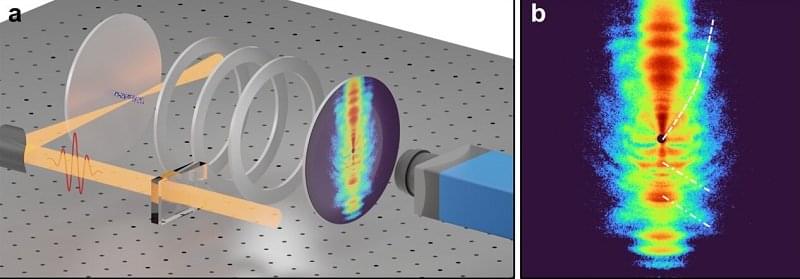
A team of researchers, led by Professor Dong Eon Kim from Pohang University of Science and Technology and Professor X. Lai at the Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, has made significant strides in ultrafast imaging. They have successfully observed two distinct holographic patterns—resembling spider legs and fishbones—within molecules for the first time. […].