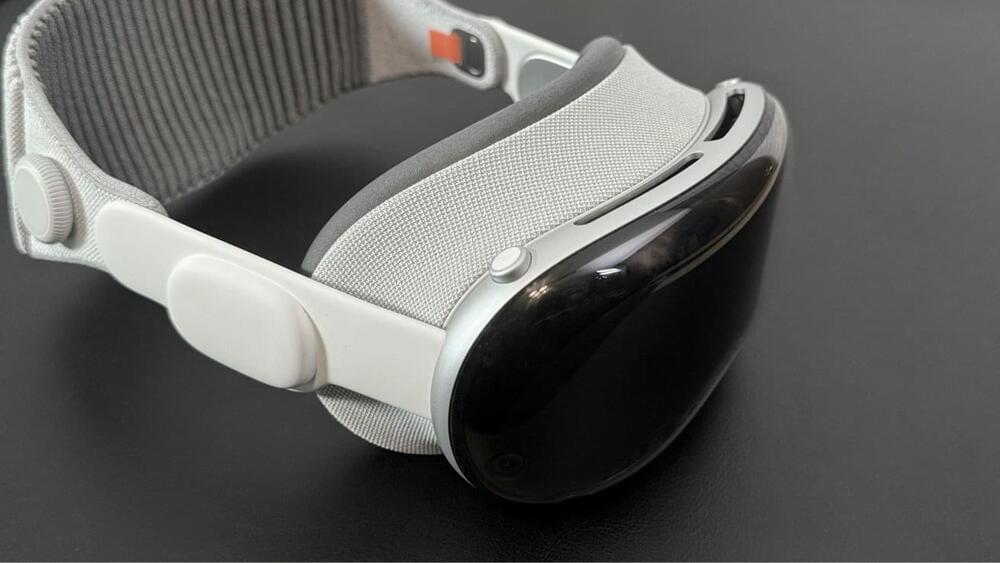
Working to promote the Apple Vision Pro as a business tool instead of solely an entertainment one, Apple has highlighted half a dozen firms from Porsche to Microsoft, who have incorporated the headset into their work.
While perhaps most attention that the Apple Vision Pro has received concerns its immersive video for entertainment, Apple has always aimed it equally at businesses. Now Apple wants to press hard on the idea of Apple Vision Pro being a tool that companies need.
“There’s tremendous opportunity for businesses to reimagine what’s possible using Apple Vision Pro at work,” Susan Prescott, Apple’s vice president of Worldwide Developer Relations and Enterprise Marketing, said in a statement. “We’re thrilled to see the innovative ways organizations are already using Apple Vision Pro, from planning fire response operations to iterating on the most intricate details of an engine design — and this is just the beginning.”