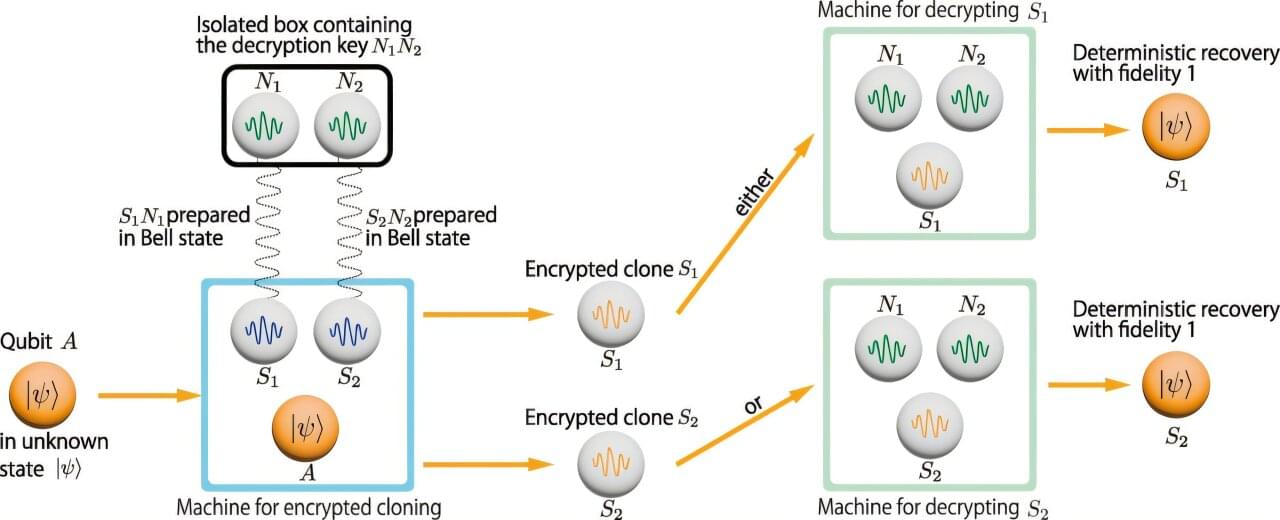
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo have made a breakthrough in quantum computing that elegantly bypasses the fundamental “no cloning” problem. The research, “Encrypted Qubits can be Cloned,” appears in Physical Review Letters.
Quantum computing is an exciting technological frontier, where information is stored and processed in tiny units—called qubits. Qubits can be stored, for example, in individual electrons, photons (particles of light), atoms, ions or tiny currents.
Universities, industry, and governments around the world are spending billions of dollars to perfect the technology for controlling these qubits so that they can be combined into large, reliable quantum computers. This technology will have powerful applications, including in cybersecurity, materials science, medical research and optimization.