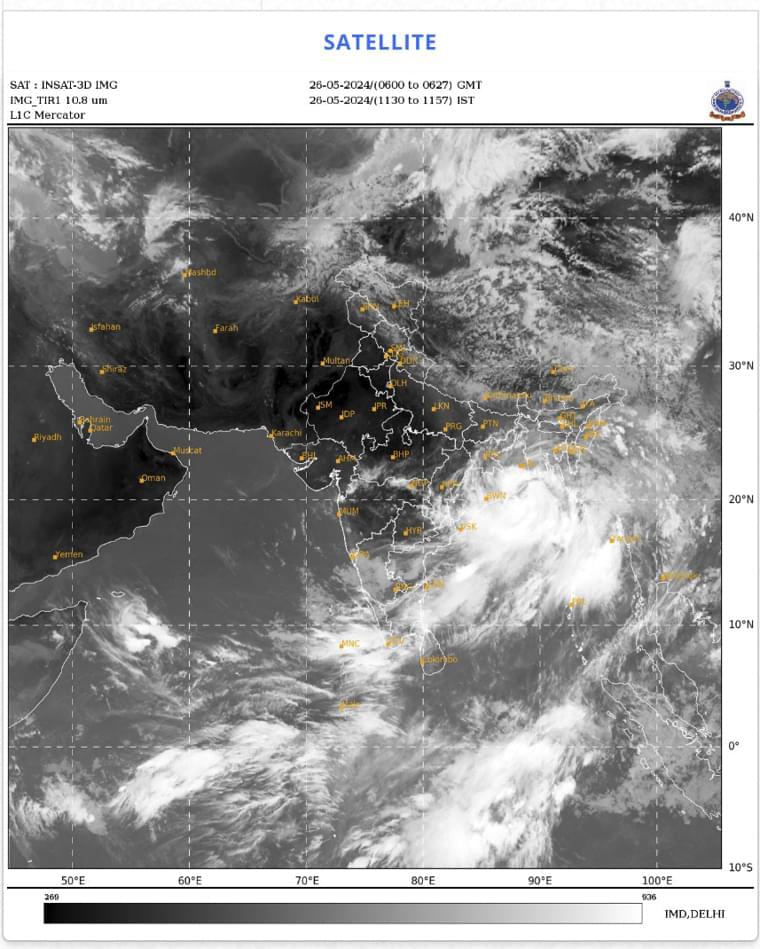
NEW DELHI (AP) — Bangladesh evacuated nearly 800,000 people from vulnerable areas on Sunday as the country and neighboring India awaited the arrival of a severe cyclone that has formed over the Bay of Bengal. The storm is expected to cross Bangladesh and India’s West Bengal coasts around midnight Sunday. The India Meteorological Department said it is expected to reach maximum wind speeds of up to 120 kilometers per hour (75 mph), with gusts up…
This fun and innovative project employs a rotary encoder and Arduino to capture rotational data and translate it into car movements in VR.
“If you frame it as an either/or question, it’s too simplistic,” says Utah State University evolutionary biologist Zachariah Gompert. “The answer isn’t ‘completely random’ or ‘completely deterministic and predictable.’ And yet, examining short time scales, we can find predictable, repeatable evolutionary patterns.”
Gompert and colleagues report evidence of repeatable evolution in populations of stick insects in the May 24, 2024, online edition of the American Association for the Advancement of Science’s journal Science Advances. Collaborating authors on the paper include Gompert’s long-time collaborator Patrik Nosil and other researchers from France’s University of Montpelier, Brazil’s Federal University of São Paulo, the University of Nevada, Reno and Notre Dame University. The research is supported by the National Science Foundation and the European Research Council.
The team examined three decades of data on the frequency of cryptic color-pattern morphs in the stick insect species Timema cristinae in ten naturally replicate populations in California. T. cristinae is polymorphic in regard to its body color and pattern. Some insects are green, which allows the wingless, plant-feeding insect to blend in with California lilac (Ceanothus spinosus) shrubs. In contrast, green striped morphs disappear against chamise (Adenostoma fasciculatum) shrubs.
“Batteries are the crux of many of the most important emerging technologies in both the civilian world and, important to our profession, on the battlefield,” said United States Military Academy Cadet Michael Williams. “More energy dense batteries allow, for instance, greater range on electric vehicles, longer battery lives for radios, and longer flight times for drones. Our work helps make manufacturing these batteries easier.”
Cadets Michael Williams, Avery Patel, and Nancy Astable have been working on a long-term project with their faculty mentors Dr. Enoch Nagelli, Dr. Simuck Yuk, and Army Col. John Burpo to develop new ways to maximize energy storage and generation for the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command’s Armaments Center. In collaboration with Cornell University, the team at USMA’s Department of Chemistry and Life Sciences is pursuing innovative approaches to increasing the quality and use of batteries and fuel cells.
The value of conducting scientific research to solve real-world problems is clear to the cadets.