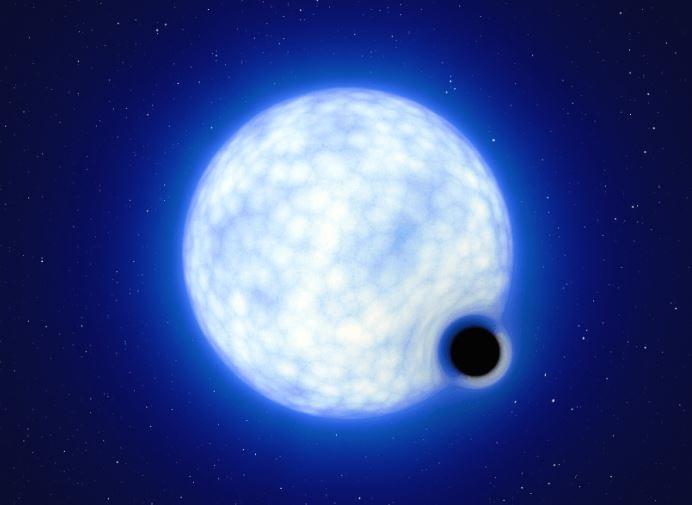
University of Copenhagen astrophysicists help explain a mysterious phenomenon, whereby stars suddenly vanish from the night sky. Their study of an unusual binary star system has resulted in convincing evidence that massive stars can completely collapse and become black holes without a supernova explosion.
One day, the star at the center of our own solar system, the Sun, will begin to expand until it engulfs Earth. It will then become increasingly unstable until it eventually contracts into a small and dense object known as a white dwarf.
However, if the Sun were of a weight class roughly eight times greater or more, it would probably go out with a huge bang — as a supernova. Its collapse would culminate into an explosion, ejecting energy and mass into space with enormous force, prior to leaving behind a neutron star or a black hole in its wake.